Abstract
In human cells treated with interferons, there is an increase in the amount of HLA-A,B,C and beta 2-microglobulin exposed on the cell surface. We have used a cloned HLA-A,B,C cDNA probe to demonstrate by molecular hybridization that this effect of interferon is preceded by a large increase in the amount of HLA mRNA in the cell. This effect was found in five different human cell lines, with purified leukocyte and fibroblast interferons. The increase in HLA mRNA is comparable in its kinetics and dose-response to the induction of (2'-5') oligo(A) synthetase mRNA by interferons. Therefore, interferons seem to activate at least two cellular genes which have different biochemical functions.
Full text
PDF
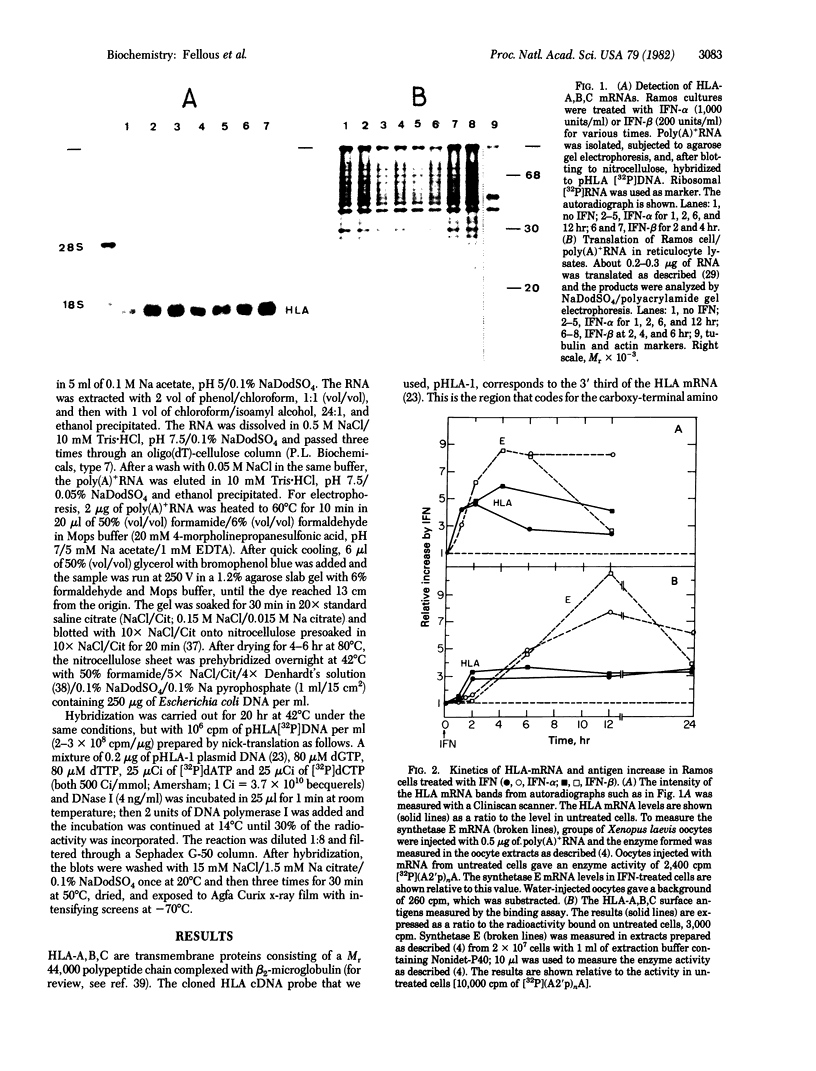

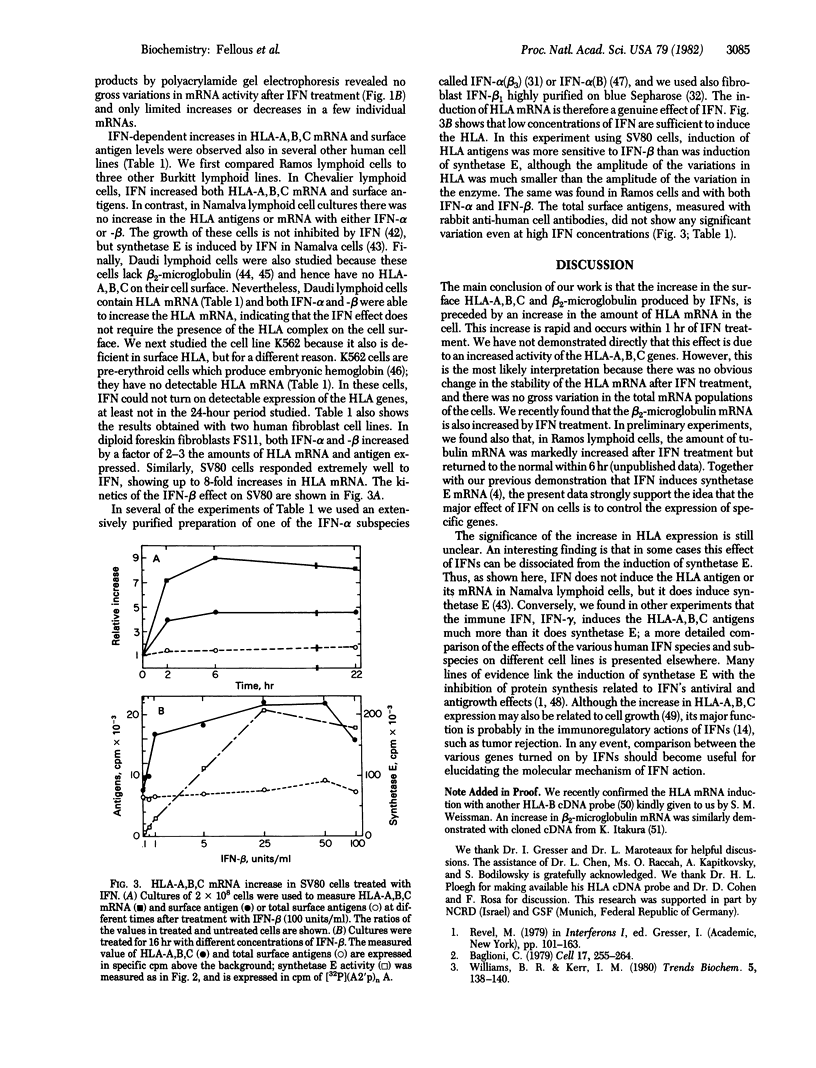

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A., Strander H., Cantell K. Sensitivity of the Epstein-Barr virus transformed human lymphoid cell lines to interferon. J Gen Virol. 1975 Aug;28(2):207–217. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-28-2-207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baglioni C. Interferon-induced enzymatic activities and their role in the antriviral state. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90151-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baglioni C., Maroney P. A., West D. K. 2'5'Oligo(A) polymerase activity and inhibition of viral RNA synthesis in interferon-treated HeLa cells. Biochemistry. 1979 May 1;18(9):1765–1770. doi: 10.1021/bi00576a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball L. A. Induction of 2'5'-oligoadenylate synthetase activity and a new protein by chick interferon. Virology. 1979 Apr 30;94(2):282–296. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90462-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger R., Bernheim A., Fellous M., Brouet J. C. Cytogenetic study of a European Burkitt's lymphoma cell line. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 May;62(5):1187–1192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrabose K., Cuatrecasas P., Pottathil R. Changes in fatty acyl chains of phospholipids induced by interferon in mouse sarcoma S-180 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Feb 12;98(3):661–668. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Broeze R. J., Lengyel P. Accumulation of an mRNA and protein in interferon-treated Ehrlich ascites tumour cells. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):523–525. doi: 10.1038/279523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellous M., Kamoun M., Gresser I., Bono R. Enhanced expression of HLA antigens and beta 2-microglobulin on interferon-treated human lymphoid cells. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jun;9(6):446–449. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Leung D. W., Dull T. J., Gross M., Lawn R. M., McCandliss R., Seeburg P. H., Ullrich A., Yelverton E., Gray P. W. The structure of eight distinct cloned human leukocyte interferon cDNAs. Nature. 1981 Mar 5;290(5801):20–26. doi: 10.1038/290020a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon I., Stevenson D. Kinetics of decay in the expression of interferon-dependent mRNAs responsible for resistance to virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):452–456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. L., Rubin B. Y., Holmes S. L. Interferon action: induction of specific proteins in mouse and human cells by homologous interferons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4817–4821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heron I., Hokland M., Berg K. Enhanced expression of beta2-microglobulin and HLA antigens on human lymphoid cells by interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6215–6219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan B. R., Bregegere F., Kourilsky P. Human HLA gene segment isolated by hybridization with mouse H-2 cDNA probes. