Abstract
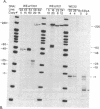
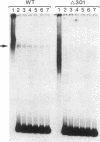
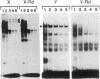
A conserved sequence motif exists at the 5' end of all major histocompatibility complex class II genes. This motif consists of the 14-base X and Y boxes separated by a short stretch of variable sequence. In this report, we provide evidence that the X and Y boxes play an important role in controlling transcription of the murine class II gene E kappa alpha. We have developed transgenic mouse lines that carry E alpha genes cleanly deleted for either the X or Y box and have compared the expression of these mutant transgenes with that of a nondeleted control. Both the X and Y segments appear critical for accurate and efficient transcription of E kappa alpha. The most drastic effect is seen with gamma-interferon-treated macrophages, where deletion of the Y box completely abrogates transcription initiated by the normal promoter. In addition, we identify proteins from nuclear extracts that bind specifically to the X or Y box.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Strominger J. L. Molecular genetics of the human major histocompatibility complex. Adv Hum Genet. 1986;15:197–247. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8356-1_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M., Pelham H. R. Heat shock regulatory elements function as an inducible enhancer in the Xenopus hsp70 gene and when linked to a heterologous promoter. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):753–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90789-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Pujol-Borrell R., Hanafusa T., Feldmann M. Role of aberrant HLA-DR expression and antigen presentation in induction of endocrine autoimmunity. Lancet. 1983 Nov 12;2(8359):1115–1119. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90629-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Trumbauer M. E., Yagle M. K., Palmiter R. D. Factors affecting the efficiency of introducing foreign DNA into mice by microinjecting eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4438–4442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Weinheimer S. P., McKnight S. L. A genetic approach to promoter recognition during trans induction of viral gene expression. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):53–59. doi: 10.1126/science.3018926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S., Metherall J. E., Yamakawa M., Pan J., Weissman S. M., Forget B. G. A point mutation in the A gamma-globin gene promoter in Greek hereditary persistence of fetal haemoglobin. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):325–326. doi: 10.1038/313325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dembic Z., Ayane M., Klein J., Steinmetz M., Benoist C. O., Mathis D. J. Inbred and wild mice carry identical deletions in their E alpha MHC genes. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):127–131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02326.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell R. A., Allen H., Huber B., Wake C., Widera G. Organization and expression of the MHC of the C57 black/10 mouse. Immunol Rev. 1985 Jul;84:29–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelinas R., Endlich B., Pfeiffer C., Yagi M., Stamatoyannopoulos G. G to A substitution in the distal CCAAT box of the A gamma-globin gene in Greek hereditary persistence of fetal haemoglobin. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):323–325. doi: 10.1038/313323a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Eisenberg S. P., Coen D. M., McKnight S. L. Alternate utilization of two regulatory domains within the Moloney murine sarcoma virus long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1959–1968. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundström T., Zenke W. M., Wintzerith M., Matthes H. W., Staub A., Chambon P. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis by microscale 'shot-gun' gene synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3305–3316. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R. E., Krumlauf R., Camper S. A., Brinster R. L., Tilghman S. M. Diversity of alpha-fetoprotein gene expression in mice is generated by a combination of separate enhancer elements. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):53–58. doi: 10.1126/science.2432657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly A., Trowsdale J. Complete nucleotide sequence of a functional HLA-DP beta gene and the region between the DP beta 1 and DP alpha 1 genes: comparison of the 5' ends of HLA class II genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1607–1621. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Meur M., Gerlinger P., Benoist C., Mathis D. Correcting an immune-response deficiency by creating E alpha gene transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Jul 4;316(6023):38–42. doi: 10.1038/316038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Benoist C. O., Williams V. E., 2nd, Kanter M. R., McDevitt H. O. The murine E alpha immune response gene. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):745–754. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Benoist C., Williams V. E., 2nd, Kanter M., McDevitt H. O. Several mechanisms can account for defective E alpha gene expression in different mouse haplotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):273–277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tilly K., Maniatis T. Fine structure genetic analysis of a beta-globin promoter. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):613–618. doi: 10.1126/science.3457470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan D. M., Larhammar D., Wilson M. C., Peterson P. A., Quaranta V. Structure of the human Ia-associated invariant (gamma)-chain gene: identification of 5' sequences shared with major histocompatibility complex class II genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4484–4488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Maki R. A., Clayton L. K., Tonegawa S. Complete primary structures of the E beta chain and gene of the mouse major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5520–5524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Vigneron M., Matthes H., Wildeman A., Zenke M., Chambon P. Requirement of stereospecific alignments for initiation from the simian virus 40 early promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):121–126. doi: 10.1038/319121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]