Abstract
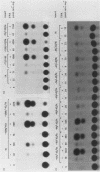
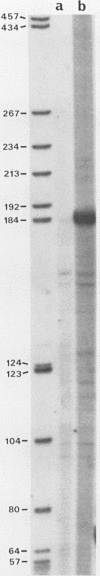
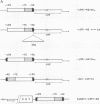
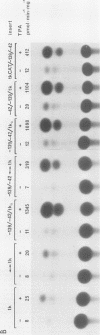
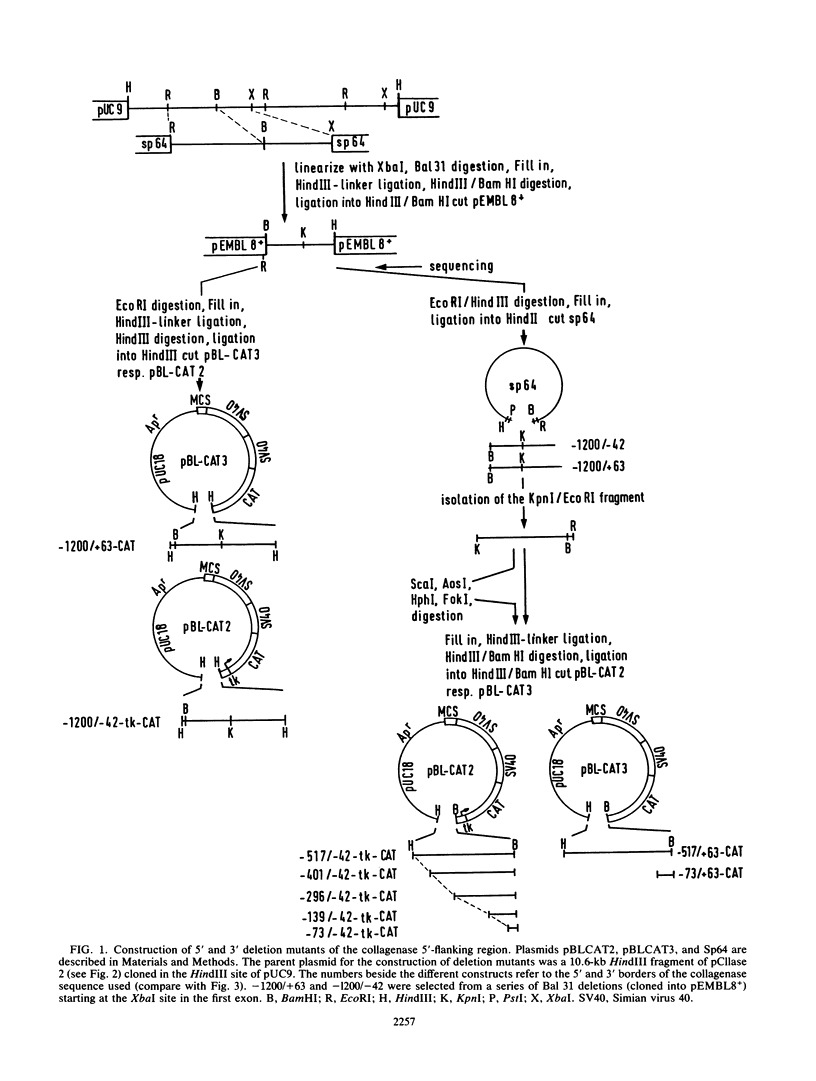
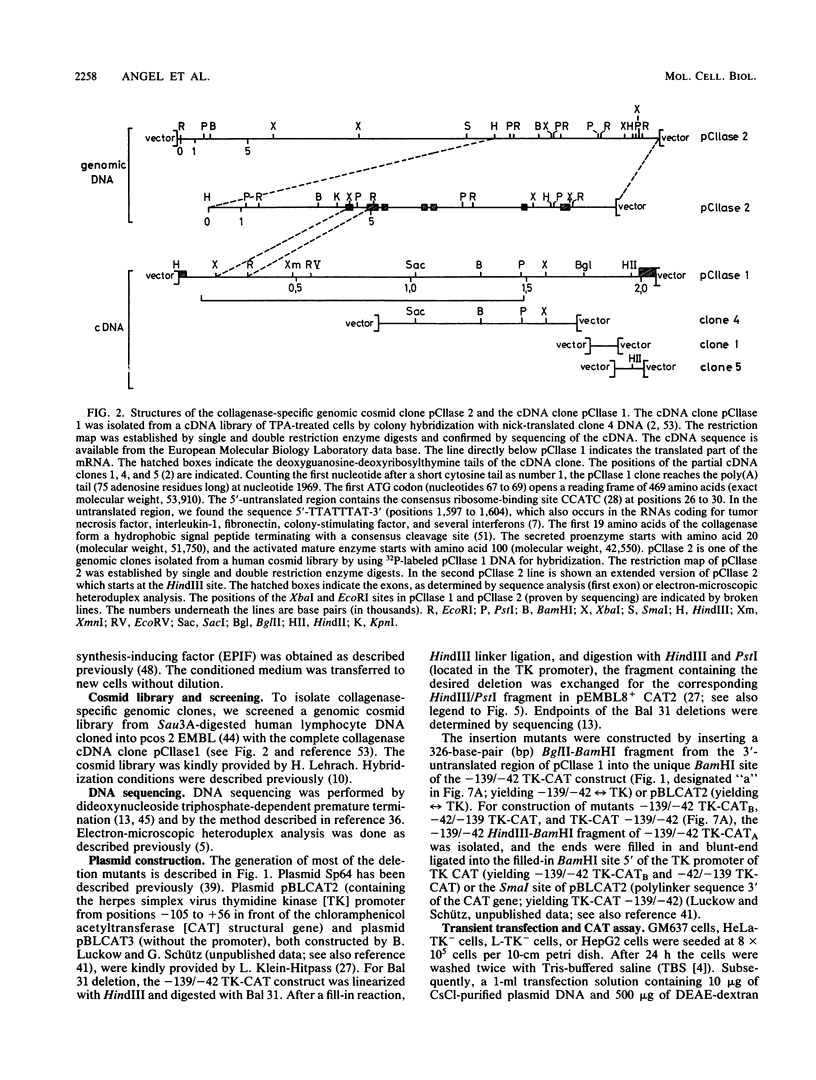
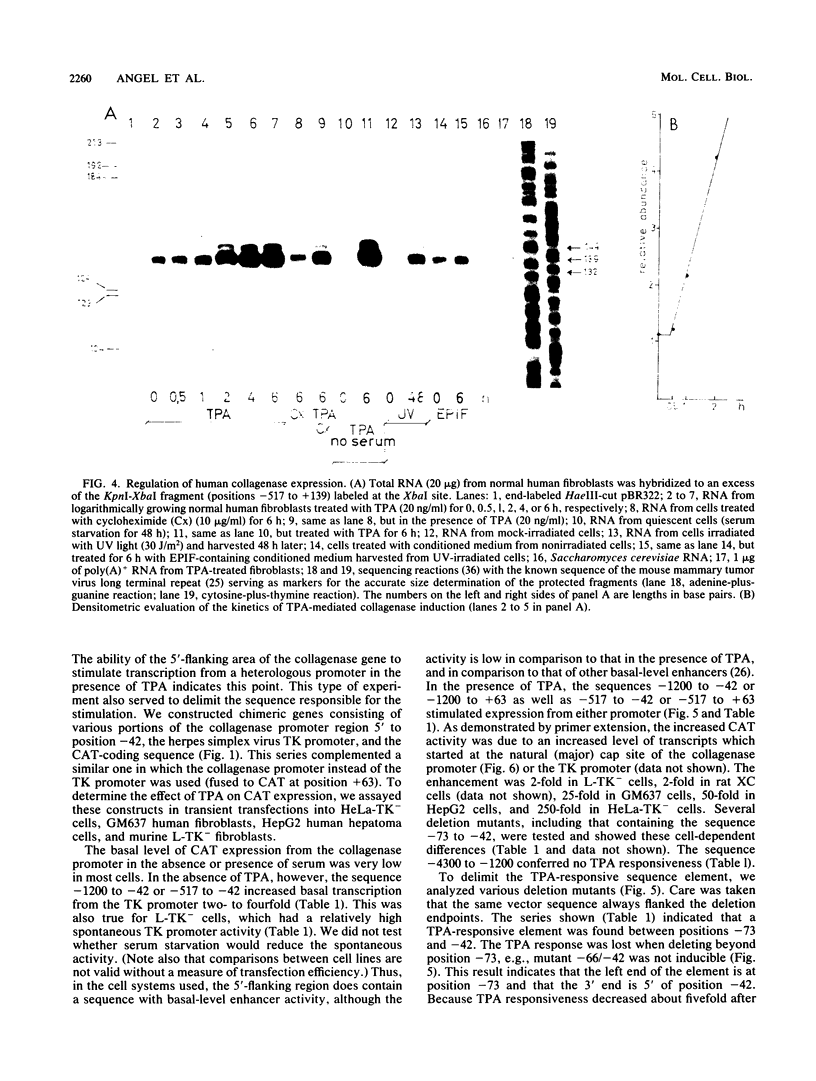
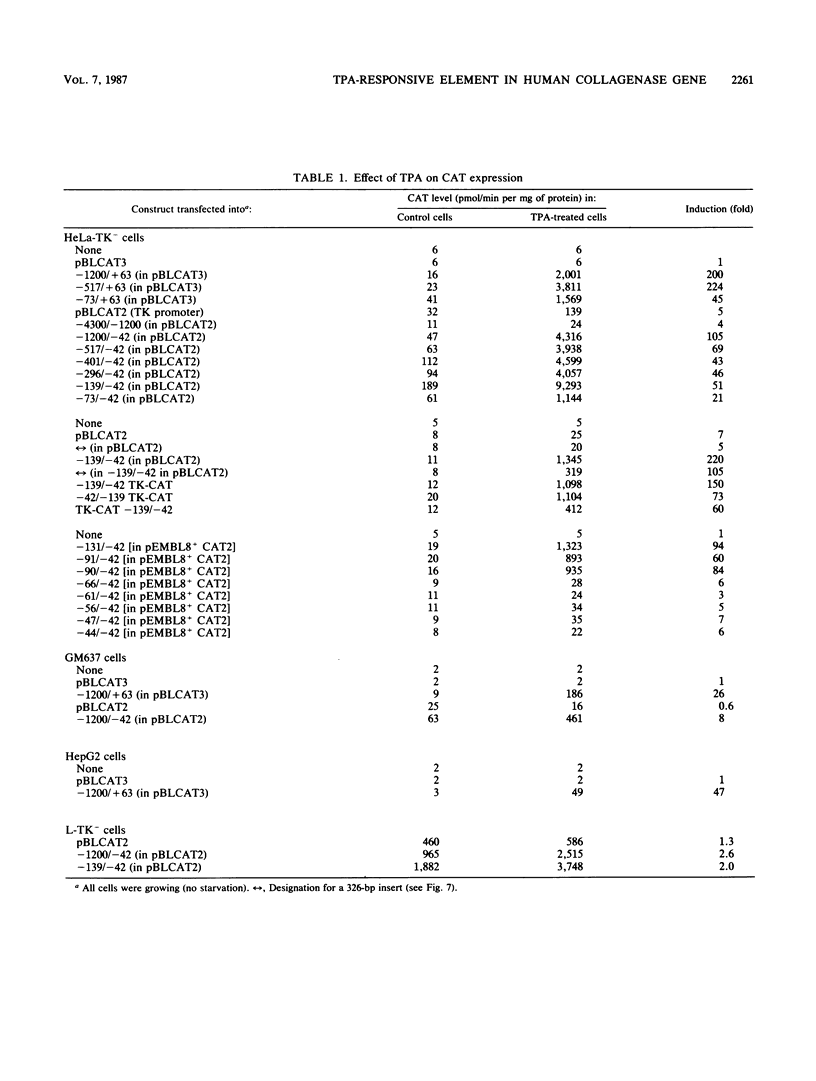
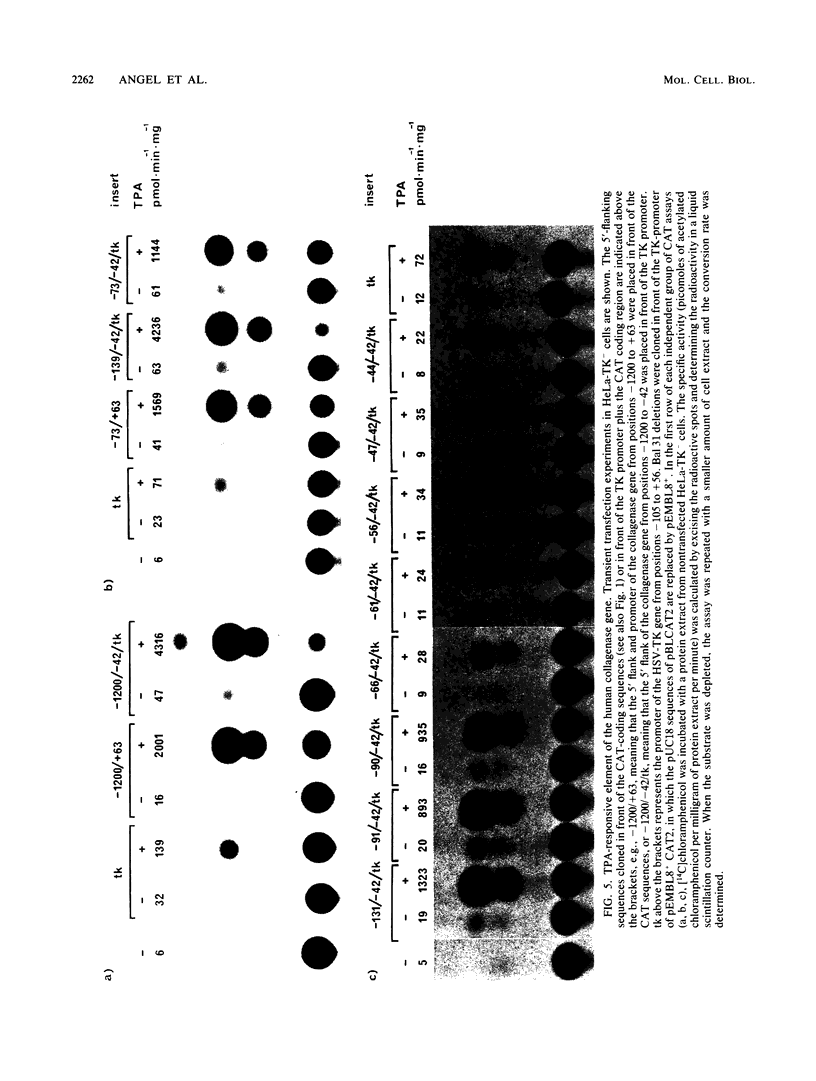
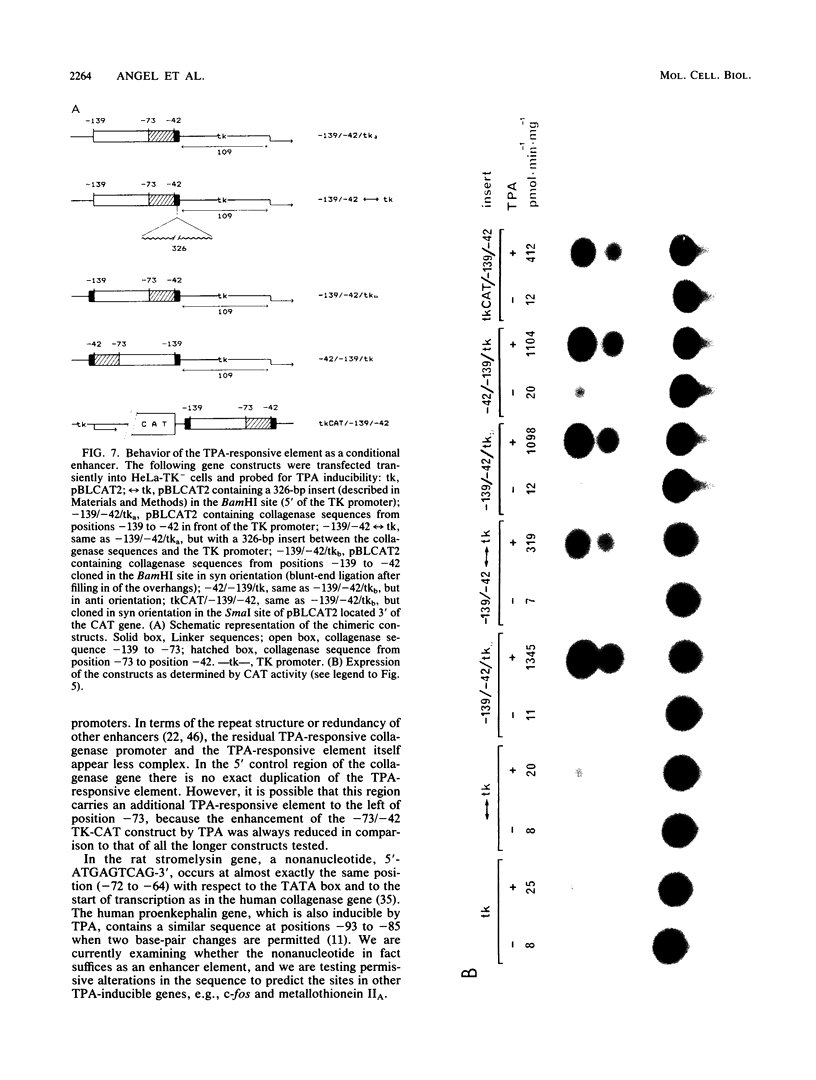
Genomic clones coding for human fibroblast collagenase were isolated. By constructing and transfecting mutants with 5' and 3' deletion mutations of the 5' control region of the gene into human or murine cells, we delimited a 32-base-pair sequence at positions -73 to -42 which is required for the induction of transcription by the tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate. The DNA element behaves as a 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate-inducible enhancer: it mediates the stimulation of transcription to the heterologous herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase promoter and acts in a position- and orientation-independent manner. Differences in enhancer efficiency in different cell lines are interpreted to indicate differences in the activity of a trans-acting factor.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggeler J., Frisch S. M., Werb Z. Changes in cell shape correlate with collagenase gene expression in rabbit synovial fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1662–1671. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Pöting A., Mallick U., Rahmsdorf H. J., Schorpp M., Herrlich P. Induction of metallothionein and other mRNA species by carcinogens and tumor promoters in primary human skin fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1760–1766. