Abstract
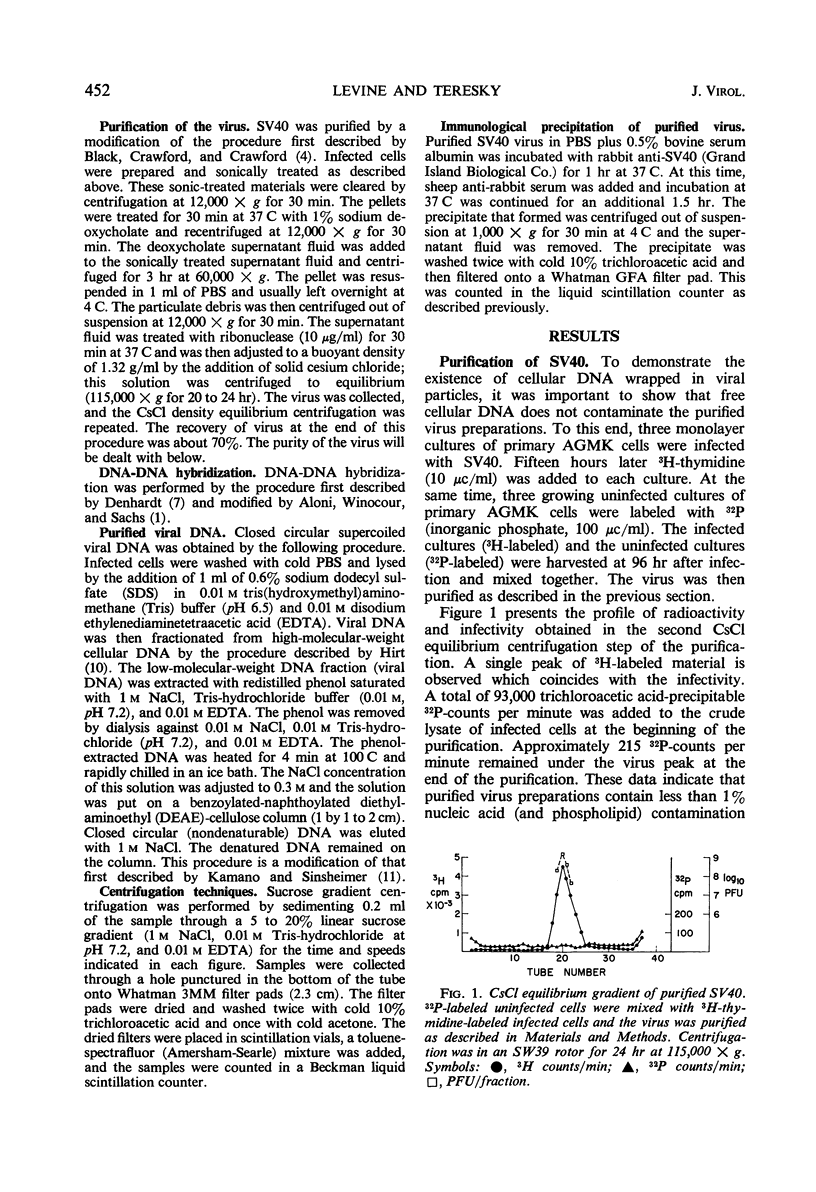
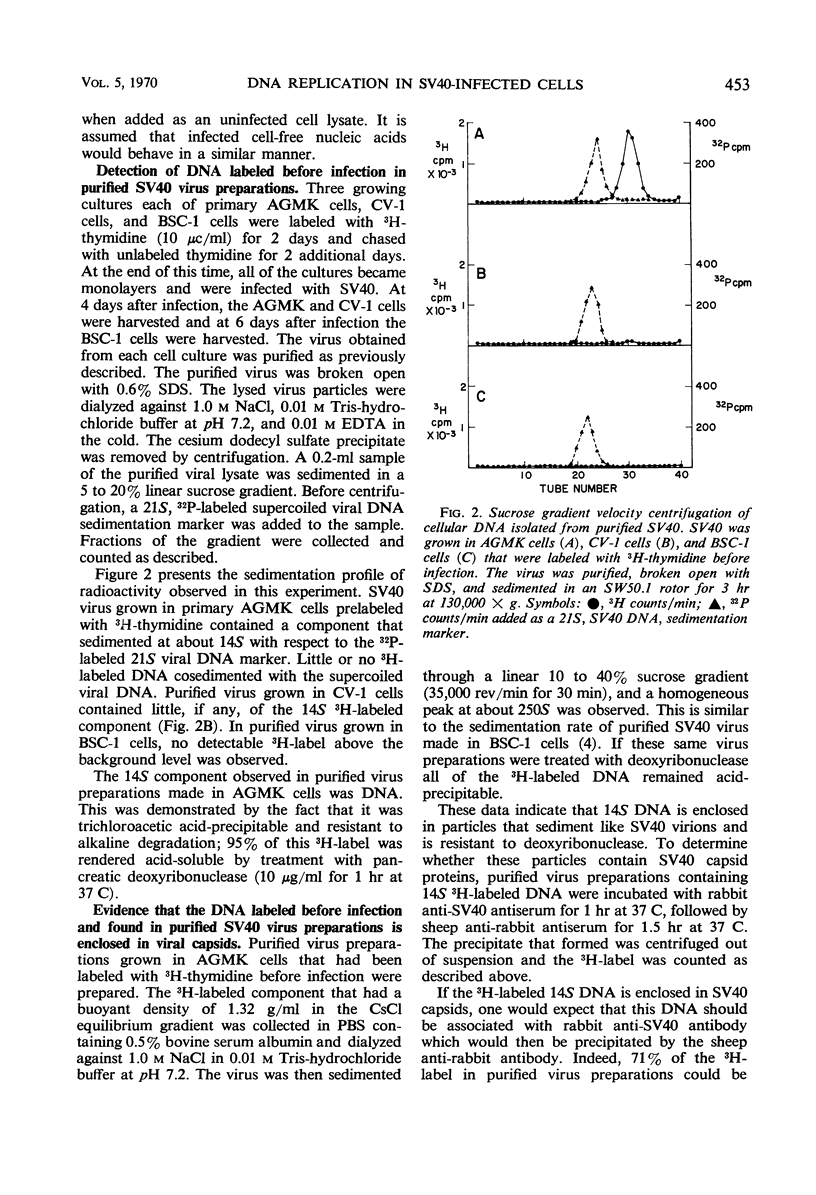
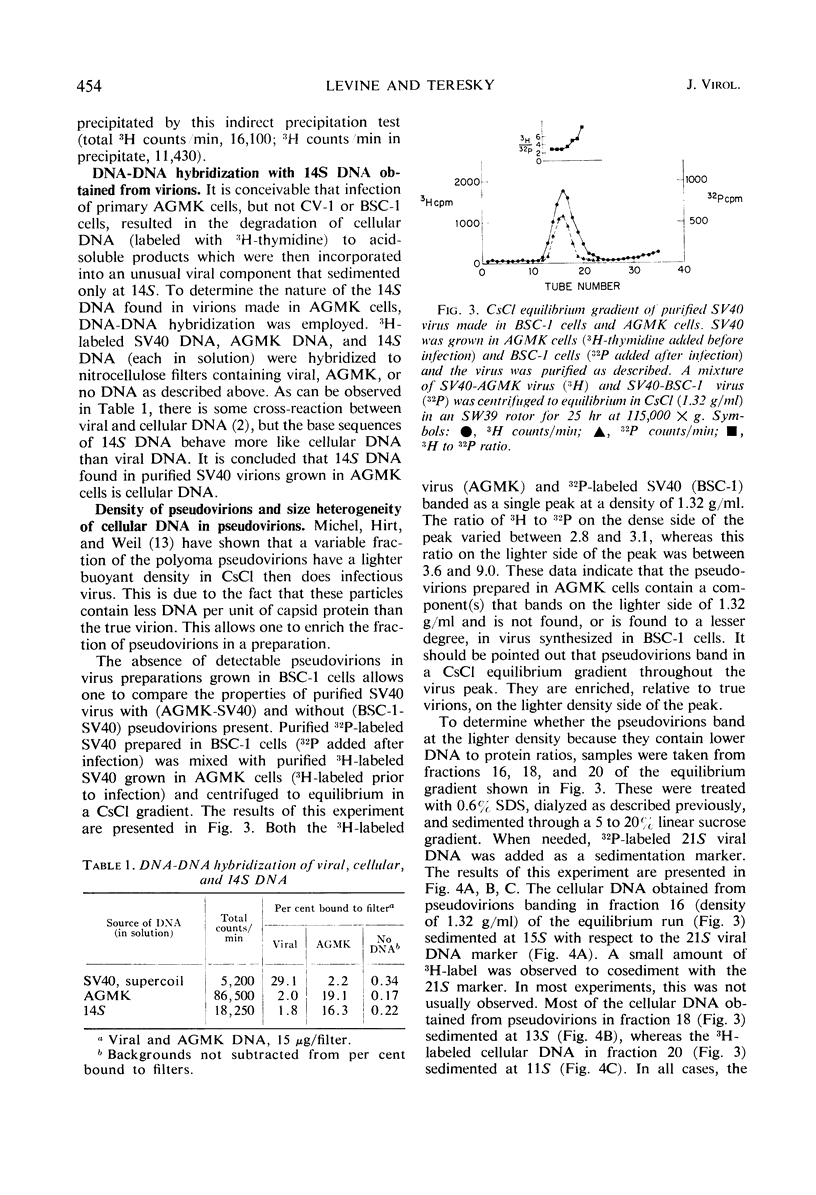
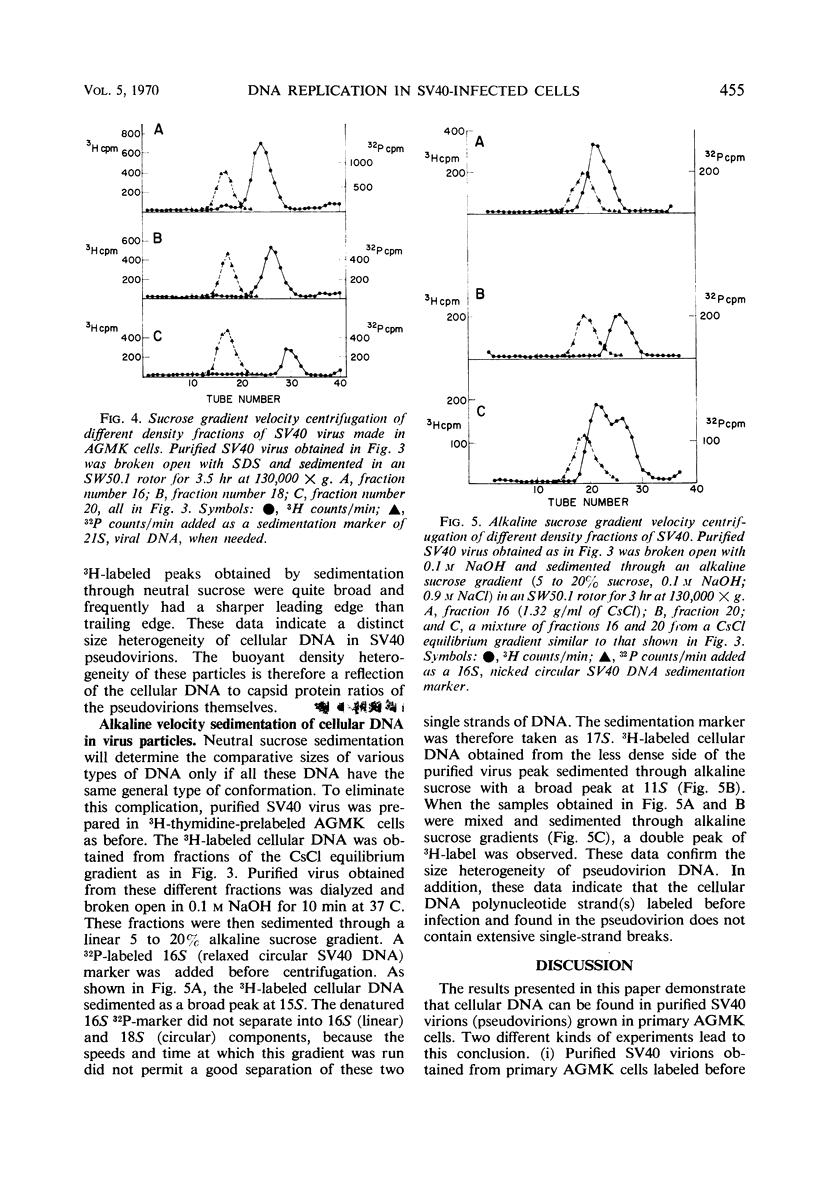
Purified simian virus 40 (SV40) virions, grown in primary African green monkey kidney cells labeled prior to infection with 3H-thymidine, contain a variable quantity of 3H-labeled deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). This DNA is resistant to deoxyribonuclease, sediments at 250S, and is enclosed in a particle that can be precipitated with SV40-specific antiserum. DNA-DNA hybridization experiments demonstrate that this 3H-labeled component in purified SV40 virions is cellular DNA. When this 3H-labeled DNA is released from purified virus with sodium dodecyl sulfate, it has an average sedimentation constant of 14S. Sedimentation through neutral and alkaline sucrose gradients shows that this 14S DNA is composed of a collection of different sizes of DNA molecules that sediment between 11 and 15S. As a result of this size heterogeneity, SV40 virions containing cellular DNA (pseudovirions) have a variable DNA to capsid protein ratio and exhibit a spectrum of buoyant densities in a CsCl equilibrium gradient. Pseudovirions are enriched, relative to true virions, on the lighter density side of infectious SV40 virus banded to equilibrium in a CsCl