Abstract
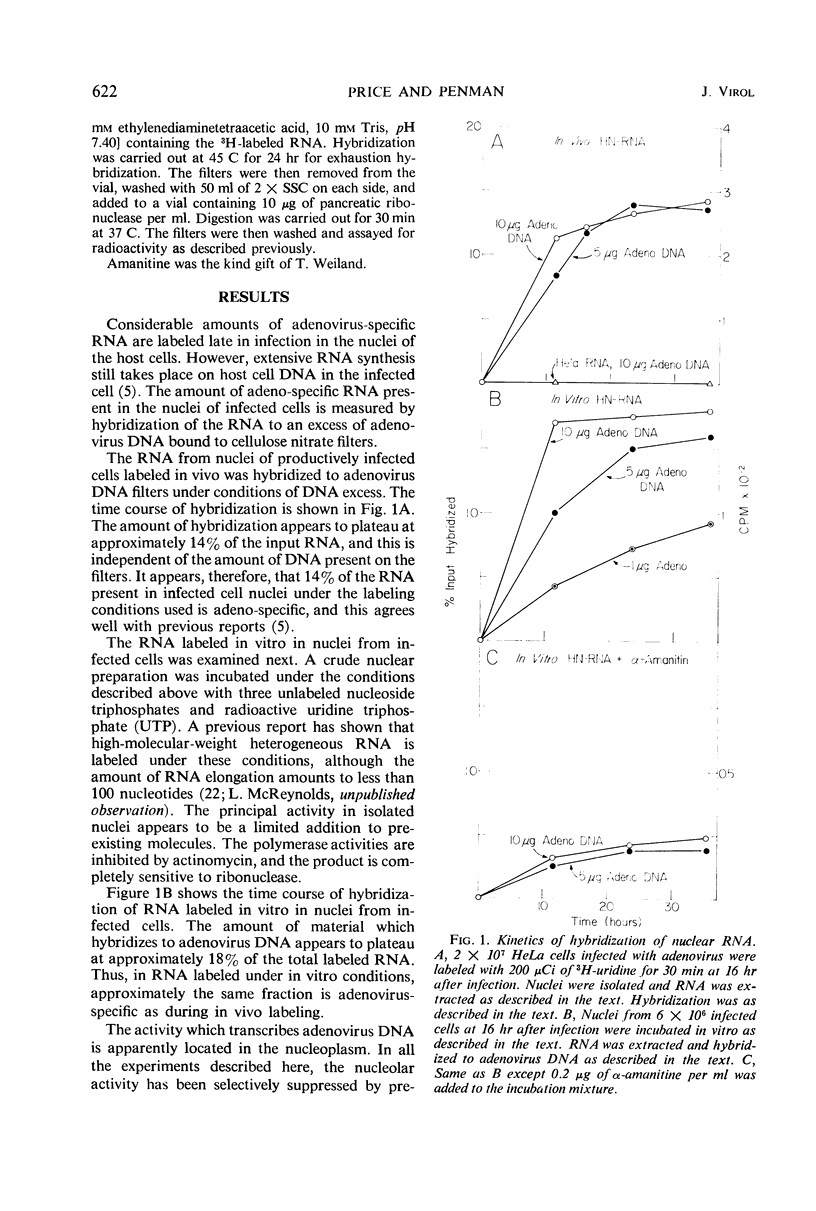
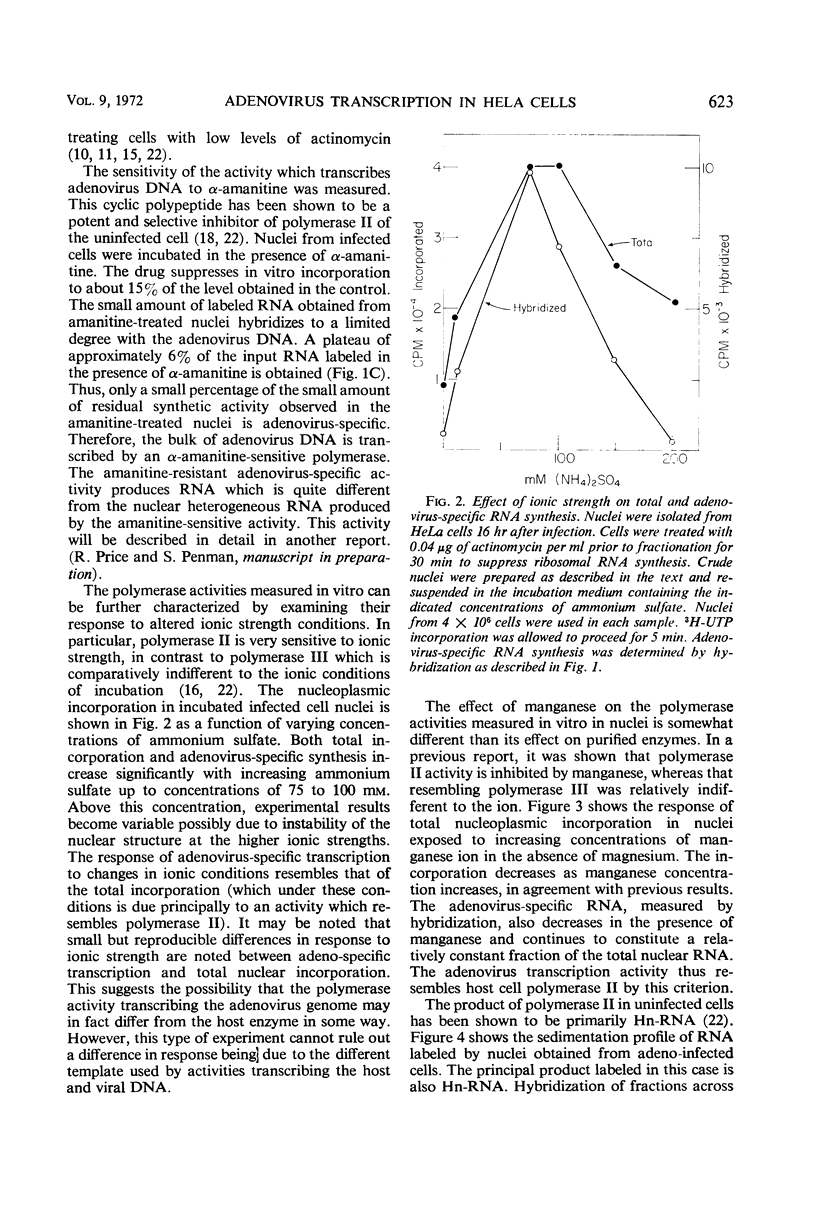
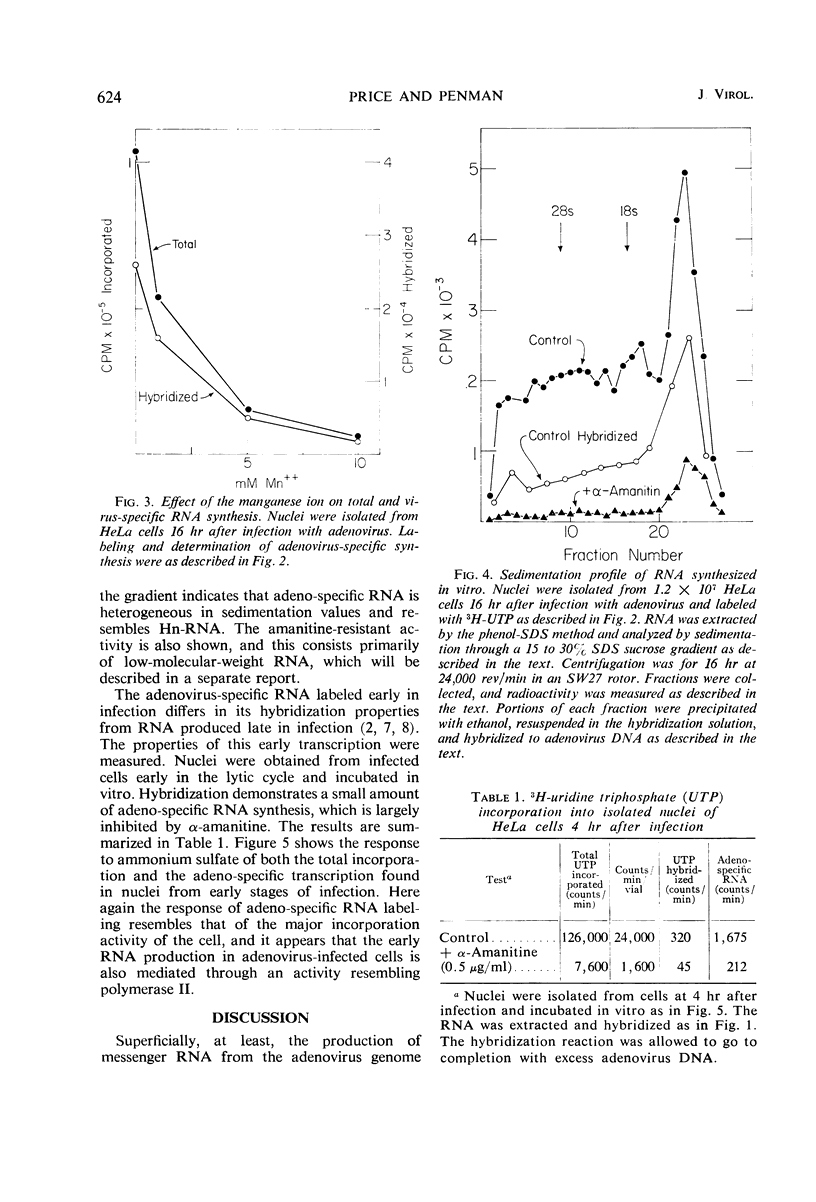
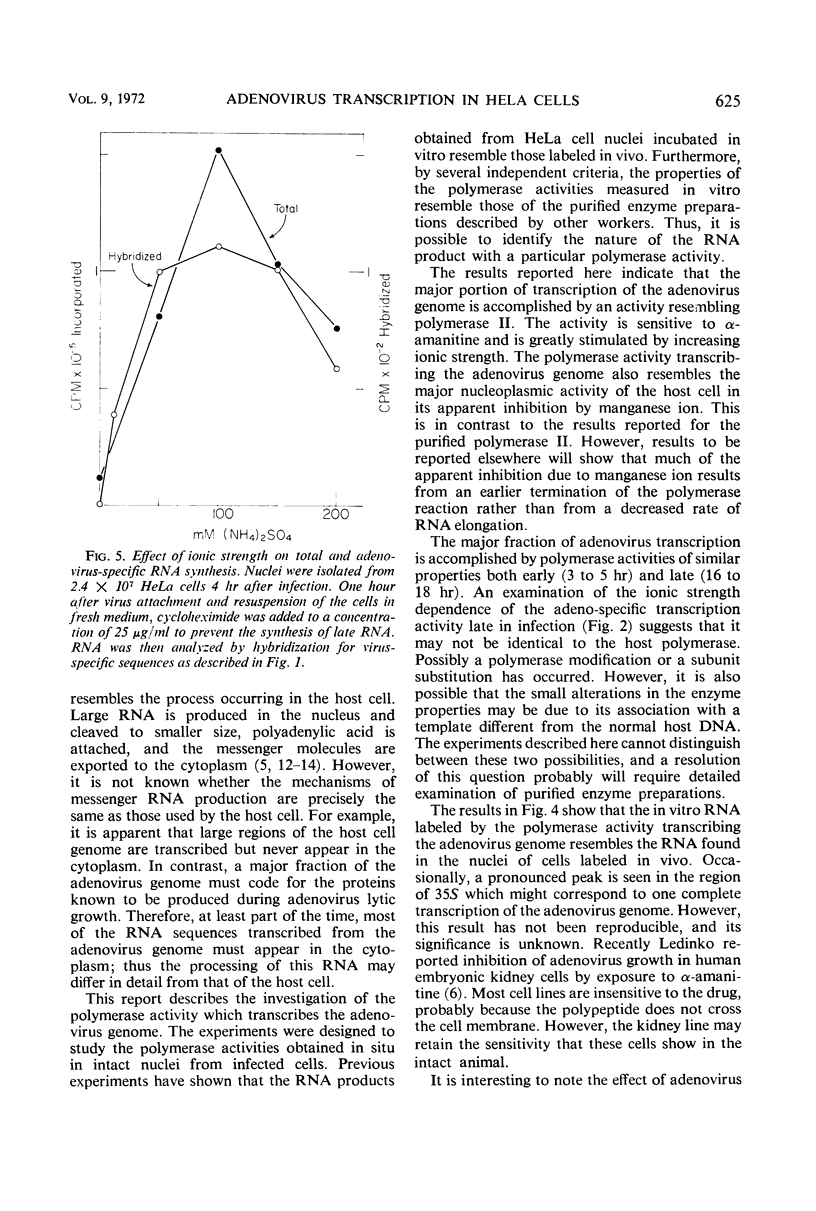
The properties of the ribonucleic acid (RNA) polymerase activity which transcribes the major portion of the adenovirus genome were studied. Nuclei were prepared from infected cells and incubated in vitro. Virus-specific RNA was determined by hybridization to adenovirus deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Adenovirus DNA is transcribed principally by an activity which resembles closely polymerase II of the host cell. This activity is inhibited by α-amanitine and stimulated by (NH4)2SO4. Its product is high-molecular-weight heterogeneous RNA. The polymerase activity measured early in infection (3 to 5 hr) resembles that found late in infection (16 to 18 hr).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Doerfler W. Nonproductive infection of baby hamster kidney cells (BHK21) with adenovirus type 12. Virology. 1969 Aug;38(4):587–606. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinaga K., Green M. Mechanism of viral carcinogenesis by DNA mammalian viruses. VII. Viral genes transcribed in adenovirus type 2 infected and transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Feb;65(2):375–382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie D., Spiegelman S. A quantitative assay for DNA-RNA hybrids with DNA immobilized on a membrane. