Abstract
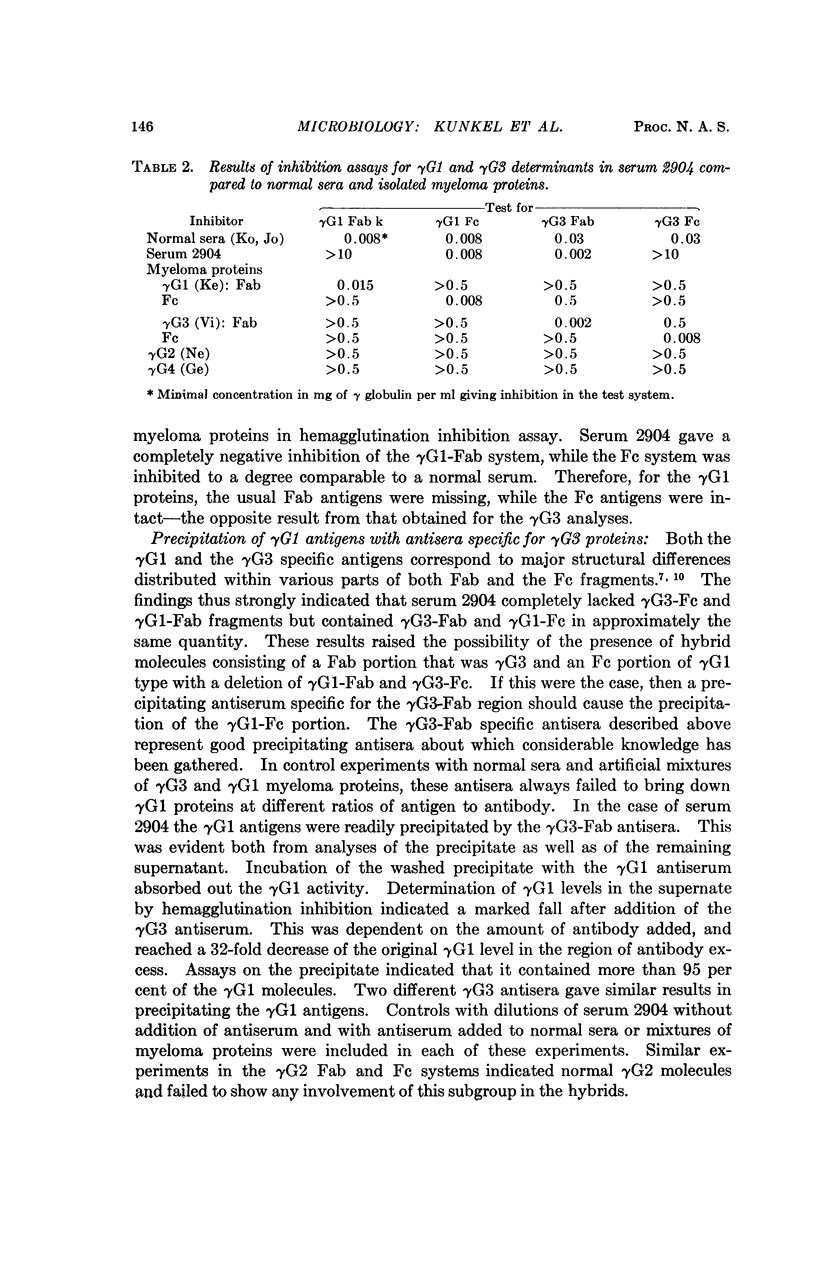
No explanation has been available concerning the γ globulin defect in a unique family with one member whose serum was devoid of all the usual Gm genetic antigens. In the present study, it was found that this serum lacks ordinary γG1 and γG3 proteins and contains instead hybrid molecules of the type γG3-γG1. These were demonstrated most clearly by the precipitation of γG1 proteins with antisera specific for γG3 antigens. The analogy to the delta-beta chain hybrids, established for Lepore-type hemoglobins, was striking. An unequal homologous crossover involving mispairing of heavy chain cistrons would readily explain the deletion of genetic markers.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAGLIONI C. The fusion of two peptide chains in hemoglobin Lepore and its interpretation as a genetic deletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Nov 15;48:1880–1886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.11.1880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREY H. M., KUNKEL H. G. H CHAIN SUBGROUPS OF MYELOMA PROTEINS AND NORMAL 7S GAMMA-GLOBULIN. J Exp Med. 1964 Aug 1;120:253–266. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårtensson L. Genes and immunoglobulins. Vox Sang. 1966 Sep-Oct;11(5):521–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1966.tb04251.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig J. B. Heterogeneity of anti-gamma-globulin factors detected by pepsin-digested human gamma G-globulin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;66(3):369–382. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.66.3.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER R. R. The hydrolysis of rabbit y-globulin and antibodies with crystalline papain. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:119–126. doi: 10.1042/bj0730119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prahl J. W. The C-terminal sequences of the heavy chains of human immunoglobulin G myeloma proteins of differing isotopes and allotypes. Biochem J. 1967 Dec;105(3):1019–1028. doi: 10.1042/bj1051019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINBERG A. G., GOLDBLUM R. A GENETIC STUDY OF THE ANTIGENS ASSOCIATED WITH THE GM(B) FACTOR OF HUMAN GAMMA GLOBULIN. Am J Hum Genet. 1965 Mar;17:133–147. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg A. G., Muir W. A., McIntire S. A. Two unusual Gm alleles: their implications for the genetics of the Gm antigens. Am J Hum Genet. 1968 May;20(3):258–278. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner N. L., Herzenberg L. A., Goldstein G. Immunoglobulin isoantigens (allotypes) in the mouse. II. Allotypic analysis of three gammaG2-myeloma proteins from (NZB x BALB/c)F1 hybrids and of normal gammaG2-globulins. J Exp Med. 1966 Apr 1;123(4):707–721. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.4.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Kunkel H. G., Litwin S. D. Studies of the Vi (gamma-2c) subgroup of gamma-globulin. A relationship between concentration and genetic type among normal individuals. J Exp Med. 1967 Jan 1;125(1):177–190. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]