Abstract
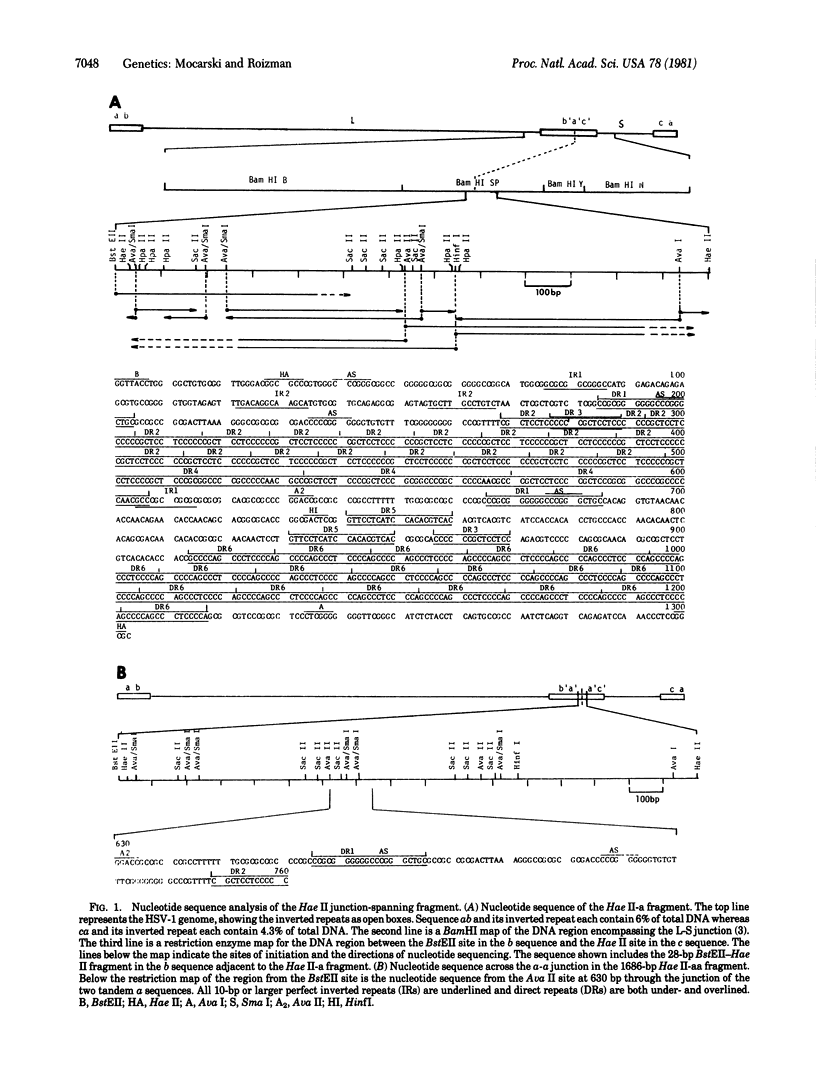
The genome of herpes simplex virus-1 consists of two covalently linked components, L and S, that invert relative to each other. The L and S components consist of unique DNA sequences bracketed by inverted repeats. The inverted repeats of the L component are designated ab and b′ a′ and those of the S component are designated a′ c′ and ca. The number of a sequences at the termini and at the L-S component junction varies from one to several copies. Insertion into the middle of the L component of a DNA fragment consisting of 156 base pairs (bp) of the b sequence, an entire a sequence of 501 bp, and 618 bp of the c sequence created a new site through which additional inversions in the genome occurred. Comparison of the nucleotide sequences of DNA fragments containing one and two a sequences defined the domain of the a sequence. The single a sequence consists of two 20-bp direct repeats (designated as DR1) bracketing a region that contains 19 tandem direct repeats of a 12-bp sequence (DR2) adjacent to three direct repeats of a 37-bp sequence (DR4), in addition to short stretches of unique sequences. The fragment with two tandem a sequences contained three copies of DR1—i.e., the intervening DR1 was shared by the two a sequences. Furthermore, one a sequence contained 22 copies of DR2 and two copies of DR4 whereas the second a sequence contained 19 copies of DR2 and two copies of DR4. These observations suggest that (i) amplification of the number of terminal and internal a sequences is the consequence of intramolecular or intermolecular recombination through DR1, (ii) the number of copies of DR2 and DR4 within the a sequence is not fixed and may vary as a consequence of unequal crossing over or slippage, and (iii) inversion results from intramolecular recombination between terminal and inverted a sequences.
Keywords: nucleotide sequence, recombination specific sequence, inversion assay, direct and inverted repeats
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkner K. L., Folk W. R. Polynucleotide kinase exchange reaction: quantitave assay for restriction endonuclease-generated 5'-phosphoroyl termini in DNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3176–3184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delius H., Clements J. B. A partial denaturation map of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA: evidence for inversions of the unique DNA regions. J Gen Virol. 1976 Oct;33(1):125–133. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-1-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward G. S., Jacob R. J., Wadsworth S. C., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA: evidence for four populations of molecules that differ in the relative orientations of their long and short components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4243–4247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob R. J., Morse L. S., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. XII. Accumulation of head-to-tail concatemers in nuclei of infected cells and their role in the generation of the four isomeric arrangements of viral DNA. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):448–457. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.448-457.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieff E. D., Bachenheimer S. L., Roizman B. Size, composition, and structure of the deoxyribonucleic acid of herpes simplex virus subtypes 1 and 2. J Virol. 1971 Aug;8(2):125–132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.2.125-132.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locker H., Frenkel N. BamI, KpnI, and SalI restriction enzyme maps of the DNAs of herpes simplex virus strains Justin and F: occurrence of heterogeneities in defined regions of the viral DNA. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):429–441. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.429-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Post L. E., Roizman B. Molecular engineering of the herpes simplex virus genome: insertion of a second L-S junction into the genome causes additional genome inversions. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):243–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90172-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A. Transformation in Escherichia coli: cryogenic preservation of competent cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):349–351. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.349-351.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Conley A. J., Mocarski E. S., Roizman B. Cloning of reiterated and nonreiterated herpes simplex virus 1 sequences as BamHI fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4201–4205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B. The structure and isomerization of herpes simplex virus genomes. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):481–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick P., Berthelot N. Inverted repetitions in the chromosome of herpes simplex virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):667–678. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth S., Hayward G. S., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. V. Terminally repetitive sequences. J Virol. 1976 Feb;17(2):503–512. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.2.503-512.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth S., Jacob R. J., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. II. Size, composition, and arrangement of inverted terminal repetitions. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1487–1497. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1487-1497.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M. J., Summers W. C. Structure of the joint region and the termini of the DNA of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):374–387. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.374-387.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartell R. M., Reznikoff W. S. Cloning DNA restriction endonuclease fragments with protruding single-stranded ends. Gene. 1980 May;9(3-4):307–319. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90329-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]