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):829–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. Oncogenic viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:701–756. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.003413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas J. J., Ginsberg H. S. Synthesis of virus-specific ribonucleic acid in KB cells infected with type 2 adenovirus. J Virol. 1971 Aug;8(2):203–214. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.2.203-214.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons J. T., Gardner J., Green M. Biochemical studies on adenovirus multiplication, XIX. Resolution of late viral RNA species in the nucleus and cytoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):557–560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S., Rosbash M., Penman M. Messenger and heterogeneous nuclear RNA in HeLa cells: differential inhibition by cordycepin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1878–1885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S., Vesco C., Penman M. Localization and kinetics of formation of nuclear heterodisperse RNA, cytoplasmic heterodisperse RNA and polyribosome-associated messenger RNA in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1968 May 28;34(1):49–60. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P. On ribosome biogenesis. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Dec;23:527–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L., Wall R., Glickman G., Darnell J. E. Addition of polyadenylate sequences to virus-specific RNA during adenovirus replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2806–2809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raskas H. J. Release of adenovirus messenger RNA from isolated nuclei. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 29;233(39):134–136. doi: 10.1038/newbio233134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. K., Newman J. F. Use of low concentrations of actinomycin D in the study of RNA synthesis in Ehrlich ascites cells. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(1):63–73. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Multiple forms of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in eukaryotic organisms. Nature. 1969 Oct 18;224(5216):234–237. doi: 10.1038/224234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Multiple ribonucleic acid polymerases and ribonucleic acid synthesis during sea urchin development. Biochemistry. 1970 Jun 9;9(12):2543–2553. doi: 10.1021/bi00814a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific nucleolar and nucleoplasmic RNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):675–682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. C., Green M. Biochemical studies on adenovirus multiplication, xi. Evidence of a cytoplasmic site for the synthesis of viral-coded proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):243–246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velicer L. F., Ginsberg H. S. Cytoplasmic synthesis of type 5 adenovirus capsid proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1264–1271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. D., Kates J. State of adenovirus 2 deoxyribonucleic acid in the nucleus and its mode of transcription: studies with isolated viral deoxyribonucleic acid-protein complexes and isolated nuclei. J Virol. 1972 Apr;9(4):627–635. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.4.627-635.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylber E. A., Penman S. Products of RNA polymerases in HeLa cell nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2861–2865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