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Pöting A., Lücke-Huhle C., Herrlich P. 12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-induced gene sequences in human primary diploid fibroblasts and their expression in SV40-transformed fibroblasts. J Cell Biochem. 1985;29(4):351–360. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240290408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack C. DNA electron microscopy. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1981;10(2):113–169. doi: 10.3109/10409238109114551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinckerhoff C. E., Benoit M. C., Culp W. J. Autoregulation of collagenase production by a protein synthesized and secreted by synovial fibroblasts: cellular mechanism for control of collagen degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1916–1920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. DNA sequences bound specifically by glucocorticoid receptor in vitro render a heterologous promoter hormone responsive in vivo. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J. R., Murphy G., Werb Z. Stromelysin, a connective tissue-degrading metalloendopeptidase secreted by stimulated rabbit synovial fibroblasts in parallel with collagenase. Biosynthesis, isolation, characterization, and substrates. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12367–12376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Birnberg N. C., Seasholtz A., Herbert E., Goodman H. M. A cyclic AMP- and phorbol ester-inducible DNA element. 1986 Sep 25-Oct 1Nature. 323(6086):353–356. doi: 10.1038/323353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Zavadil-Grob C., Ucla C., Mach B. Induction of human interleukin 1 mRNA measured by collagenase- and prostaglandin E2-stimulating activity in rheumatoid synovial cells. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Oct;14(10):898–901. