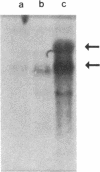
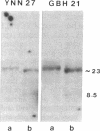
Abstract
Polymyxin B is an antibiotic that kills sensitive cells by disrupting their membranes. We have cloned a wild-type yeast gene that, when present on a high-copy-number plasmid, renders the cells resistant to the drug. The nucleotide sequence of this gene is presented. A single open reading frame within the sequence has the potential to encode a polypeptide (molecular mass of 77.5 kDa) that shows strong homologies to polypeptides of the protein kinase family. The gene, PBS2, located on chromosome X, is not allelic to the previously described PBS1 gene (where PBS signifies polymyxin B sensitivity). Although pbs1 mutations confer resistance to high levels of polymyxin B, double mutants, pbs1 pbs2, are not resistant to the drug, indicating that PBS2 is essential for pbs1 activity. Models based on the proposed protein kinase activity of the PBS2 gene product are presented to explain the interaction between PBS1 and PBS2 gene products involved in conferring polymyxin B resistance on yeast cells.
Full text
PDF
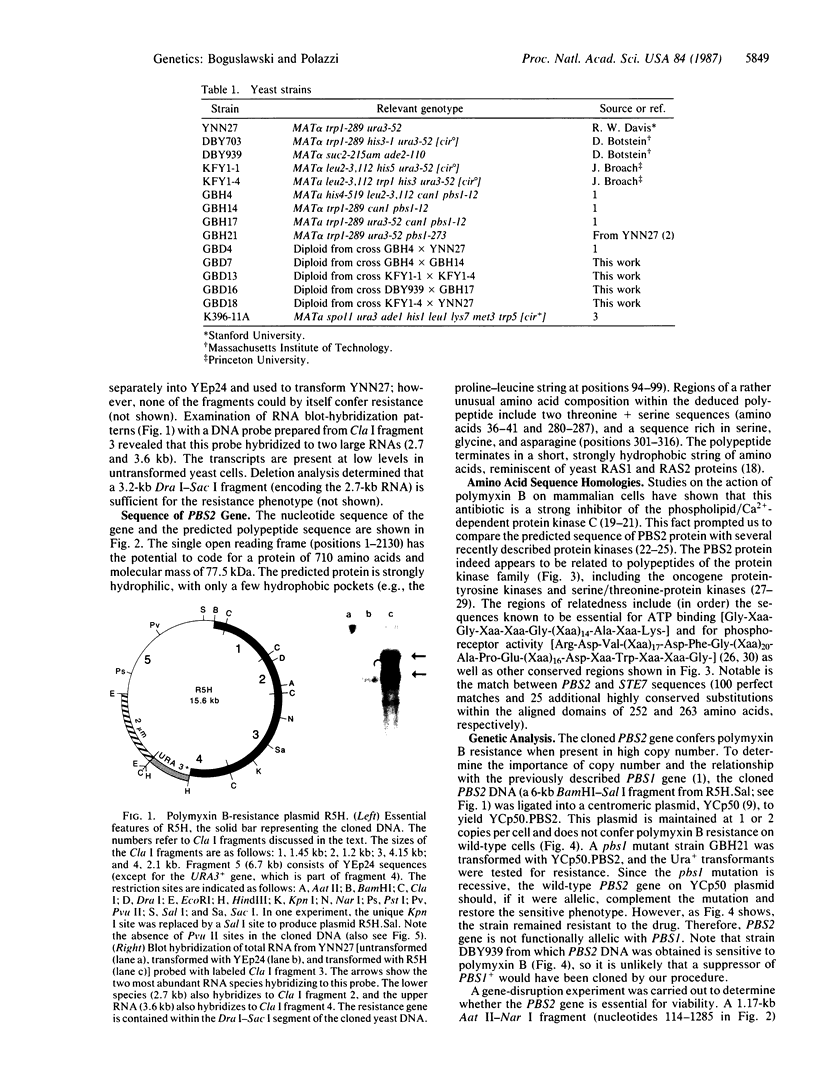
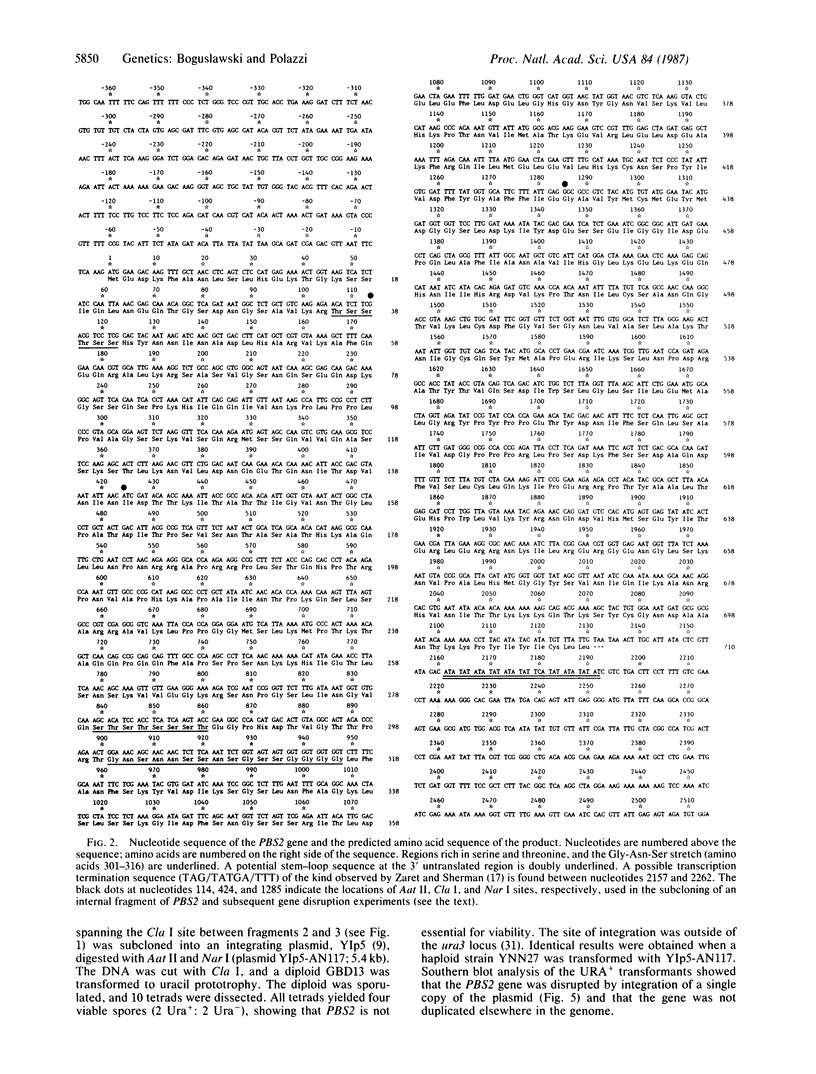


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguslawski G. Effects of polymyxin B sulfate and polymyxin B nonapeptide on growth and permeability of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;199(3):401–405. doi: 10.1007/BF00330749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguslawski G. Polymyxin B nonapeptide inhibits mating in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Feb;29(2):330–332. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.2.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. An electrophoretic karyotype for yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3756–3760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celenza J. L., Carlson M. A yeast gene that is essential for release from glucose repression encodes a protein kinase. Science. 1986 Sep 12;233(4769):1175–1180. doi: 10.1126/science.3526554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falco S. C., Botstein D. A rapid chromosome-mapping method for cloned fragments of yeast DNA. Genetics. 1983 Dec;105(4):857–872. doi: 10.1093/genetics/105.4.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groffen J., Heisterkamp N., Reynolds F. H., Jr, Stephenson J. R. Homology between phosphotyrosine acceptor site of human c-abl and viral oncogene products. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):167–169. doi: 10.1038/304167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Taylor S. S., Sefton B. M. Direct evidence that oncogenic tyrosine kinases and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase have homologous ATP-binding sites. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):589–592. doi: 10.1038/310589a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapholz S., Esposito R. E. A new mapping method employing a meiotic rec-mutant of yeast. Genetics. 1982 Mar;100(3):387–412. doi: 10.1093/genetics/100.3.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf J. L., Lee M. H., Sultzman L. A., Kriz R. W., Loomis C. R., Hewick R. M., Bell R. M. Cloning and expression of multiple protein kinase C cDNAs. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90874-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lörincz A. T., Reed S. I. Primary structure homology between the product of yeast cell division control gene CDC28 and vertebrate oncogenes. