Abstract
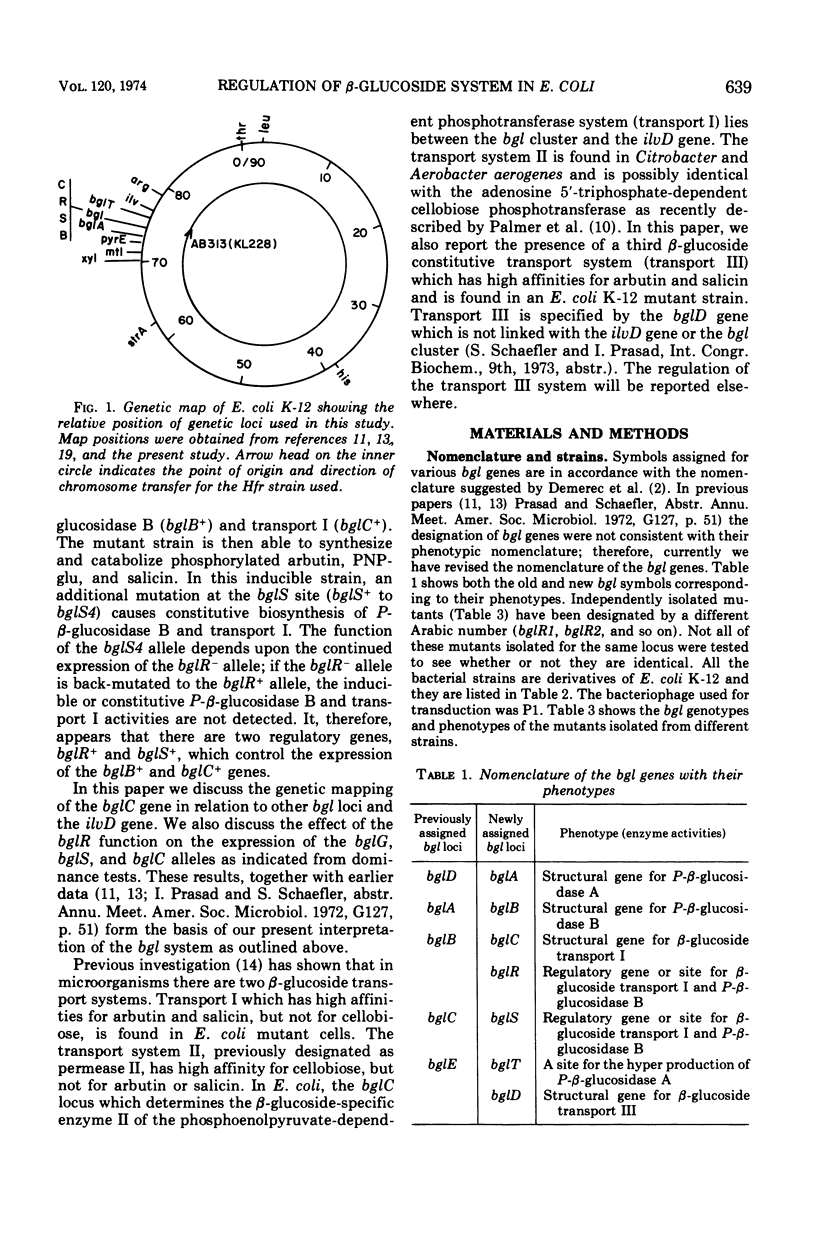
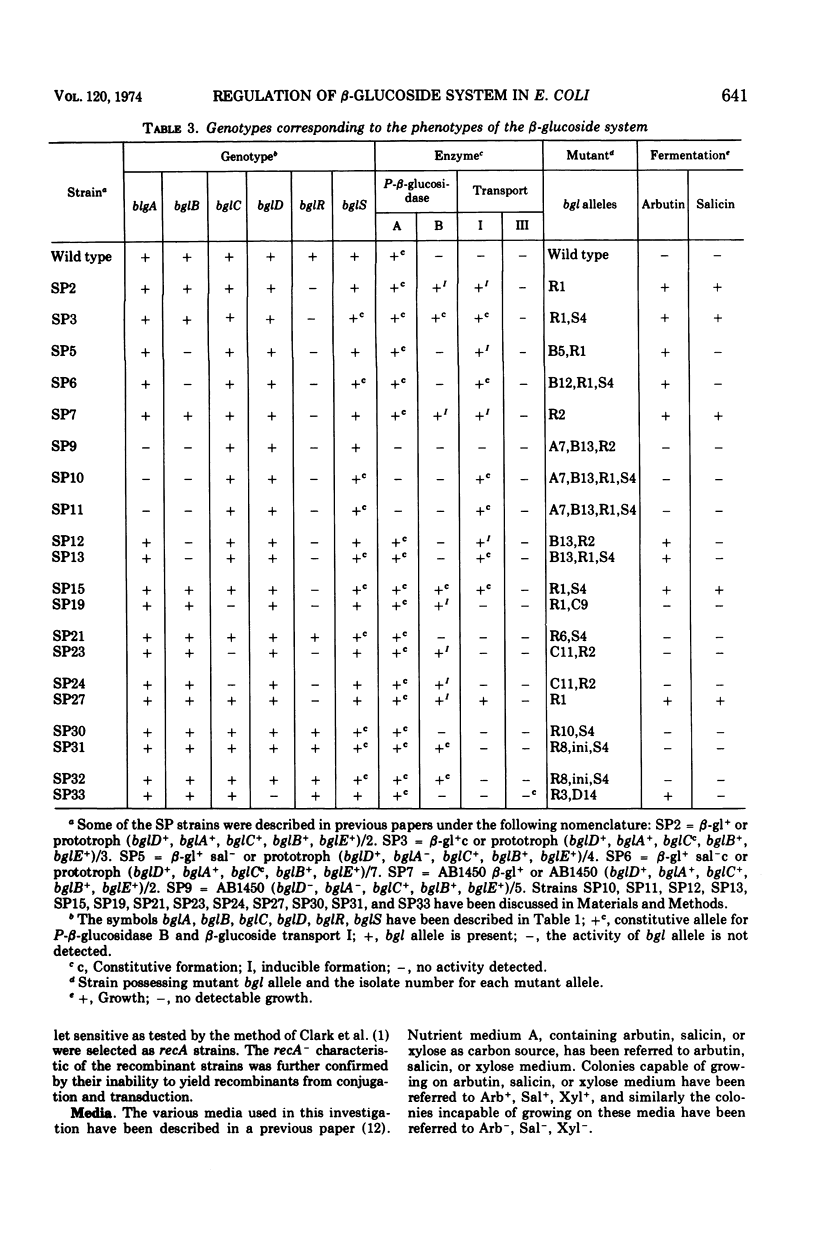
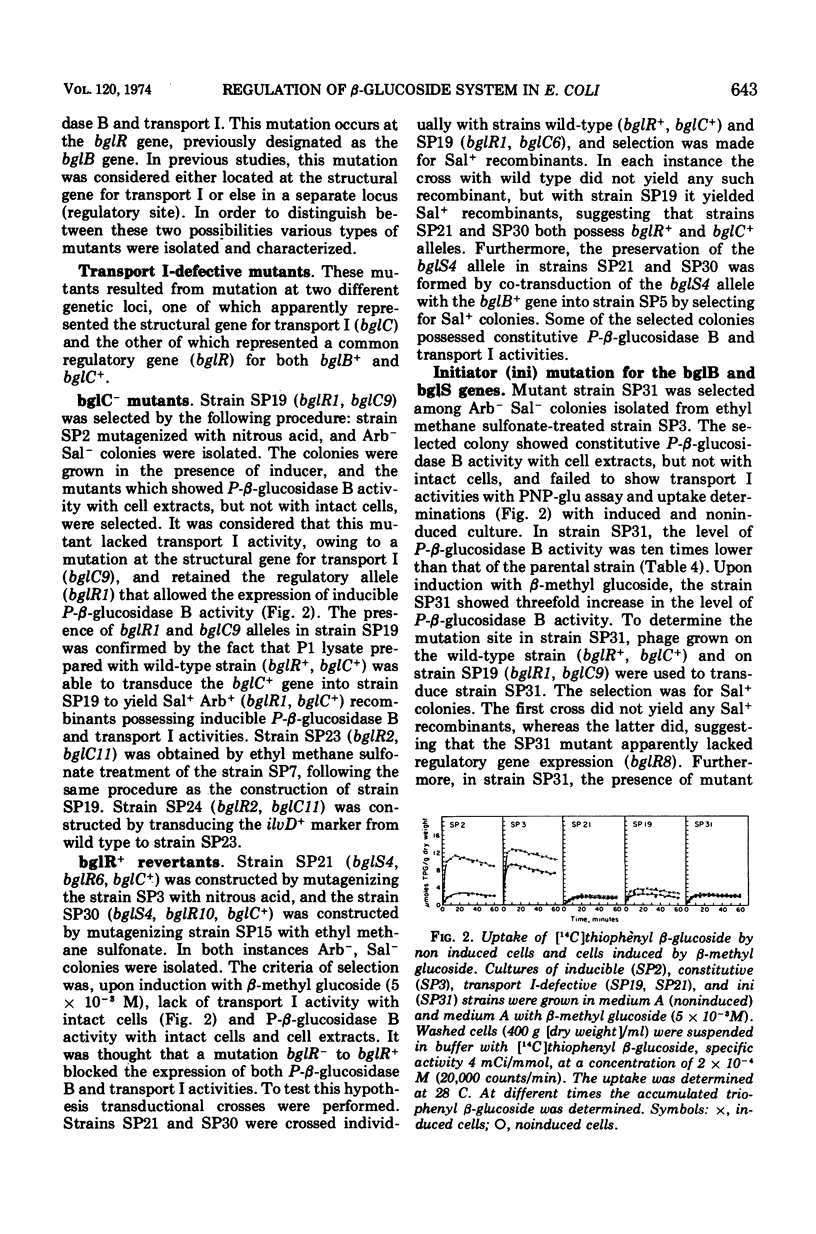
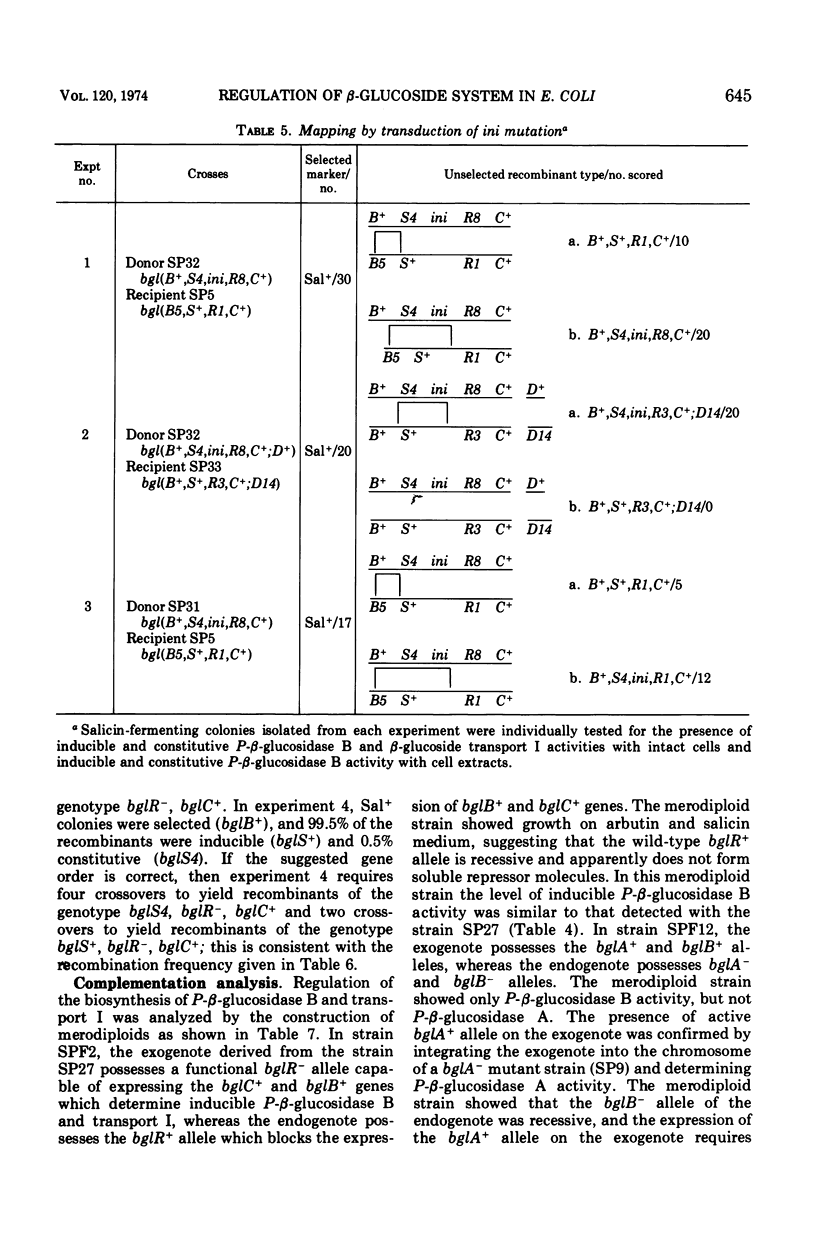
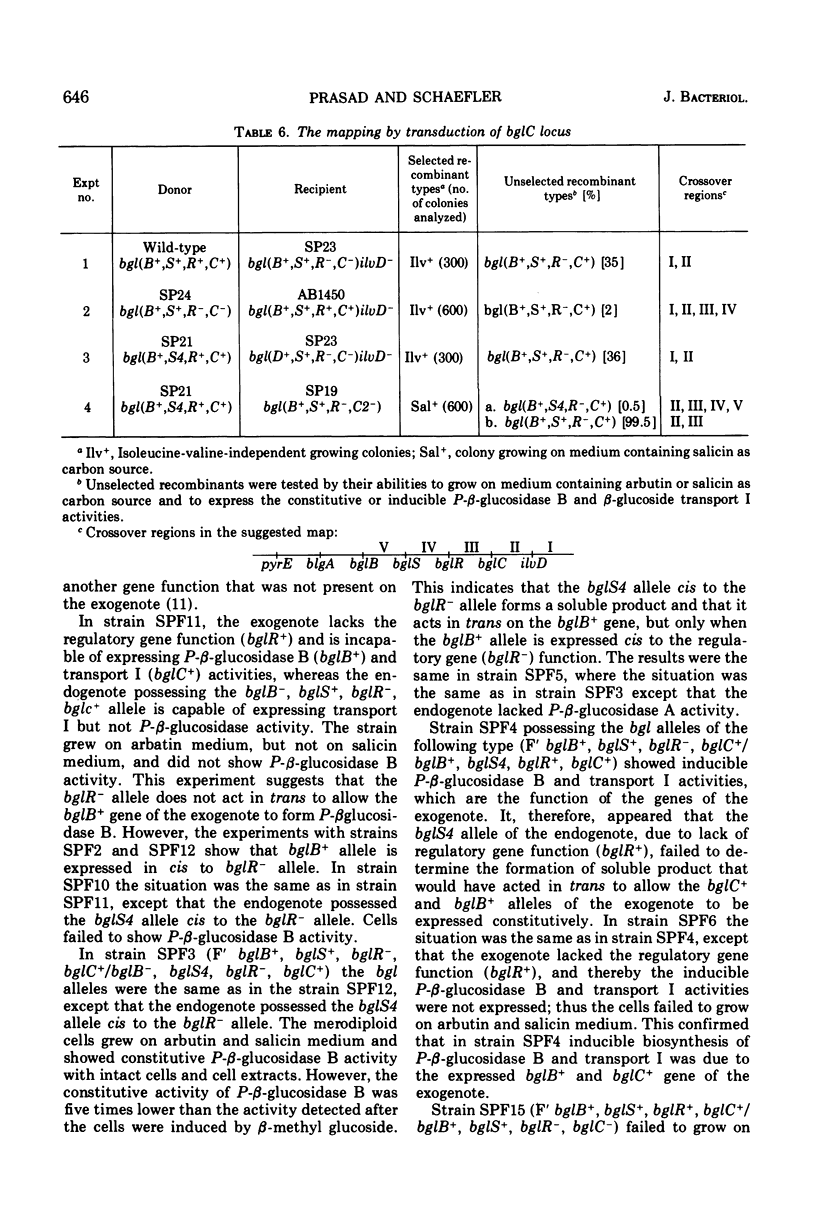
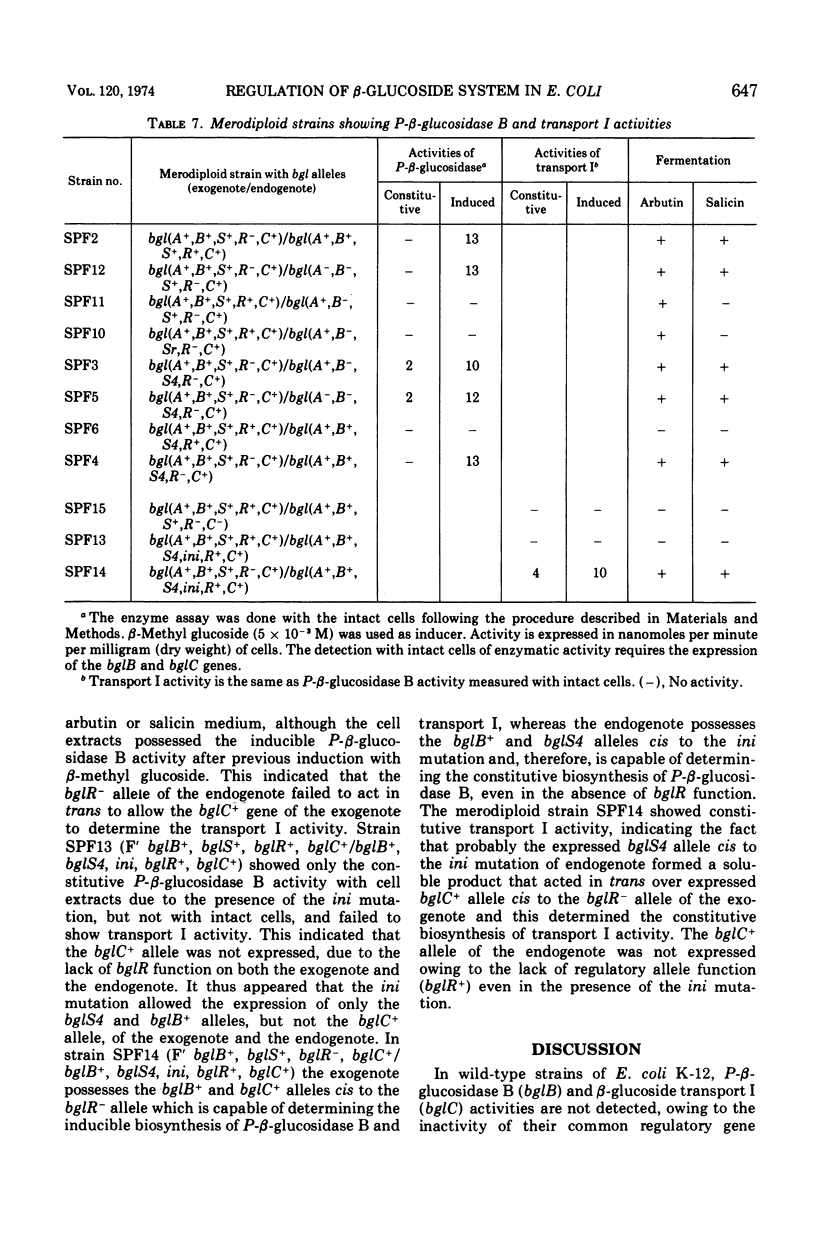
In Escherichia coli wild-type cells, a mutation at the β-glucoside regulatory gene (bglR+ to bglR−) leads to simultaneous expression of inducible phospho-β-glucosidase B (bglB+) and a β-glucoside-specific species of enzyme II (β-glucoside transport I [bglC+]); an additional mutation (bglS+ to bglS4) allows these enzymes to be formed constitutively. The bgl alleles have been mapped in the following order: pyrE, bglA, bglB, bglS, bglR, bglC, ilvD. The back mutation in the regulatory allele (bglR− to bglR+) caused the cessation of the expression of the bglB+, bglS+ or bglS4, bglC+ alleles. However, a mutation in a strain with bglB+, bglS4, bglR8, bglC+ alleles, at the ini site that lies between