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolberg D. S., Hollingsworth R., Hertle M., Bissell M. J. Wounding and its role in RSV-mediated tumor formation. Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):676–678. doi: 10.1126/science.2996144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durum S. K., Schmidt J. A., Oppenheim J. J. Interleukin 1: an immunological perspective. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:263–287. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.001403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Burstein H., Maniatis T. The human beta-interferon gene enhancer is under negative control. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):601–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. H., Sheldon L. A., Fletcher C. F., Brinckerhoff C. E. Isolation of a collagenase cDNA clone and measurement of changing collagenase mRNA levels during induction in rabbit synovial fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1981–1985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslinger A., Karin M. Upstream promoter element of the human metallothionein-IIA gene can act like an enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8572–8576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Clarke J. The SV40 enhancer is composed of multiple functional elements that can compensate for one another. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):461–470. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90332-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrlich P., Angel P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Mallick U., Pöting A., Hieber L., Lücke-Huhle C., Schorpp M. The mammalian genetic stress response. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1986;25:485–504. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(86)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N., van Ooyen A. J., Kennedy N., Herrlich P., Ponta H., Groner B. Subfragments of the large terminal repeat cause glucocorticoid-responsive expression of mouse mammary tumor virus and of an adjacent gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3637–3641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Schorpp M., Wagner U., Ryffel G. U. An estrogen-responsive element derived from the 5' flanking region of the Xenopus vitellogenin A2 gene functions in transfected human cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90705-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner I. The phenomenon of the acute phase response. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:39–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L., Holmgren-König M., Khoury G. Transcriptional "silencer" element in rat repetitive sequences associated with the rat insulin 1 gene locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3151–3155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A. Tumor invasion and metastases--role of the extracellular matrix: Rhoads Memorial Award lecture. Cancer Res. 1986 Jan;46(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallick U., Rahmsdorf H. J., Yamamoto N., Ponta H., Wegner R. D., Herrlich P. 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate-inducible proteins are synthesized at an increased rate in Bloom syndrome fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7886–7890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Glaichenhaus N., Gesnel M. C., Breathnach R. Epidermal growth factor and oncogenes induce transcription of the same cellular mRNA in rat fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1435–1440. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03799.