Abstract
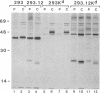
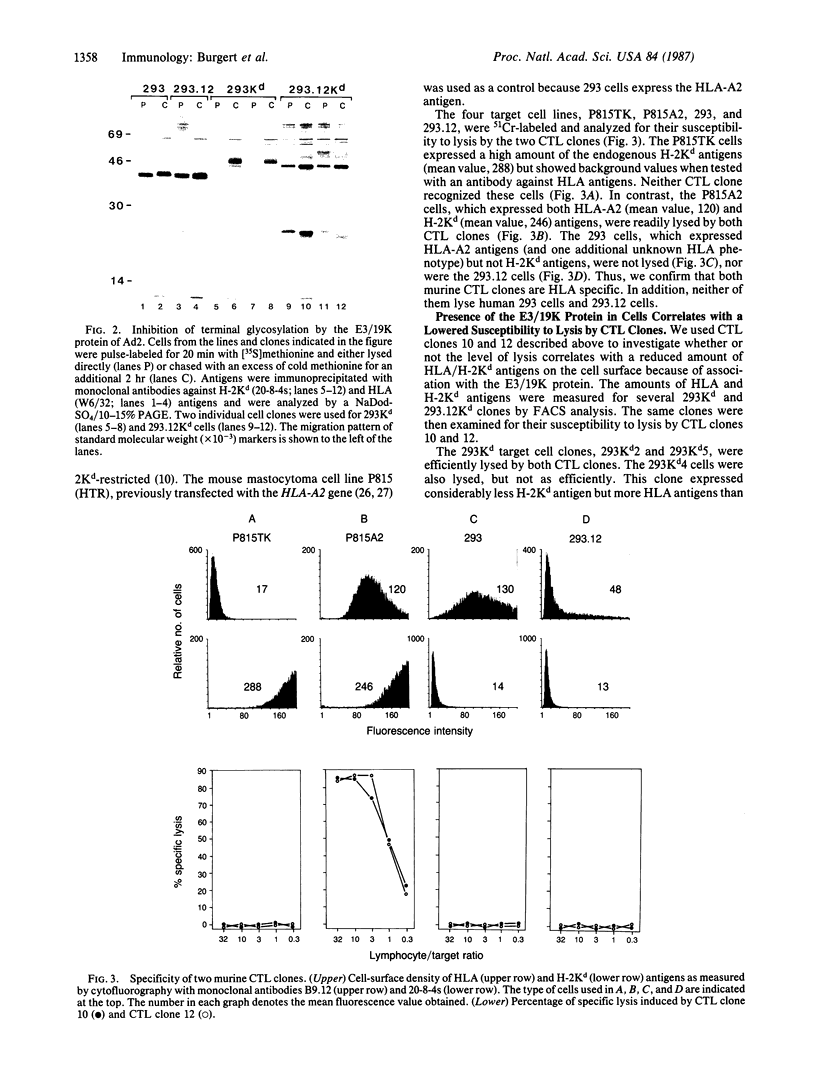
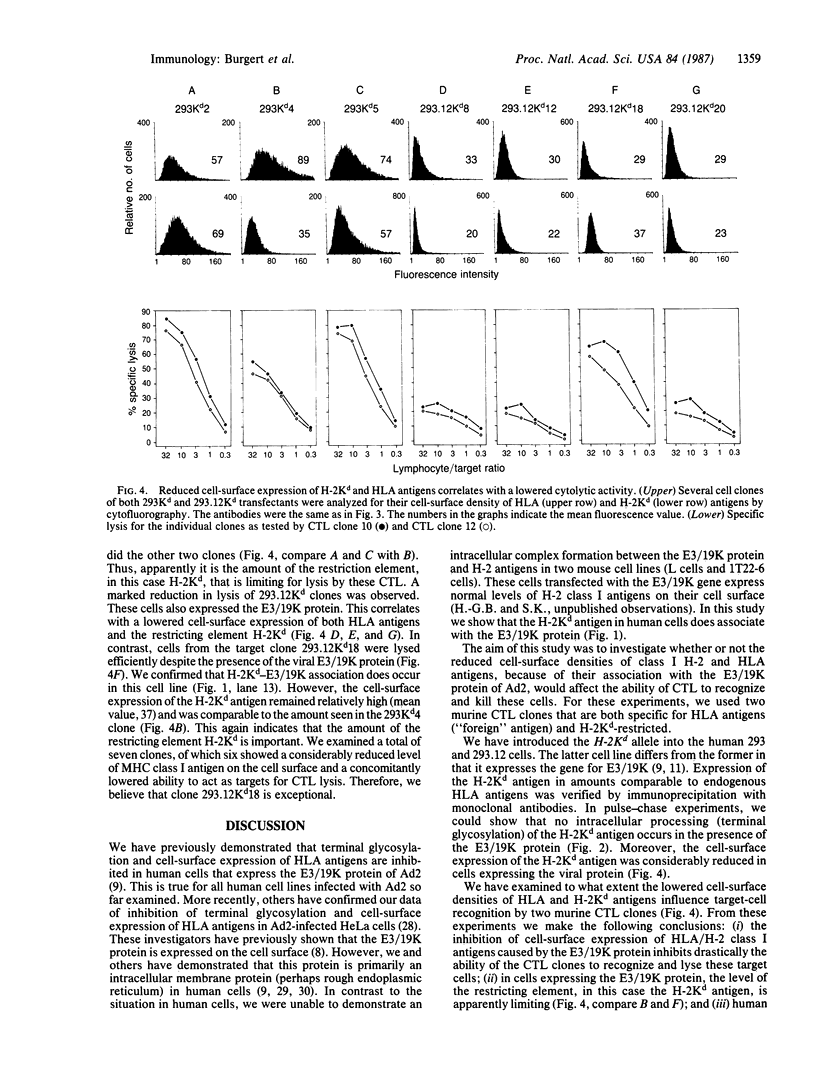
The E3 19,000-dalton protein termed "E3/19K" of adenovirus type 2 binds to human class I histocompatibility antigens (HLA antigens). Human 293.12 cultured cells that express a cloned gene for the E3/19K protein show reduced levels of HLA antigens on the cell surface compared to parental 293 cells. We have transfected these cell lines with plasmid DNA containing the murine histocompatibility H-2Kd allele to demonstrate that this antigen binds also to the E3/19K protein. The resulting association prevents the H-2Kd antigen from being terminally glycosylated and inhibits its cell-surface expression. Two murine cytolytic T-lymphocyte clones specific for HLA antigens and restricted by the H-2Kd antigen lyse the human 293Kd cells. In the presence of the E3/19K protein, a dramatically reduced cell surface density of both HLA and H-2Kd antigens was shown. This decreased amount of cell-surface HLA/H-2Kd antigens correlated with a reduction in susceptibility to lysis of the target cells. In particular, the cell-surface level of the H-2Kd antigen, which is the restricting element, was crucial for efficient lysis. Thus, the E3/19K protein of adenovirus type 2 indirectly reduces the cellular immune recognition in the in vitro system. This might be the mechanism involved in latent and persistent infections caused by adenoviruses in vivo.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson M., Päbo S., Nilsson T., Peterson P. A. Impaired intracellular transport of class I MHC antigens as a possible means for adenoviruses to evade immune surveillance. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold B., Burgert H. G., Hamann U., Hämmerling G., Kees U., Kvist S. Cytolytic T cells recognize the two amino-terminal domains of H-2 K antigens in tandem in influenza A infected cells. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90528-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard H. U., Krämmer G., Röwekamp W. G. Construction of a fusion gene that confers resistance against hygromycin B to mammalian cells in culture. Exp Cell Res. 1985 May;158(1):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90446-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgert H. G., Kvist S. An adenovirus type 2 glycoprotein blocks cell surface expression of human histocompatibility class I antigens. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):987–997. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS A. S. Latent adenovirus infections of the human respiratory tract. Am J Hyg. 1958 May;67(3):256–266. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomard E., Begue B., Sodoyer S., Maryanski J. L., Jordan B. R., Levy J. P. Murine cells expressing an HLA molecule are specifically lysed by HLA-restricted antiviral human T cells. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):153–154. doi: 10.1038/319153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González A., Jiménez A., Vázquez D., Davies J. E., Schindler D. Studies on the mode of action of hygromycin B, an inhibitor of translocation in eukaryotes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 21;521(2):459–469. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90287-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaster K. R., Burgett S. G., Rao R. N., Ingolia T. D. Analysis of a bacterial hygromycin B resistance gene by transcriptional and translational fusions and by DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 11;11(19):6895–6911. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.19.6895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. The major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. Science. 1979 Feb 9;203(4380):516–521. doi: 10.1126/science.104386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B. H., Orr H. T. Cloning and complete sequence of an HLA-A2 gene: analysis of two HLA-A alleles at the nucleotide level. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2727–2733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Ostberg L., Persson H., Philipson L., Peterson P. A. Molecular association between transplantation antigens and cell surface antigen in adenovirus-transformed cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5674–5678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Roberts L., Dobberstein B. Mouse histocompatibility genes: structure and organisation of a Kd gene. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):245–254. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01413.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Wiman K., Claesson L., Peterson P. A., Dobberstein B. Membrane insertion and oligomeric assembly of HLA-DR histocompatibility antigens. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kämpe O., Bellgrau D., Hammerling U., Lind P., Päbo S., Severinsson L., Peterson P. A. Complex formation of class I transplantation antigens and a viral glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10594–10598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff T., Elkaim R., Goding C. R., Jalinot P., Sassone-Corsi P., Perricaudet M., Kédinger C., Chambon P. Individual products of the adenovirus 12S and 13S EIa mRNAs stimulate viral EIIa and EIII expression at the transcriptional level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4381–4385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemonnier F. A., Rebai N., Le Bouteiller P. P., Malissen B., Caillol D. H., Kourilsky F. M. Epitopic analysis of detergent-solubilized HLA molecules by solid-phase radioimmunoassay. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Oct 15;54(1):9–22. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J. The adenovirus early proteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;110:143–167. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46494-2_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryanski J. L., Accolla R. S., Jordan B. H2-restricted recognition of cloned HLA class I gene products expressed in mouse cells. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4340–4347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen M. J., Kissonerghis A. M., Lodish H. F. Biosynthesis of HLA-A and HLA-B antigens in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9678–9684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Mayer N. M., Sachs D. H. Monoclonal antibodies to mouse major histocompatibility complex antigens. Transplantation. 1982 Sep;34(3):113–120. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198209000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Sachs D. H. Monoclonal antibodies to mouse MHC antigens. III. Hybridoma antibodies reacting to antigens of the H-2b haplotype reveal genetic control of isotype expression. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):317–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Jansson M., Philipson L. Synthesis and genomic site for an adenovirus type 2 early glycoprotein. J Mol Biol. 1980 Feb 5;136(4):375–394. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90396-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Jörnvall H., Zabielski J. Multiple mRNA species for the precursor to an adenovirus-encoded glycoprotein: identification and structure of the signal sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6349–6353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploegh H. L., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L. Major histocompatibility antigens: the human (HLA-A, -B, -C) and murine (H-2K, H-2D) class I molecules. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):287–299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Päbo S., Weber F., Kämpe O., Schaffner W., Peterson P. A. Association between transplantation antigens and a viral membrane protein synthesized from a mammalian expression vector. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):445–453. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90426-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Signäs C., Katze M. G., Persson H., Philipson L. An adenovirus glycoprotein binds heavy chains of class I transplantation antigens from man and mouse. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):175–178. doi: 10.1038/299175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Pel A., De Plaen E., Boon T. Selection of highly transfectable variant from mouse mastocytoma P815. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1985 Sep;11(5):467–475. doi: 10.1007/BF01534840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]