gradient. Little or no cellular DNA was found in purified SV40 virus preparations grown in BSC-1 or CV-1 cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aloni Y., Winocour E., Sachs L. Characterization of the simian virus 40-specific RNA in virus-yielding and transformed cells. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):415–429. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90418-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aloni Y., Winocour E., Sachs L., Torten J. Hybridization between SV40 DNA and cellular DNA's. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 14;44(2):333–345. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90179-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACK P. H., CRAWFORD E. M., CRAWFORD L. V. THE PURIFICATION OF SIMIAN VIRUS 40. Virology. 1964 Nov;24:381–387. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., Coto C., Kaplan A. S. Unstable DNA synthesized by polyoma virus-infected cells. Virology. 1966 Sep;30(1):74–81. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(66)81011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Kohne D. E. Repeated sequences in DNA. Hundreds of thousands of copies of DNA sequences have been incorporated into the genomes of higher organisms. Science. 1968 Aug 9;161(3841):529–540. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3841.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD L. V., BLACK P. H. THE NUCLEIC ACID OF SIMIAN VIRUS 40. Virology. 1964 Nov;24:388–392. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90176-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., HARTWELL L. H., VOGT M. INDUCTION OF CELLULAR DNA SYNTHESIS BY POLYOMA VIRUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:403–410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilead Z., Ginsberg H. S. Characterization of a Tumorlike Antigen in Type 12 and Type 18 Adenovirus-Infected Cells. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):120–125. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.120-125.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komano T., Sinsheimer R. L. Preparation and purification of phi X-RF component I. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 29;155(1):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Ginsberg H. S. Mechanism by which fiber antigen inhibits multiplication of type 5 adenovirus. J Virol. 1967 Aug;1(4):747–757. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.4.747-757.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. R., Hirt B., Weil R. Mouse cellular DNA enclosed in polyoma viral capsids (pseudovirions). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1381–1388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozer H. L., Takemoto K. K. Site of host restriction of simian virus 40 mutants in an established African green monkey kidney cell line. J Virol. 1969 Oct;4(4):408–415. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.4.408-415.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto K. K., Todaro G. J., Habel K. Recovery of SV40 virus with genetic markers of original inducing virus from SV40-transformed mouse cells. Virology. 1968 May;35(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90299-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil R., Michel M. R., Ruschmann G. K. Induction of cellular DNA synthesis by polyoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jun;53(6):1468–1475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.6.1468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winocour E., Kaye A. M., Stollar V. Synthesis and transmethylation of DNA in polyoma-infected cultures. Virology. 1965 Oct;27(2):156–169. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90155-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winocour E. Some aspects of the interaction between polyoma virus and cell DNA. Adv Virus Res. 1969;14:153–200. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60559-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


