Abstract
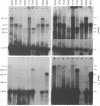
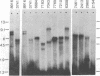
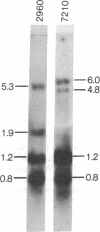
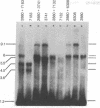
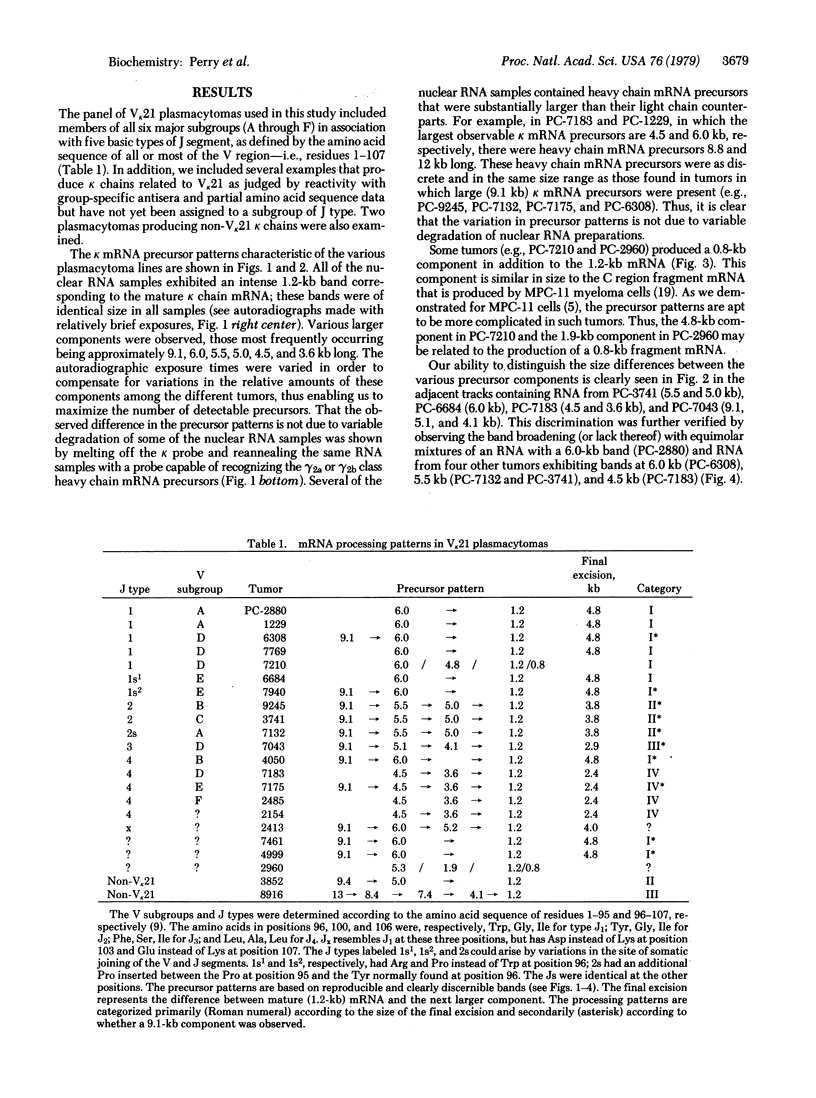
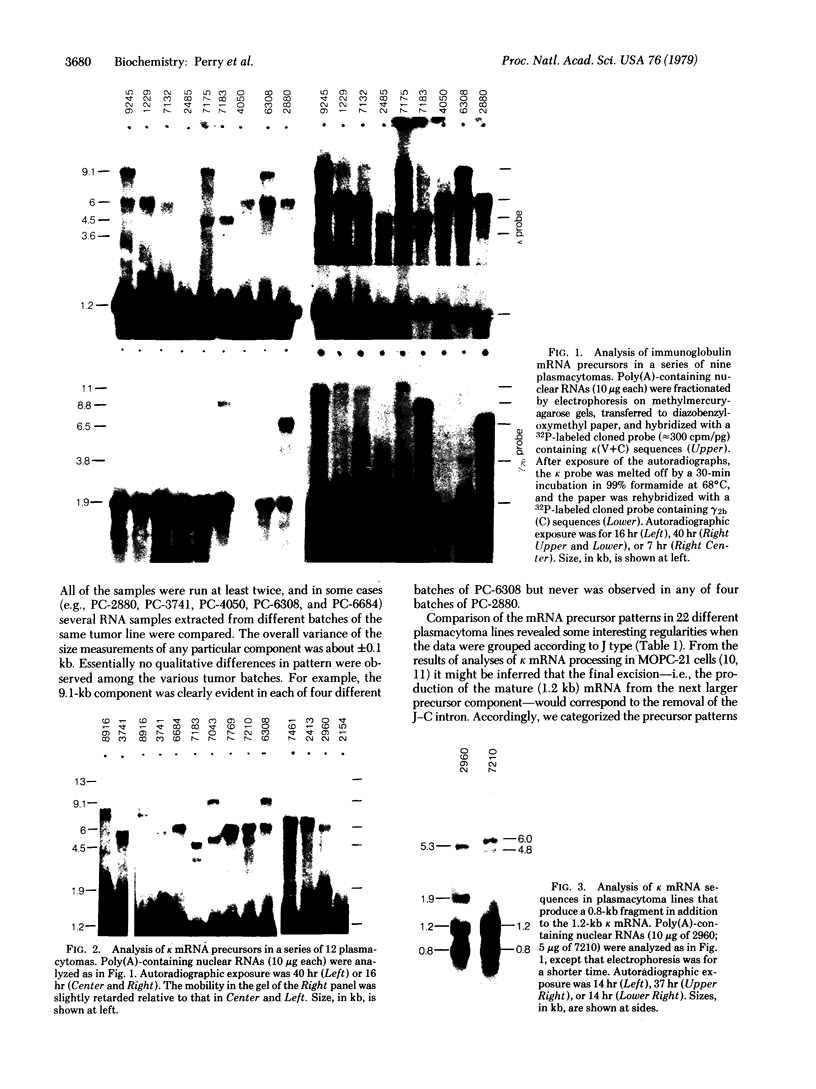
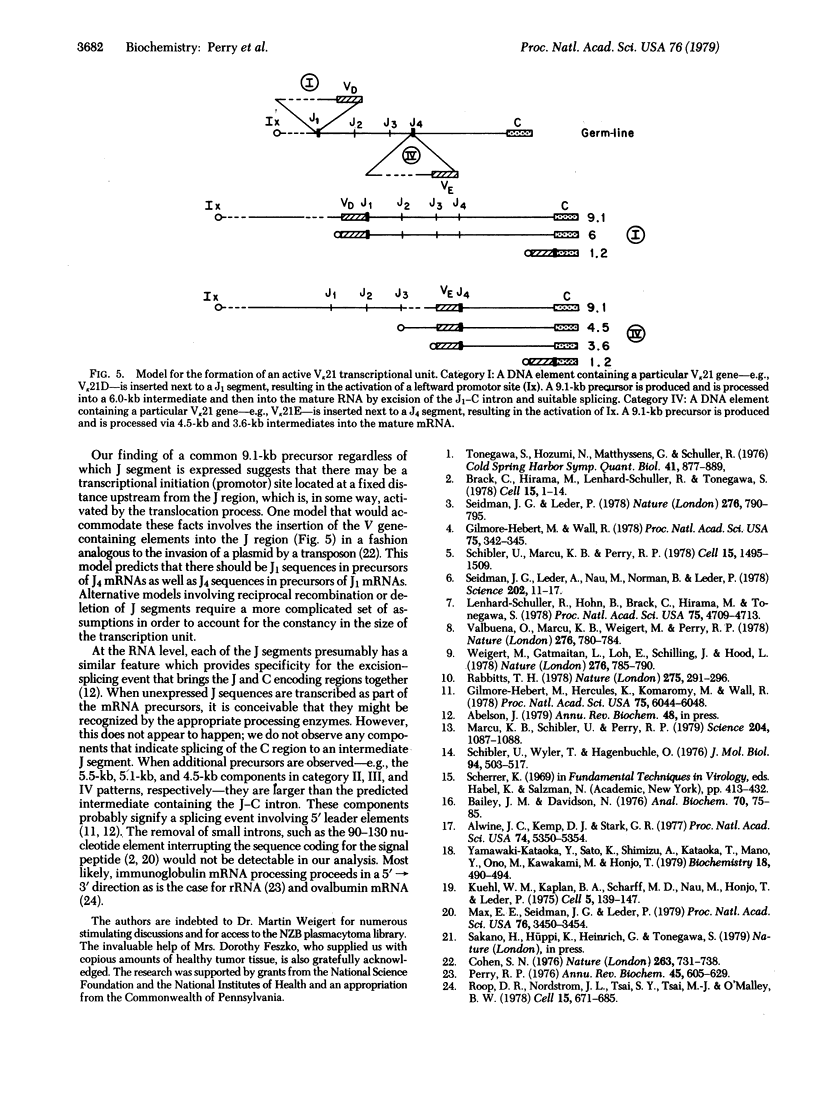
To help elucidate the mechanisms of formation and expression of active immunoglobulin genes, we have made a systematic study of the processing patterns of the mRNAs that code for a closely related family of κ chains. Among the members of this family, represented by the Vκ21 group of plasmacytomas, are examples in which six different germ-line V genes are joined to four different J segments in various combinations. The mRNA precursors were identified by hybridizing a cloned κ-cDNA probe to poly(A)-containing nuclear RNAs that were size fractionated on methylmercury-agarose gels and transferred to diazotized paper. Based on the length of the segment excised in the last detectable processing step, which presumably represents the removal of the J-C intron, the precursor patterns were classified into four primary categories that correlated well with the type of J segment being expressed. The J segments were thus located at distances ranging from 2.4 to 4.8 kilobases from the constant-region gene. Different V genes joined to the same J segment exhibited similar precursor patterns, suggesting that the size of the translocated V segment may be relatively uniform among members of the Vκ21 group. A large (9.1 kilobases) component, which is likely to represent a primary transcription product, was observed in all processing categories, regardless of which J segment was being utilized. This surprising observation leads to some interesting predictions about the mechanism of V-J translocation.
Keywords: gene rearrangement, J segments, transcription unit, processing
