Abstract
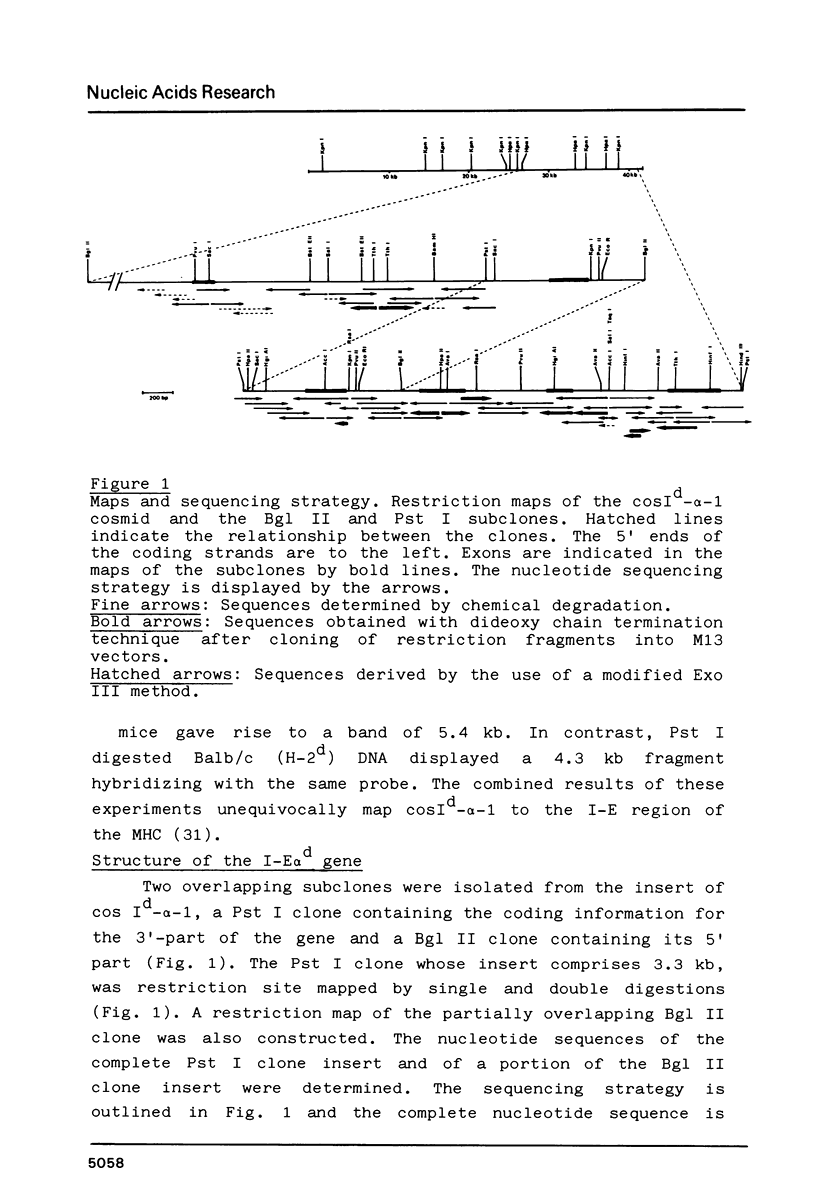
We have isolated and sequenced the complete murine I-E alpha immune response gene of the H-2db haplotype. The I-E alpha d gene consists of 5300 basepairs and is organized into five or possibly six exons that correspond to different domains of the alpha chain. The amino acid sequence deduced from the I-E alpha gene shows 75% homology to its human counterpart, the HLA-DR alpha chain. The absence of I-E antigen in H-2 mice is due to lack of E alpha chain synthesis. We show here that this defect is caused by a deletion in the 5' end of the I-E alpha b gene.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Korman A. J., Roux-Dosseto M., Bono R., Strominger J. L. cDNA clone for the heavy chain of the human B cell alloantigen DC1: strong sequence homology to the HLA-DR heavy chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6337–6341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Benoist C., O'Hare K., Gannon F., Chambon P. Ovalbumin gene: evidence for a leader sequence in mRNA and DNA sequences at the exon-intron boundaries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4853–4857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron D. J., McDevitt H. O. Analysis of HLA-D region-associated molecules with monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6567–6571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook R. G., Siegelman M. H., Capra J. D., Uhr J. W., Vitetta E. S. Structural studies on the murine Ia alloantigens. IV. NH2-terminal sequence analysis of allelic products of the I-A and I-E/C subregions. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2232–2237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen S. E., Freed J. H., Nathenson S. G. Structural and serological properties of murine Ia alloantigens. Transplant Rev. 1976;30:236–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb00222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T., Lawn R. M., O'Connell C., Spritz R. A., DeRiel J. K., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M., Slightom J. L. The structure and evolution of the human beta-globin gene family. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. A., Margulies D. H., Camerini-Otero R. D., Ozato K., Seidman J. G. Structure and expression of a mouse major histocompatibility antigen gene, H-2Ld. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1994–1998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. N., Jones E. A., Van Heyningen V., Solomon E., Bobrow M., Miggiano V., Bodmer W. F. The beta2-microglobulin gene is on chromosome 15 and not in the HL-A region. Nature. 1975 Mar 20;254(5497):267–269. doi: 10.1038/254267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F. G., Lund T., Murray E. J., Mellor A. L., Dahl H. H., Flavell R. A. The construction of cosmid libraries which can be used to transform eukaryotic cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6715–6732. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. P., Murphy D. B., McDevitt H. O. Variable synthesis and expression of E alpha and Ae (E beta) Ia polypeptide chains in mice of different H-2 haplotypes. Immunogenetics. 1981;12(3-4):321–337. doi: 10.1007/BF01561674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Juretic A., Baxevanis C. N., Nagy Z. A. The traditional and a new version of the mouse H-2 complex. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):455–460. doi: 10.1038/291455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman A. J., Auffray C., Schamboeck A., Strominger J. L. The amino acid sequence and gene organization of the heavy chain of the HLA-DR antigen: homology to immunoglobulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6013–6017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratzin H., Yang C. Y., Götz H., Pauly E., Kölbel S., Egert G., Thinnes F. P., Wernet P., Altevogt P., Hilschmann N. Primärstruktur menschlicher Histokompatibilitätsantigene der Klasse II. 1. Mitteilung: Aminosäuresequenz der N-terminalen 198 Reste der beta-Kette des HLA-Dw2,2;DR2,2-Alloantigens. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1981 Dec;362(12):1665–1669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Roberts L., Dobberstein B. Mouse histocompatibility genes: structure and organisation of a Kd gene. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):245–254. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01413.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larhammar D., Gustafsson K., Claesson L., Bill P., Wiman K., Schenning L., Sundelin J., Widmark E., Peterson P. A., Rask L. Alpha chain of HLA-DR transplantation antigens is a member of the same protein superfamily as the immunoglobulins. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):153–161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larhammar D., Schenning L., Gustafsson K., Wiman K., Claesson L., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Complete amino acid sequence of an HLA-DR antigen-like beta chain as predicted from the nucleotide sequence: similarities with immunoglobulins and HLA-A, -B, and -C antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3687–3691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larhammar D., Wiman K., Schenning L., Claesson L., Gustafsson K., Peterson P. A., Rask L. Evolutionary relationship between HLA-DR antigen beta-chains, HLA-A, B, C antigen subunits and immunoglobulin chains. Scand J Immunol. 1981 Dec;14(6):617–622. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00603.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Trowsdale J., Travers P. J., Carey J., Grosveld F., Jenkins J., Bodmer W. F. Sequence of an HLA-DR alpha-chain cDNA clone and intron-exon organization of the corresponding gene. Nature. 1982 Oct 21;299(5885):750–752. doi: 10.1038/299750a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liesegang B., Radbruch A., Rajewsky K. Isolation of myeloma variants with predefined variant surface immunoglobulin by cell sorting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3901–3905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P., Rosenthal N., Efstratidadis A., Gilbert W., Kolodner R., Tizard R. The structure and evolution of the two nonallelic rat preproinsulin genes. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):545–558. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Benoist C. O., Williams V. E., 2nd, Kanter M. R., McDevitt H. O. The murine E alpha immune response gene. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):745–754. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Benoist C., Williams V. E., 2nd, Kanter M., McDevitt H. O. Several mechanisms can account for defective E alpha gene expression in different mouse haplotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):273–277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt H. O., Benacerraf B. Genetic control of specific immune responses. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:31–74. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60477-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNicholas J., Steinmetz M., Hunkapiller T., Jones P., Hood L. DNA sequence of the gene encoding the E alpha Ia polypeptide of the BALB/c mouse. Science. 1982 Dec 17;218(4578):1229–1232. doi: 10.1126/science.6815800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. W., Sher B. T., Sun Y. H., Eakle K. A., Hood L. DNA sequence of a gene encoding a BALB/c mouse Ld transplantation antigen. Science. 