Abstract
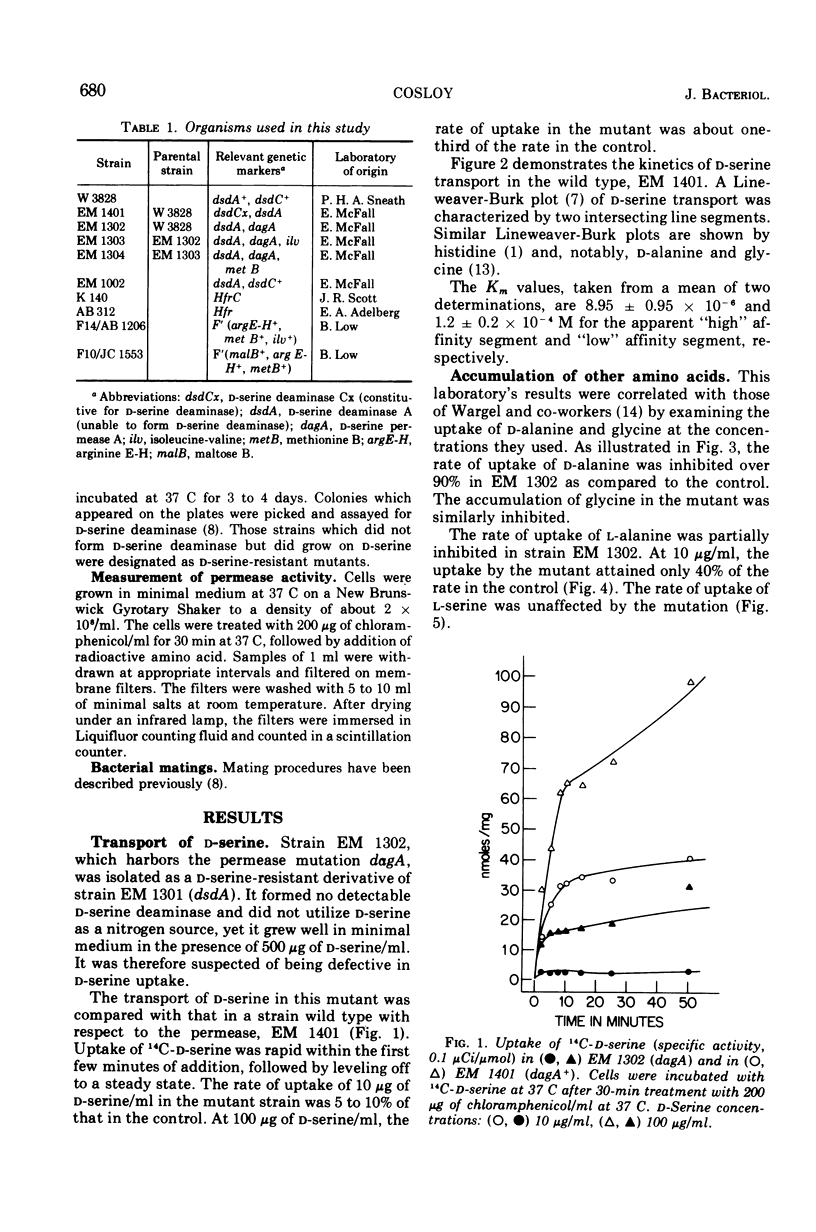
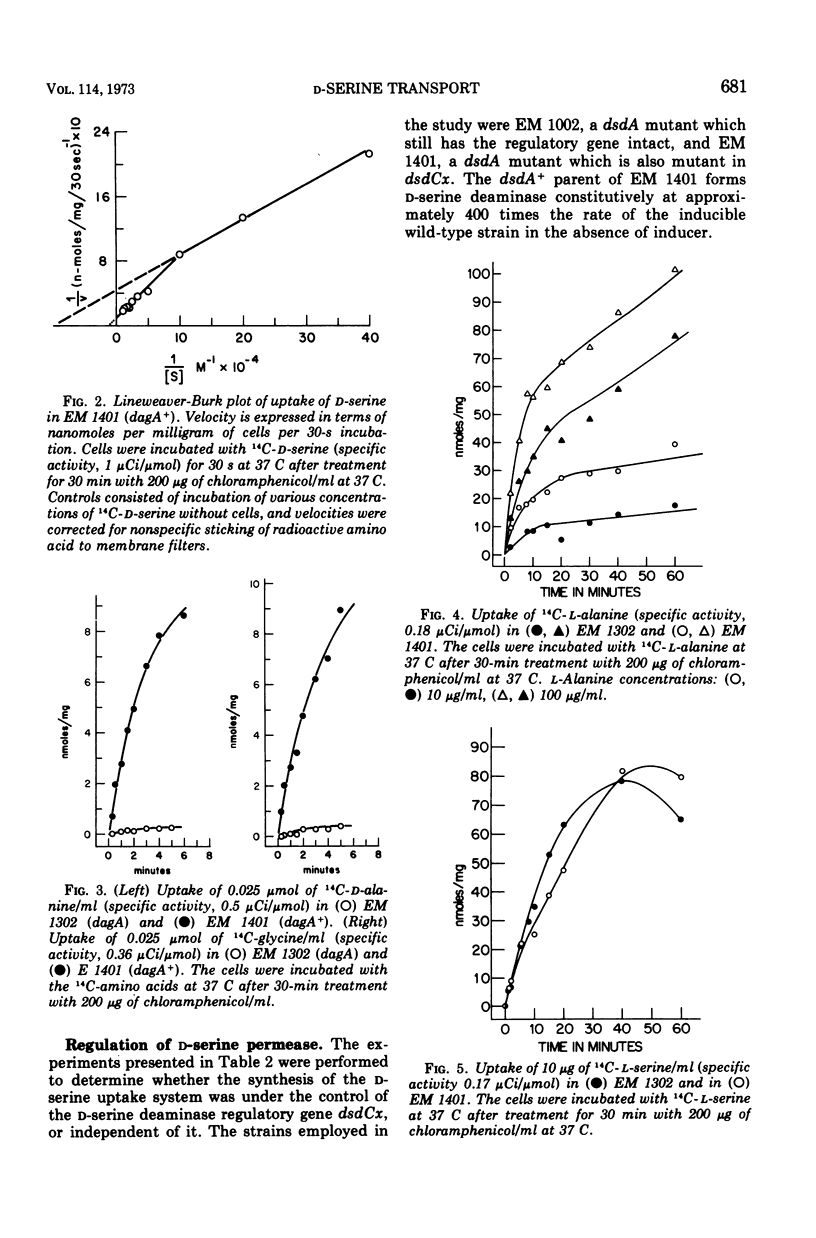
The d-serine transport system in Escherichia coli K-12 was studied by use of a mutant unable to form d-serine deaminase, yet resistant to d-serine. The mutant is greatly impaired in its ability to accumulate d-serine, d-alanine, and glycine. Transport of l-alanine is partially affected but transport of l-serine is unaffected. The mutant is also resistant to d-cycloserine, indicating that d-serine is transported by the system responsible for uptake of d-cycloserine. The d-serine transport system is not inducible, but appears to be formed constitutively, as are the transport systems of most amino acids. The transport mutation appears to be multistep and maps to the right of malB on the E. coli linkage map.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES G. F. UPTAKE OF AMINO ACIDS BY SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jan;104:1–18. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(64)80028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D. Formation of aromatic amino acid pools in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):177–188. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.177-188.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D. Maintenance and exchange of the aromatic amino acid pool in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):70–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.70-81.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss R., 3rd, Charamella L. J., Berg C. M., Harris P. E. Kinetic and genetic analyses of D-cycloserine inhibition and resistance in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1238–1250. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1238-1250.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KESSEL D., LUBIN M. STABILITY OF ALPHA-HYDROGEN OF AMINO ACIDS DURING ACTIVE TRANSPORT. Biochemistry. 1965 Mar;4:561–565. doi: 10.1021/bi00879a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFall E. Mapping of the d-serine deaminase region in Escherichia coli K-12. Genetics. 1967 Jan;55(1):91–99. doi: 10.1093/genetics/55.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno J. R., Oxender D. L. Amino acid transport systems in Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 25;243(22):5914–5920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld H., Feigelson P. Product induction in Pseudomonas acidovorans of a permease system which transports L-tryptophan. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):705–714. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.705-714.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ J. H., MAAS W. K., SIMON E. J. An impaired concentrating mechanism for amino acids in mutants of Escherichia coli resistant to L-canavanine and D-serine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Apr;32:582–583. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90650-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. L. Current linkage map of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Jun;34(2):155–175. doi: 10.1128/br.34.2.155-175.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wargel R. J., Hadur C. A., Neuhaus F. C. Mechanism of D-cycloserine action: transport mutants for D-alanine, D-cycloserine, and glycine. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1028–1035. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1028-1035.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wargel R. J., Shadur C. A., Neuhaus F. C. Mechanism of D-cycloserine action: transport systems for D-alanine, D-cycloserine, L-alanine, and glycine. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):778–788. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.778-788.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