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack C., Hirama M., Lenhard-Schuller R., Tonegawa S. A complete immunoglobulin gene is created by somatic recombination. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N. Transposable genetic elements and plasmid evolution. Nature. 1976 Oct 28;263(5580):731–738. doi: 10.1038/263731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore-Hebert M., Wall R. Immunoglobulin light chain mRNA is processed from large nuclear RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):342–345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore-Herbert M., Hercules K., Komaromy M., Wall R. Variable and constant regions are separated in the 10-kbase transcription unit coding for immunoglobulin kappa light chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6044–6048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehl W. M., Kaplan B. A., Scharff M. D. Characterization of light chain and light chain constant region fragment mRNAs in MPC 11 mouse myeloma cells and variants. Cell. 1975 Jun;5(2):139–147. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenhard-Schuller R., Hohn B., Brack C., Hirama M., Tonegawa S. DNA clones containing mouse immunoglobulin kappa chain genes isolated by in vitro packaging into phage lambda coats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4709–4713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B., Schibler U., Perry R. P. Nuclear transcripts of mouse heavy chain immunoglobulin genes contain only the expressed class of C-region sequences. Science. 1979 Jun 8;204(4397):1087–1088. doi: 10.1126/science.109919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Seidman J. G., Leder P. Sequences of five potential recombination sites encoded close to an immunoglobulin kappa constant region gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3450–3454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P. Processing of RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:605–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H. Evidence for splicing of interrupted immunoglobulin variable and constant region sequences in nuclear RNA. Nature. 