Abstract
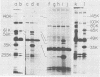
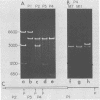
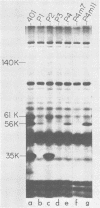
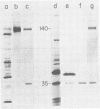
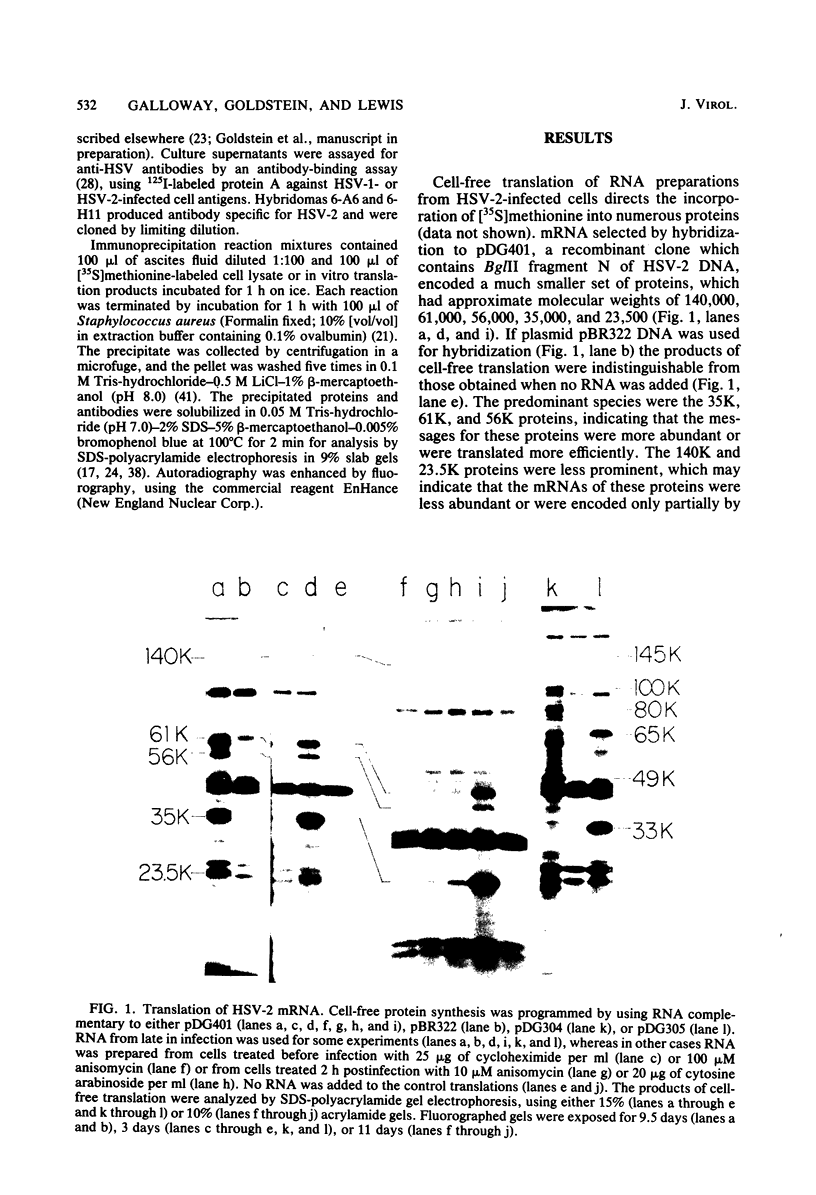
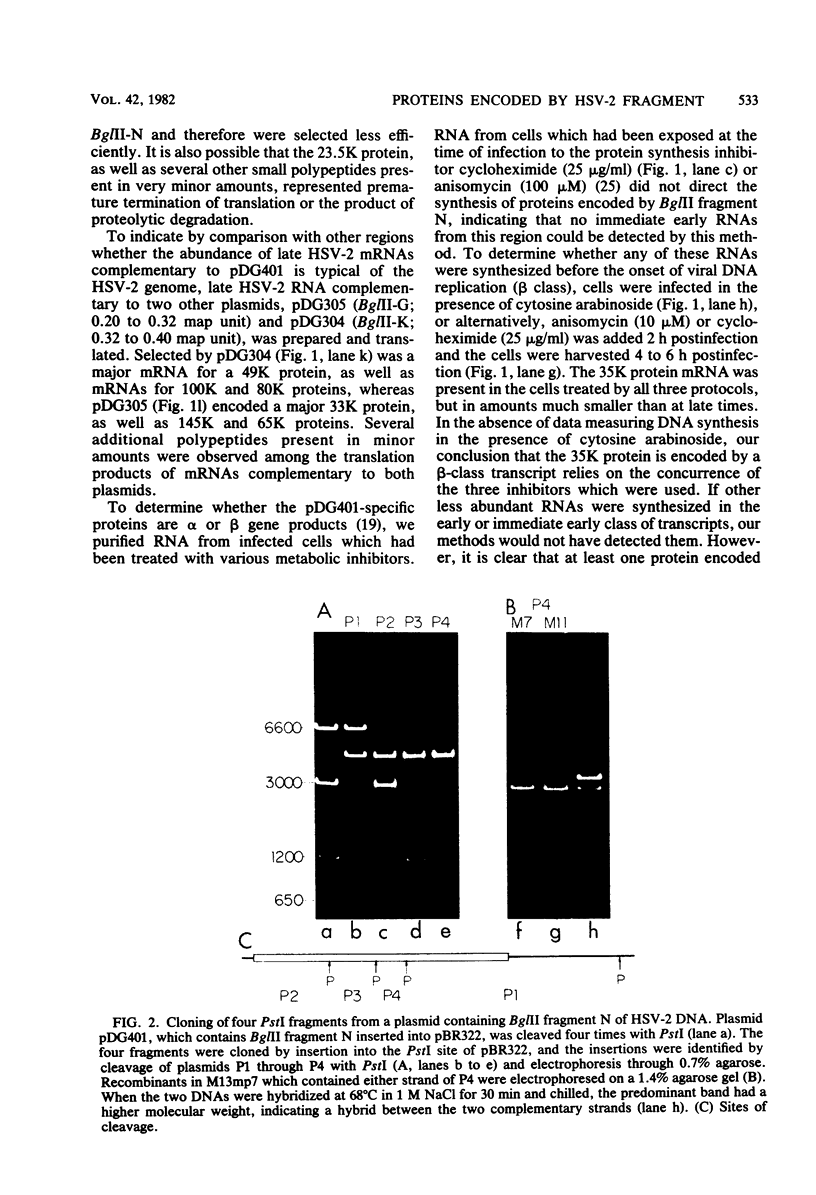
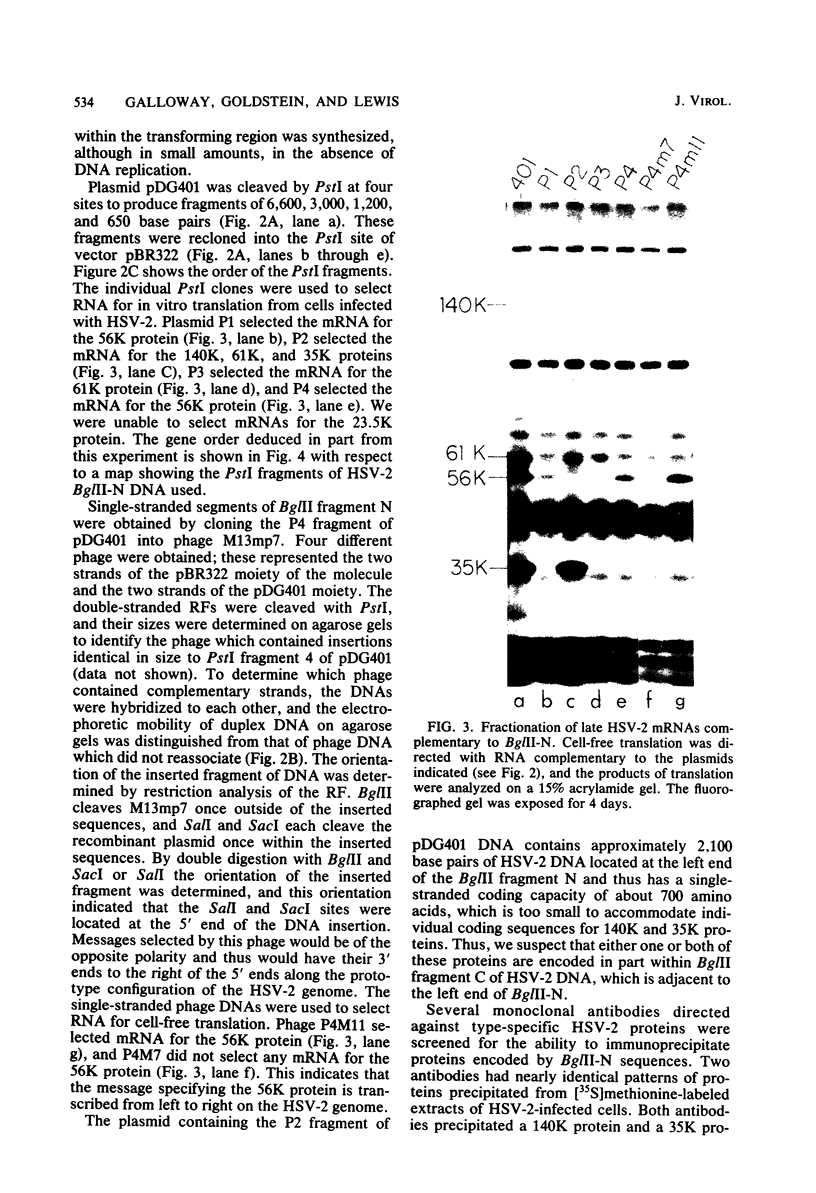
Cloned BglII fragment N (map units 0.58 to 0.625) of herpes simplex virus type 2 DNA has been shown to transform rodent cells to an oncogenic phenotype (Galloway and McDougall, J. Virol. 38: 749-760, 1981). RNA homologous to this fragment directs the synthesis of five polypeptides in a cell-free translation system. The approximate molecular weights of these proteins are 140,000, 61,000, 56,000, 35,000, and 23,500. The 35,000-dalton protein is the major species late in infection and is the only species detected before the onset of viral DNA replication. The arrangement of the sequences encoding these proteins along the herpes simplex virus type 2 genome was determined by hybridization of the RNA to cloned PstI fragment of BglII-N and to single-stranded DNA segments cloned into M13mp7. Both the hybridization experiments and immunoprecipitation with monoclonal antibodies suggested that the 140,000- and 35,000-dalton proteins are at least partially colinear and share antigenic determinants.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. W., Lewis J. B., Atkins J. F., Gesteland R. F. Cell-free synthesis of adenovirus 2 proteins programmed by fractionated messenger RNA: a comparison of polypeptide products and messenger RNA lengths. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2756–2760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. P., Frink R. J., Devi G. B., Gaylord B. H., Costa R. H., Wagner E. K. Detailed characterization of the mRNA mapping in the HindIII fragment K region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):1011–1027. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.1011-1027.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Topp W., Sambrook J. The arrangement of simian virus 40 sequences in the DNA of transformed cells. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):269–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camacho A., Spear G. Transformation of hamster embryo fibroblasts by a specific fragment of the herpes simplex virus genome. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):993–1002. