Abstract
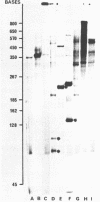
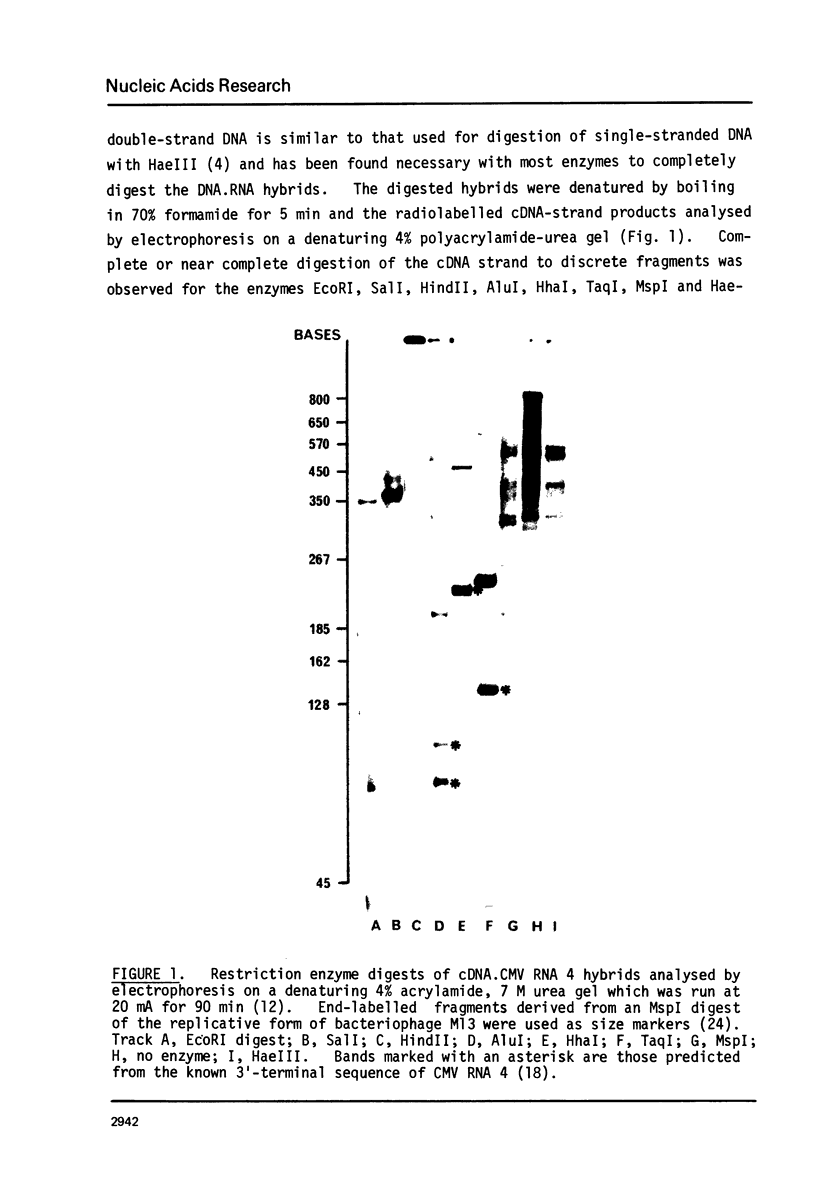
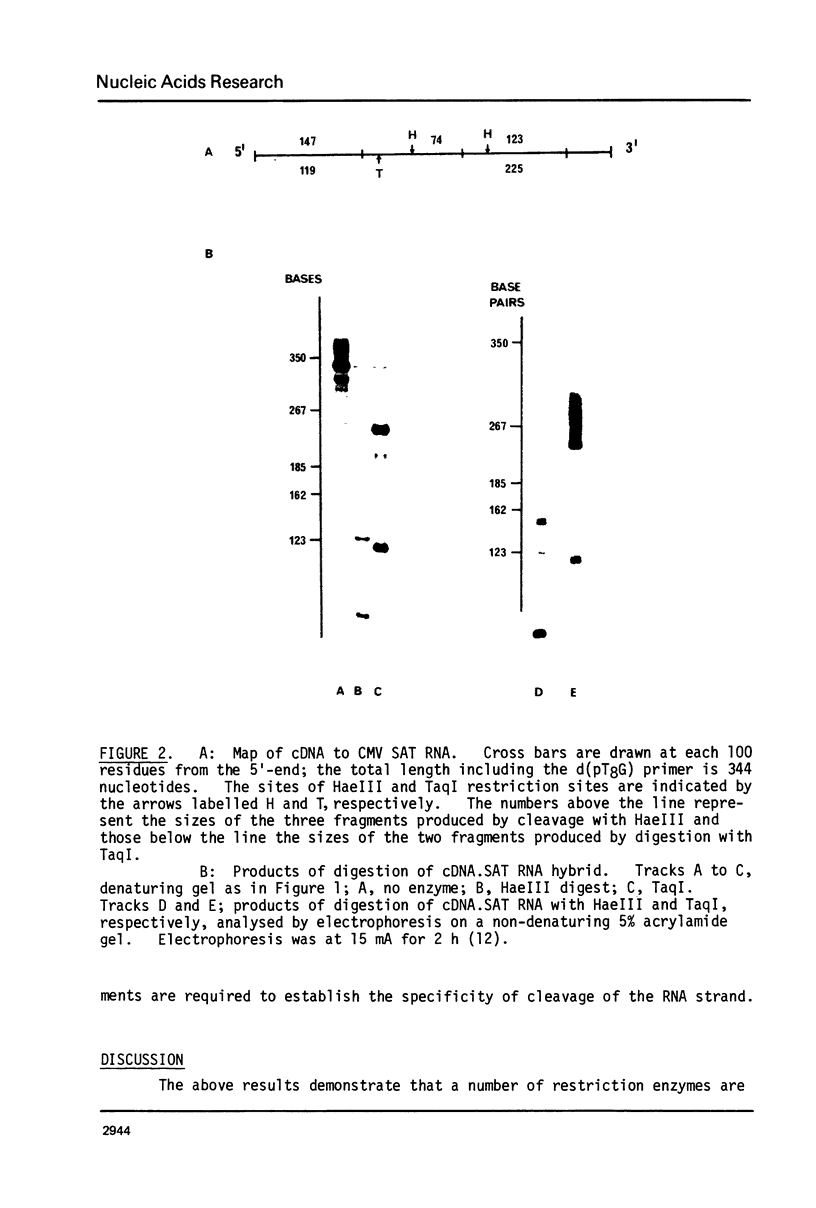
The action of a number of restriction enzymes on DNA.RNA hybrids has been examined using hybrids synthesised with RNAs of cucumber mosaic virus as templates. The enzymes EcoRI, HindII, SalI, MspI, HhaI, AluI, TaqI and HaeIII cleaved the DNA strand of the hybrids (and possible also the RNA strand) into specific fragments. For four of these enzymes, HhaI, AluI, TaqI and HaeIII, comparison of the restriction fragments produced with the known sequences of the viral RNAs confirmed that they were recognising and cleaving the DNA strand of the hybrids at their correct recognition sequences. It is likely that the ability to utilise DNA.RNA hybrids as substrates is a general property of Type II restriction enzymes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop J. O. A DNA sequence cleaved by restriction endonuclease R.EcoRI in only one strand. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 15;128(4):545–549. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90292-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakesley R. W., Dodgson J. B., Nes I. F., Wells R. D. Duplex regions in "single-stranded" phiX174 DNA are cleaved by a restriction endonuclease from Haemophilus aegyptius. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7300–7306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakesley R. W., Wells R. D. 'Single-stranded' DNA from phiX174 and M13 is cleaved by certain restriction endonucleases. Nature. 1975 Oct 2;257(5525):421–422. doi: 10.1038/257421a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godson G. N., Roberts R. J. dna, single stranded/*metab. Virology. 1976 Sep;73(2):561–567. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90421-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould A. R., Palukaitis P., Symons R. H., Mossop D. W. Characterization of a satellite RNA associated with cucumber mosaic virus. Virology. 1978 Feb;84(2):443–455. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90261-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould A. R., Symons R. H. Determination of the sequence homology between the four RNA species of cucumber mosaic virus by hybridization analysis with complementary DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Nov;4(11):3787–3802. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.11.3787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlyn P. H., Browniee G. G., Cheng C. C., Gait M. J., Milstein C. Complete sequence of constant and 3' noncoding regions of an immunoglobulin mRNA using the dideoxynucleotide method of RNA sequencing. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1067–1075. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi K., Zinder N. D. Site-specific cleavage of single-stranded DNA by a Hemophilus restriction endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2555–2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kacian D. L., Myers J. C. Synthesis of extensive, possibly complete, DNA copies of poliovirus RNA in high yields and at high specific activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2191–2195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Enhanced autoradiographic detection of 32P and 125I using intensifying screens and hypersensitized film. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):314–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80609-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J. C., Spiegelman S. Sodium pyrophosphate inhibition of RNA.DNA hybrid degradation by reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5329–5333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans D., Smith H. O. Restriction endonucleases in the analysis and restructuring of dna molecules. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:273–293. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.001421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J. Restriction endonucleases. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1976 Nov;4(2):123–164. doi: 10.3109/10409237609105456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H., Shine J., Martial J. A., Ullrich A., Baxter J. D., Goodman H. M. Nucleotide sequence of part of the gene for human chorionic somatomammotropin: purification of DNA complementary to predominant mRNA species. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90193-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons R. H. Extensive sequence homology at the 3'-termini of the four RNAs of cucumber mosaic virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 25;7(4):825–837. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.4.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons R. H. The rapid, simple and improved preparation of high specific activity alpha-[32P]dATP and alpha-[32P]ATP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Dec;4(12):4347–4355. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.12.4347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M. Purification and further properties of single-strand-specific nuclease from Aspergillus oryzae. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):192–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmern D., Kaesberg P. 3'-terminal nucleotide sequence of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA determined by reverse transcriptase and chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4257–4261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]