the bglS4 and the bglR8 allele, allowed the expression of the bglS4 and bglB+ alleles, but showed no affect on the expression of the bglC+ allele. It is suggested that the ini mutation possesses a promotor-type function that in the absence of regulatory allele function (bglR8) renews the functioning of only the bglS4 and bglB+ alleles. The complementation studies have shown that the bglB+, bglS+ or bglS4, bglC+ alleles are expressed only in cis to the bglR− allele. In the constitutive strain (bglB+, bglS4, bglR−, bglC+), the expressed bglS4 allele formed a soluble product that acts in trans over the bglB+ and bglC+ alleles and that appears effective only when the bglB+ and the bglC+ alleles are expressed in cis to the bglR− allele. It thus showed that the constitutive biosynthesis of phospho-β-glucosidase B and β-glucoside transport I is under positive control. Since the regulatory allele bglR− lies between the bglS4 and the blgC+ alleles, and acts in cis, it appears that the mutation (bglR+ to bglR−) allows the initiation of transcription in one direction to express the bglS4, bglB+ alleles and in the other to express the bglC+ allele. The structural genes bglB and bglC lie adjacent to the regulatory genes bglR and bglS, and the structural genes are coordinately controlled by the regulatory genes. It is, therefore, proposed that the bglB, bglS, bglR, bglC genes form a bgl operon.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CLARK A. J., MARGULIES A. D. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF RECOMBINATION-DEFICIENT MUTANTS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:451–459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
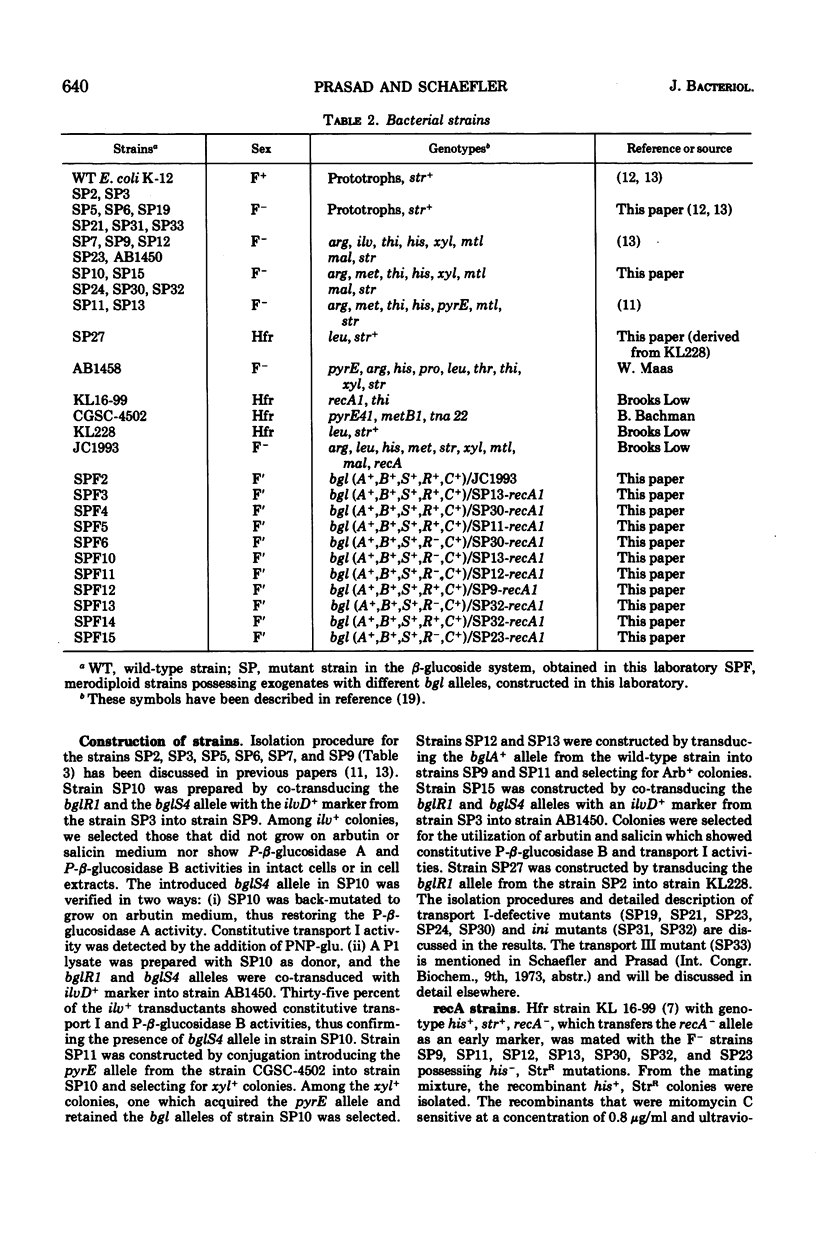
- Demerec M., Adelberg E. A., Clark A. J., Hartman P. E. A proposal for a uniform nomenclature in bacterial genetics. Genetics. 1966 Jul;54(1):61–76. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. F., Wilson G. The role of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent kinase system in beta-glucoside catabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):988–995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guha A. Divergent orientation of transcription from the biotin locus of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 28;56(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. Formation of merodiploids in matings with a class of Rec- recipient strains of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 May;60(1):160–167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. Rapid mapping of conditional and auxotrophic mutations in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):798–812. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.798-812.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low K. B. Escherichia coli K-12 F-prime factors, old and new. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):587–607. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.587-607.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolin P., Bauerle R. H. Determinants for regulation and initiation of expression of tryptophan genes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:311–320. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. E., Anderson R. L. Cellobiose metabolism in Aerobacter aerogenes. 3. Cleavage of cellobiose monophosphate by a phospho- -glucosidase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 10;247(11):3420–3423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad I., Young B., Schaefler S. Genetic determination of the constitutive biosynthesis of phospho- -glucosidase A in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):909–915. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.909-915.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefler S. Inducible system for the utilization of beta-glucosides in Escherichia coli. I. Active transport and utilization of beta-glucosides. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):254–263. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.254-263.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefler S., Maas W. K. Inducible system for the utilization of beta-glucosides in Escherichia coli. II. Description of mutant types and genetic analysis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):264–272. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.264-272.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefler S., Malamy A. Taxonomic investigations on expressed and cryptic phospho-beta-glucosidases in Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):422–433. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.422-433.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefler S., Schenkein I. Beta-glucoside permeases and phospho beta-glucosidases in Aerobacter aerogenes: relationship with cryptic phospho beta-glucosidases in Enterobacteriaceae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):285–292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. O., Beckwith J. R. Mutagens which cause deletions in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1969 Feb;61(2):371–376. doi: 10.1093/genetics/61.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szybalski W., Kubinski H., Sheldrick P. Pyrimidine clusters on the transcribing strand of DNA and their possible role in the initiation of RNA synthesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:123–127. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. L., Trotter C. D. Linkage map of Escherichia coli strain K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):504–524. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.504-524.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


