Abstract
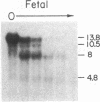
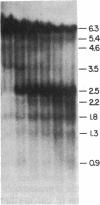
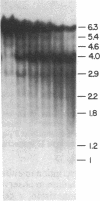
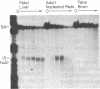
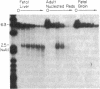
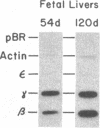
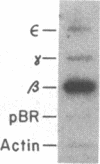
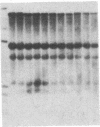
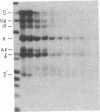
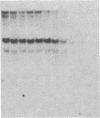
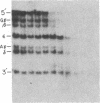
The DNase I-hypersensitive sites in the human embryonic beta-globin gene region have been mapped in erythroid-enriched fractions of disaggregated fetal livers, in adult nucleated red blood cells, and in fetal brain tissue. Our analysis of a region extending 11 kilobases (kb) 5' of the epsilon-globin gene reveals many minor nuclease-hypersensitive sites and one major site located 6.1 kb upstream of the epsilon-globin gene. All of these hypersensitive sites are erythroid-specific, and the major site is stable throughout erythroid development. As assayed by nuclear runoff transcription, little or no epsilon-globin gene expression is detectable in fetal or adult erythroid cells. Thus, the presence of the major hypersensitive site 5' of the epsilon-globin gene in both fetal and adult erythroid cells demonstrates that this site is not specifically correlated with transcription of the gene or with a particular stage of development. Rather, this site may reflect an early event in erythroid differentiation. In addition, DNase I has been used to probe the overall sensitivity of epsilon-globin chromatin in fetal erythroid cells. Our findings indicate that the epsilon-globin gene as well as the other genes in the beta-globin cluster reside within the chromatin domain that is more DNase I-sensitive than "bulk" chromatin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alan M., Grindlay G. J., Stefani L., Paul J. Epsilon globin gene transcripts originating upstream of the mRNA cap site in K562 cells and normal human embryos. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5133–5147. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan M., Lanyon W. G., Paul J. Multiple origins of transcription in the 4.5 Kb upstream of the epsilon-globin gene. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):187–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90221-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan M., Zhu J. D., Montague P., Paul J. Differential response of multiple epsilon-globin cap sites to cis- and trans-acting controls. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):399–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90495-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baralle F. E., Shoulders C. C., Goodbourn S., Jeffreys A., Proudfoot N. J. The 5' flanking region of human epsilon-globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 10;8(19):4393–4404. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.19.4393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baralle F. E., Shoulders C. C., Proudfoot N. J. The primary structure of the human epsilon-globin gene. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):621–626. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90425-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Gallo R. C., Gallagher R. E. Continuous growth and differentiation of human myeloid leukaemic cells in suspension culture. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):347–349. doi: 10.1038/270347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Segni G., Carrara G., Tocchini-Valentini G. R., Shoulders C. C., Baralle F. E. Selective in vitro transcription of one of the two Alu family repeats present in the 5' flanking region of the human epsilon-globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6709–6722. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Eisenman R., Gelinas R., Weintraub H. Developmental aspects of chromatin structure and gene expression. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1983;134:159–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Kohwi-Shigematsu T., Gelinas R., Stamatoyannopoulos G., Papayannopoulou T. Human fetal to adult hemoglobin switching: changes in chromatin structure of the beta-globin gene locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7551–7555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Weintraub H. Propagation of globin DNAase I-hypersensitive sites in absence of factors required for induction: a possible mechanism for determination. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayday A. C., Gillies S. D., Saito H., Wood C., Wiman K., Hayward W. S., Tonegawa S. Activation of a translocated human c-myc gene by an enhancer in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus. 1984 Jan 26-Feb 1Nature. 307(5949):334–340. doi: 10.1038/307334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson S., Nienhuis A. W. Developmental regulation of human globin genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:1071–1108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.005231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krowczynska A., Yenofsky R., Brawerman G. Regulation of messenger RNA stability in mouse erythroleukemia cells. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 20;181(2):231–239. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90087-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q., Powers P. A., Smithies O. Nucleotide sequence of 16-kilobase pairs of DNA 5' to the human epsilon-globin gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):14901–14910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Gunderson N., Groudine M. Enhanced transcription of c-myc in bursal lymphoma cells requires continuous protein synthesis. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1126–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.2999973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Fritsch E. F., Lauer J., Lawn R. M. The molecular genetics of human hemoglobins. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:145–178. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavilio F., Giampaolo A., Carè A., Migliaccio G., Calandrini M., Russo G., Pagliardi G. L., Mastroberardino G., Marinucci M., Peschle C. Molecular mechanisms of human hemoglobin switching: selective undermethylation and expression of globin genes in embryonic, fetal, and adult erythroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6907–6911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papayannopoulou T., Kalmantis T., Stamatoyannopoulos G. Cellular regulation of hemoglobin switching: evidence for inverse relationship between fetal hemoglobin synthesis and degree of maturity of human erythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6420–6424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peschle C., Mavilio F., Carè A., Migliaccio G., Migliaccio A. R., Salvo G., Samoggia P., Petti S., Guerriero R., Marinucci M. Haemoglobin switching in human embryos: asynchrony of zeta----alpha and epsilon----gamma-globin switches in primitive and definite erythropoietic lineage. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):235–238. doi: 10.1038/313235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peschle C., Migliaccio A. R., Migliaccio G., Petrini M., Calandrini M., Russo G., Mastroberardino G., Presta M., Gianni A. M., Comi P. Embryonic----Fetal Hb switch in humans: studies on erythroid bursts generated by embryonic progenitors from yolk sac and liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2416–2420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. H., Smithies O. Human globin psi B2 is not a globin-related sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7809–7818. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D., London I. M. Mapping of DNase I-hypersensitive sites in the upstream DNA of human embryonic epsilon-globin gene in K562 leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2718–2722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D., Solomon W., Li Q., London I. M. The "beta-like-globin" gene domain in human erythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6384–6388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weatherall D. J., Clegg J. B. Thalassemia revisited. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):7–9. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J., Allan M., Paul J. The chromatin structure of the human epsilon globin gene: nuclease hypersensitive sites correlate with multiple initiation sites of transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):9191–9204. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.9191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]