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Leroy P., Ruhlmann C., Gesnel M. C., Breathnach R. Isolation of the oncogene and epidermal growth factor-induced transin gene: complex control in rat fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1679–1686. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCroskery P. A., Arai S., Amento E. P., Krane S. M. Stimulation of procollagenase synthesis in human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts by mononuclear cell factor/interleukin 1. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 21;191(1):7–12. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80983-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Robbins E., Rifkin D. B. Tumor invasion through the human amniotic membrane: requirement for a proteinase cascade. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):487–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90613-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miksicek R., Heber A., Schmid W., Danesch U., Posseckert G., Beato M., Schütz G. Glucocorticoid responsiveness of the transcriptional enhancer of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):283–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90745-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poustka A., Rackwitz H. R., Frischauf A. M., Hohn B., Lehrach H. Selective isolation of cosmid clones by homologous recombination in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4129–4133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Wildeman A., Chambon P. A trans-acting factor is responsible for the simian virus 40 enhancer activity in vitro. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):458–463. doi: 10.1038/313458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholer H., Haslinger A., Heguy A., Holtgreve H., Karin M. In vivo competition between a metallothionein regulatory element and the SV40 enhancer. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):76–80. doi: 10.1126/science.3006253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorpp M., Mallick U., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. UV-induced extracellular factor from human fibroblasts communicates the UV response to nonirradiated cells. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):861–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90421-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme J., De Ley M., Opdenakker G., Billiau A., De Somer P., Van Beeumen J. Homogeneous interferon-inducing 22K factor is related to endogenous pyrogen and interleukin-1. Nature. 1985 Mar 21;314(6008):266–268. doi: 10.1038/314266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. E. Compilation of published signal sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5145–5164. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzman S. A., Weitberg A. B., Clark E. P., Stossel T. P. Phagocytes as carcinogens: malignant transformation produced by human neutrophils. Science. 1985 Mar 8;227(4691):1231–1233. doi: 10.1126/science.3975611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitham S. E., Murphy G., Angel P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Smith B. J., Lyons A., Harris T. J., Reynolds J. J., Herrlich P., Docherty A. J. Comparison of human stromelysin and collagenase by cloning and sequence analysis. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):913–916. doi: 10.1042/bj2400913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolley D. E. Collagenolytic mechanisms in tumor cell invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1984;3(4):361–372. doi: 10.1007/BF00051460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]