Abstract
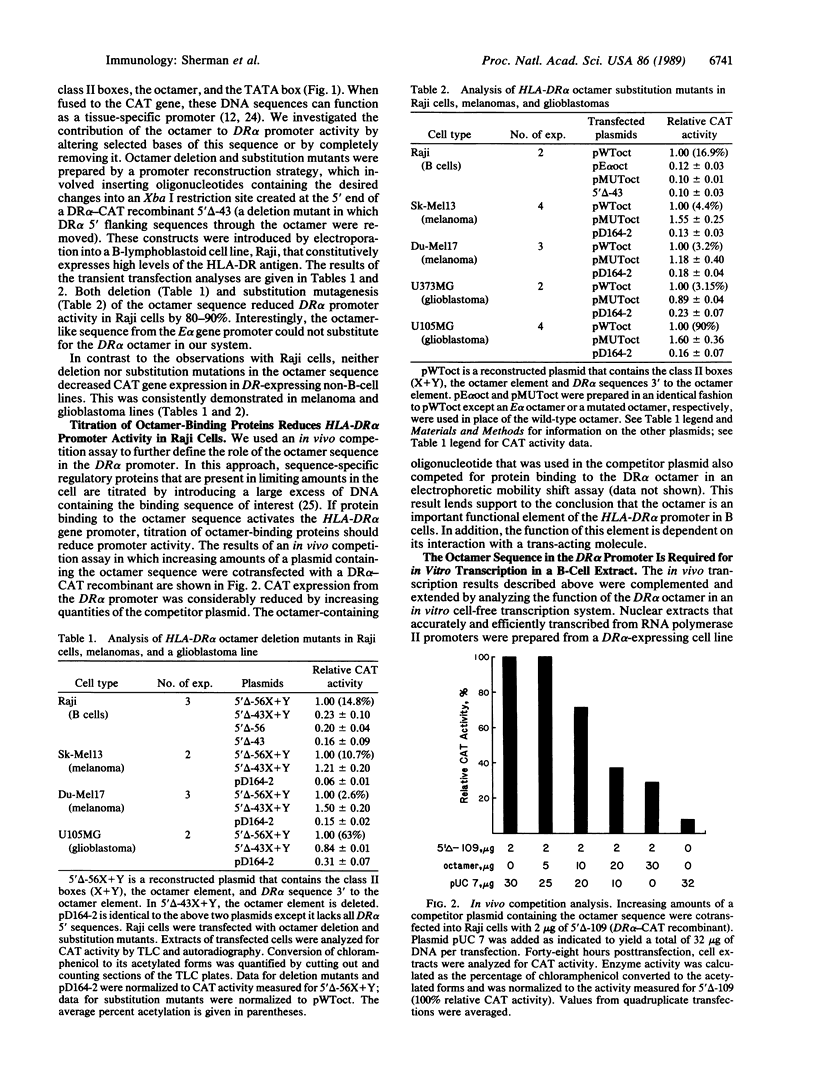
The human class II gene, HLA-DR alpha, contains an octanucleotide sequence ATTTGCAT located approximately 40 base pairs upstream of the transcription initiation site. We have investigated the transcriptional function of the DR alpha octamer in human B-lymphoblastoid cells and non-B cells. Deletion and substitution mutagenesis of the octamer sequence greatly reduced the activity of the DR alpha promoter in both in vivo and in vitro cell-free transcription systems of B-cell origin. Conversely, these mutations did not affect promoter activity in several non-B-cell lines that express the DR alpha gene. Removal of octamer-binding proteins by in vivo titration with an octamer-containing competitor plasmid reduced DR alpha promoter activity in B-lymphoblastoid cells. These results suggest that a protein-octamer interaction, most likely involving the B-cell-specific octamer binding protein (OTF-2), is required for DR alpha promoter function in B-lymphoblastoid cells but not in non-B cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basta P. V., Sherman P. A., Ting J. P. Identification of an interferon-gamma response region 5' of the human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen DR alpha chain gene which is active in human glioblastoma multiforme lines. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 15;138(4):1275–1280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman Y., Rice D., Grosschedl R., Baltimore D. Two regulatory elements for immunoglobulin kappa light chain gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7041–7045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington M. N., Chedid M., Ting J. P., Ward F. E. Differential expression of the HLA-DR genes in various melanoma cell lines treated with interferon-gamma: methylation of the HLA-DR alpha gene in these lines is not correlated with its expression. Hum Immunol. 1987 Feb;18(2):151–161. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(87)90012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das H. K., Lawrance S. K., Weissman S. M. Structure and nucleotide sequence of the heavy chain gene of HLA-DR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3543–3547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Zachau H. G. Correct transcription of an immunoglobulin kappa gene requires an upstream fragment containing conserved sequence elements. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):71–74. doi: 10.1038/310071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher C., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Purification and characterization of OTF-1, a transcription factor regulating cell cycle expression of a human histone H2b gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Matthias P., Thali M., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. Cell type-specificity elements of the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene enhancer. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1323–1330. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton A. N., Eisinger M., Albino A. P., Cairncross J. G., Old L. J. Surface antigens of melanocytes and melanomas. Markers of melanocyte differentiation and melanoma subsets. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1755–1766. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi N. F., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Interaction of cell-type-specific nuclear proteins with immunoglobulin VH promoter region sequences. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):548–551. doi: 10.1038/323548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maffei A., Scarpellino L., Bernard M., Carra G., Jotterand-Bellomo M., Guardiola J., Accolla R. S. Distinct mechanisms regulate MHC class II gene expression in B cells and macrophages. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):942–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill E. A., Fletcher C., Burrow C. R., Heintz N., Roeder R. G., Kelly T. J. Transcription factor OTF-1 is functionally identical to the DNA replication factor NF-III. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1210–1213. doi: 10.1126/science.3413485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Maki R. A., Clayton L. K., Tonegawa S. Complete primary structures of the E beta chain and gene of the mouse major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5520–5524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Heguy A., Roeder R. G. Identification and purification of a human lymphoid-specific octamer-binding protein (OTF-2) that activates transcription of an immunoglobulin promoter in vitro. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):783–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90101-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Gruss P. Specific interaction between enhancer-containing molecules and cellular components. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90233-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Basta P. V., Moore T. L., Brown A. M., Ting J. P. Class II box consensus sequences in the HLA-DR alpha gene: transcriptional function and interaction with nuclear proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):50–56. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Basta P. V., Ting J. P. Upstream DNA sequences required for tissue-specific expression of the HLA-DR alpha gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4254–4258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Multiple sequence elements are required for maximal in vitro transcription of a human histone H2B gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3329–3340. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R., Baumruker T., Franza B. R., Jr, Herr W. A 100-kD HeLa cell octamer binding protein (OBP100) interacts differently with two separate octamer-related sequences within the SV40 enhancer. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1147–1160. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takiguchi M., Ting J. P., Buessow S. C., Boyer C., Gillespie Y., Frelinger J. A. Response of glioma cells to interferon-gamma: increase in class II RNA, protein and mixed lymphocyte reaction-stimulating ability. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Aug;15(8):809–814. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang S. Y., Nakanishi M., Peterlin B. M. B-cell-specific and interferon-gamma-inducible regulation of the HLA-DR alpha gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8598–8602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. D., Edlund T., Boulet A. M., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression controlled by the 5'-flanking region of insulin and chymotrypsin genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):557–561. doi: 10.1038/306557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]