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):183–185. doi: 10.1038/307183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A., Reed S. I. Isolation of genes by complementation in yeast: molecular cloning of a cell-cycle gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2119–2123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nel A. E., Wooten M. W., Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Miller P. J., Stevenson H. C., Galbraith R. M. Polymyxin B causes coordinate inhibition of phorbol ester-induced C-kinase activity and proliferation of B lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 16;128(3):1364–1372. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91091-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent S. A., Fenimore C. M., Bostian K. A. Vector systems for the expression, analysis and cloning of DNA sequences in S. cerevisiae. Yeast. 1985 Dec;1(2):83–138. doi: 10.1002/yea.320010202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Coussens L., Totty N., Rhee L., Young S., Chen E., Stabel S., Waterfield M. D., Ullrich A. The complete primary structure of protein kinase C--the major phorbol ester receptor. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):853–859. doi: 10.1126/science.3755547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers S., Michaelis S., Broek D., Santa Anna S., Field J., Herskowitz I., Wigler M. RAM, a gene of yeast required for a functional modification of RAS proteins and for production of mating pheromone a-factor. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90598-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rine J., Hansen W., Hardeman E., Davis R. W. Targeted selection of recombinant clones through gene dosage effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6750–6754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M., Botstein D. Structure and function of the yeast URA3 gene. Differentially regulated expression of hybrid beta-galactosidase from overlapping coding sequences in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):883–904. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Pescador R., Urdea M. S. Use of unpurified synthetic deoxynucleotide primers for rapid dideoxynucleotide chain termination sequencing. DNA. 1984 Aug;3(4):339–343. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutchfield J., Jones P. M., Howell S. L. The effects of polymyxin B, a protein kinase C inhibitor, on insulin secretion from intact and permeabilized islets of Langerhans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 14;136(3):1001–1006. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90432-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teague M. A., Chaleff D. T., Errede B. Nucleotide sequence of the yeast regulatory gene STE7 predicts a protein homologous to protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7371–7375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., Verma I. M. Homology among oncogenes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;123:73–98. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70810-7_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston F., Chumley F., Fink G. R. Eviction and transplacement of mutant genes in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:211–228. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrenn R. W., Wooten M. W. Dual calcium-dependent protein phosphorylation systems in pancreas and their differential regulation by polymyxin B1. Life Sci. 1984 Jul 16;35(3):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]