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90283-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Devi B. G., Anderson K. P., Gaylord B. H., Wagner E. K. Characterization of a major late herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):483–496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.483-496.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. J., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Preston C. M. Identification of a virus-specific polypeptide associated with a transforming fragment (BglII-N) of herpes simplex virus type 2 DNA. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):126–132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.126-132.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flannery V. L., Courtney R. J., Schaffer P. A. Expression of an early, nonstructural antigen of herpes simplex virus in cell transformed in vitro by herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):284–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.284-291.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel N., Locker H., Cox B., Roizman B., Rapp F. Herpes simplex virus DNA in transformed cells: sequence complexity in five hamster cell lines and one derived hamster tumor. J Virol. 1976 Jun;18(3):885–893. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.3.885-893.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frink R. J., Anderson K. P., Wagner E. K. Herpes simplex virus type 1 HindIII fragment L encodes spliced and complementary mRNA species. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):559–572. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.559-572.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. A., Copple C. D., McDougall J. K. Analysis of viral DNA sequences in hamster cells transformed by herpes simplex virus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):880–884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. A., McDougall J. K. Transformation of rodent cells by a cloned DNA fragment of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):749–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.749-760.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. A., Swain M. Cloning of Herpes simplex virus 2 DNA fragments in a plasmid vector. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P., Lausch R. N., Hay K. A., Rapp F. Expression of type-common envelope antigens by herpes simplex virus type 2-transformed hamster cells. Intervirology. 