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):521–523. doi: 10.1038/290521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimchi A., Shulman L., Schmidt A., Chernajovsky Y., Fradin A., Revel M. Kinetics of the induction of three translation-regulatory enzymes by interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3208–3212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimchi A., Shure H., Revel M. Anti-mitogenic function of interferon-induced (2'-5')oligo(adenylate) and growth-related variations in enzymes that synthesize and degrade this oligonucleotide. Eur J Biochem. 1981;114(1):5–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein E., Klein G., Nadkarni J. S., Nadkarni J. J., Wigzell H., Clifford P. Surface IgM-kappa specificity on a Burkitt lymphoma cell in vivo and in derived culture lines. Cancer Res. 1968 Jul;28(7):1300–1310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Dombos L., Gothoskar B. Sensitivity of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) producer and non-producer human lymphoblastoid cell lines to superinfection with EB-virus. Int J Cancer. 1972 Jul 15;10(1):44–57. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910100108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Zeuthen J., Terasaki P., Billing R., Honig R., Jondal M., Westman A., Clements G. Inducibility of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) cycle and surface marker properties of EBV-negative lymphoma lines and their in vitro EBV-converted sublines. Int J Cancer. 1976 Nov 15;18(5):639–652. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910180513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr, Fahey D. Human fibroblast interferon. An improved purification. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3609–3611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr, Korant B. D. A cell surface alteration in mouse L cells induced by interferon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):707–713. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90360-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr, Korant B. D. Fibroblast interferon induces synthesis of four proteins in human fibroblast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1824–1827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeMeur M., Glanville N., Mandel J. L., Gerlinger P., Palmiter R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene family: hormonal control of X and Y gene transcription and mRNA accumulation. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):561–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90152-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl P., Leary P., Gresser I. Enhancement by interferon of the expression of surface antigens on murine leukemia L 1210 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2785–2788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl P., Leary P., Gresser I. Enhancement by interferon of the specific cytotoxicity of sensitized lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):721–725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonai P., Steinman L. Physiological regulation of antigen binding to T cells: role of a soluble macrophage factor and of interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5662–5666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Cytotoxicity of a factor isolated from human spleen. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Feb;50(2):535–538. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.2.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlin G., Revel M., Wallach D. The interferon-induced enzyme oligo-isoadenylate synthetase: rapid determination of its in vitro products. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jan 1;110(1):190–196. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90134-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson K., Evrin P. E., Welsh K. I. Production of beta 2-microglobulin by normal and malignant human cell lines and peripheral lymphocytes. Transplant Rev. 1974;21(0):53–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1974.tb01546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer L. M., Wang E., Tamm I. Interferon effects on microfilament organization, cellular fibronectin distribution, and cell motility in human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1980 Apr;85(1):9–17. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploegh H. L., Cannon L. E., Strominger J. L. Cell-free translation of the mRNAs for the heavy and light chains of HLA-A and HLA-B antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2273–2277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploegh H. L., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L. Major histocompatibility antigens: the human (HLA-A, -B, -C) and murine (H-2K, H-2D) class I molecules. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):287–299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploegh H. L., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L. Molecular cloning of a human histocompatibility antigen cDNA fragment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6081–6085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel M., Kimchi A., Shulman L., Fradin A., Shuster R., Yakobson E., Chernajovsky Y., Schmidt A., Shure A., Bendori R. Role of interferon-induced enzymes in the antiviral and antimitogenic effects of interferon. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;350:459–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb20649.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin B. Y., Gupta S. L. Interferon-induced proteins in human fibroblasts and development of the antiviral state. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):446–454. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.446-454.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein M., Levy W. P., Moschera J. A., Lai C. Y., Hershberg R. D., Bartlett R. T., Pestka S. Human leukocyte interferon: isolation and characterization of several molecular forms. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Aug;210(1):307–318. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford T., Clegg J. B., Higgs D. R., Jones R. W., Thompson J., Weatherall D. J. Embryonic erythroid differentiation in the human leukemic cell line K562. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):348–352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar S., Glassy M. C., Ferrone S., Jones O. W. Cell cycle and the differential expression of HLA-A,B and HLA-DR antigens on human B lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7297–7301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman L., Revel M. Interferon-dependent induction of mRNA activity for (2'-5')oligo-isoadenylate synthetase. Nature. 1980 Nov 6;288(5786):98–100. doi: 10.1038/288098a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sood A. K., Pereira D., Weissman S. M. Isolation and partial nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone for human histocompatibility antigen HLA-B by use of an oligodeoxynucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):616–620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suggs S. V., Wallace R. B., Hirose T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. Use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes: isolation of cloned cDNA sequences for human beta 2-microglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6613–6617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Green H., Swift M. R. Susceptibility of human diploid fibroblast strains to transformation by SV40 virus. Science. 1966 Sep 9;153(3741):1252–1254. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3741.1252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Zeevi M., Landau T., Revel M. Identification of the translation products of human fibroblast interferon mRNA in reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;98(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13153.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler A., Laudien D., Heinrichs H., Müller C., Uchańska-Ziegler B., Wernet P. K562 cells express human major histocompatibility antigens. Immunogenetics. 1981;13(4):359–365. doi: 10.1007/BF00364503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