1982 Feb 5;215(4533):679–682. doi: 10.1126/science.7058332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy Z. A., Baxevanis C. N., Ishii N., Klein J. Ia antigens as restriction molecules in Ir-gene controlled T-cell proliferation. Immunol Rev. 1981;60:59–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S., Teranishi Y., Noda M., Notake M., Watanabe Y., Kakidani H., Jingami H., Numa S. The protein-coding sequence of the bovine ACTH-beta-LPH precursor gene is split near the signal peptide region. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):752–755. doi: 10.1038/287752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Teranishi Y., Takahashi H., Toyosato M., Notake M., Nakanishi S., Numa S. Isolation and structural organization of the human preproenkephalin gene. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):431–434. doi: 10.1038/297431a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Seidman J. G. Structure of wild-type and mutant mouse beta 2-microglobulin genes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):661–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90182-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. J., Lundin L., Sege K., Graf L., Wigzell H., Peterson P. A. Location of the mouse beta 2-microglobulin gene B2m determined by linkage analysis. Immunogenetics. 1981;14(5):449–452. doi: 10.1007/BF00373326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder L. P., Svejgaard A., Dausset J. Genetics of HLA disease association. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:169–187. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shreffler D. C., David C. S. The H-2 major histocompatibility complex and the I immune response region: genetic variation, function, and organization. Adv Immunol. 1975;20:125–195. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60208-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. J. The use of exonuclease III for preparing single stranded DNA for use as a template in the chain terminator sequencing method. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Mar;6(3):831–848. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.3.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Automation of the computer handling of gel reading data produced by the shotgun method of DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4731–4751. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Minard K., Horvath S., McNicholas J., Srelinger J., Wake C., Long E., Mach B., Hood L. A molecular map of the immune response region from the major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. Nature. 1982 Nov 4;300(5887):35–42. doi: 10.1038/300035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Moore K. W., Frelinger J. G., Sher B. T., Shen F. W., Boyse E. A., Hood L. A pseudogene homologous to mouse transplantation antigens: transplantation antigens are encoded by eight exons that correlate with protein domains. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):683–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhr J. W., Capra J. D., Vitetta E. S., Cook R. G. Organization of the immune response genes. Science. 1979 Oct 19;206(4416):292–297. doi: 10.1126/science.113876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Golden L., Zakut R., Mellor A., Fahrner K., Kvist S., Flavell R. A. The DNA sequence of the H-2kb gene: evidence for gene conversion as a mechanism for the generation of polymorphism in histocompatibilty antigens. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):453–462. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C., Kratzin H., Götz H., Thinnes F. P., Kruse T., Egert G., Pauly E., Kölbel S., Wernet P., Hilschmann N. Primärstruktur menschlicher Histokompatibilitätsantigene der Klasse II. 2. Mitteilung: Aminosäuresequenz der N-terminalen 179 Reste der alpha-Kette des HLA-Dw2/DR2-Alloantigens. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1982 Jun;363(6):671–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]