1980;14(1):50–56. doi: 10.1159/000149162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Honess R. W., Cassai E., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XII. The virion polypeptides of type 1 strains. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):640–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.640-651.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland L. E., Anderson K. P., Stringer J. R., Wagner E. K. Isolation and localization of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA abundant before viral DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):447–462. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.447-462.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jariwalla R. J., Aurelian L., Ts'o P. O. Tumorigenic transformation induced by a specific fragment of DNA from herpes simplex virus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2279–2283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessous A., Bibor-Hardy V., Suh M., Simard R. Analysis of chromosomes, nucleic acids, and polypeptides in hamster cells transformed by herpes simplex virus type 2. Cancer Res. 1979 Aug;39(8):3225–3234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Mathews M. B. Control of adenovirus early gene expression: a class of immediate early products. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab J. C., Timbury M. C. Complementation of ts mutants by a herpes simplex virus ts-transformed cell line. Nature. 1976 May 20;261(5557):233–235. doi: 10.1038/261233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse L. S., Buchman T. G., Roizman B., Schaffer P. A. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. IX. Apparent exclusion of some parental DNA arrangements in the generation of intertypic (HSV-1 X HSV-2) recombinants. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):231–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.231-248.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowinski R. C., Lostrom M. E., Tam M. R., Stone M. R., Burnette W. N. The isolation of hybrid cell lines producing monoclonal antibodies against the p15(E) protein of ecotropic murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1979 Feb;93(1):111–126. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., McGeoch D. J. Identification and mapping of two polypeptides encoded within the herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase gene sequences. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):593–605. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.593-605.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp F., Westmoreland D. Cell transformation by DNA-containing viruses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 16;458(2):167–211. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(76)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed C. L., Cohen G. H., Rapp F. Detection of a virus-specific antigen on the surface of herpes simplex virus-transformed cells. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):668–670. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.668-670.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes G. R., LaFemina R., Hayward S. D., Hayward G. S. Morphological transformation by DNA fragments of human herpesviruses: evidence for two distinct transforming regions in herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 and lack of correlation with biochemical transfer of the thymidine kinase gene. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):629–641. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Miller J. S., Roberts B. E. Purification and mapping of specific mRNAs by hybridization-selection and cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. V. Purification and structural proteins of the herpesvirion. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):143–159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.143-159.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh M., Kessous A., Poirier N., Simard R. Immunoprecipitation of polypeptides from hamster embryo cells transformed by herpes simplex virus type 2. Virology. 1980 Jul 30;104(2):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90335-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Sullivan M., Vande Woude G. F. Structures of two spliced herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early mRNA's which map at the junctions of the unique and reiterated regions of the virus DNA S component. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):431–444. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.431-444.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweig M., Heilman C. J., Jr, Rabin H., Hampar B. Shared antigenic determinants between two distinct classes of proteins in cells infected with herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):644–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.644-652.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]