1978 Sep 28;275(5678):291–296. doi: 10.1038/275291a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop D. R., Nordstrom J. L., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Transcription of structural and intervening sequences in the ovalbumin gene and identification of potential ovalbumin mRNA precursors. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):671–685. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Marcu K. B., Perry R. P. The synthesis and processing of the messenger RNAs specifying heavy and light chain immunoglobulins in MPC-11 cells. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1495–1509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Wyler T., Hagenbüchle O. Changes in size and secondary structure of the ribosomal transcription unit during vertebrate evolution. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90217-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman J. G., Leder A., Nau M., Norman B., Leder P. Antibody diversity. Science. 1978 Oct 6;202(4363):11–17. doi: 10.1126/science.99815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman J. G., Leder P. The arrangement and rearrangement of antibody genes. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):790–795. doi: 10.1038/276790a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S., Hozumi N., Matthyssens G., Schuller R. Somatic changes in the content and context of immunoglobulin genes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):877–889. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valbuena O., Marcu K. B., Weigert M., Perry R. P. Multiplicity of germline genes specifying a group of related mouse kappa chains with implications for the generation of immunoglobulin diversity. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):780–784. doi: 10.1038/276780a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigert M., Gatmaitan L., Loh E., Schilling J., Hood L. Rearrangement of genetic information may produce immunoglobulin diversity. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):785–790. doi: 10.1038/276785a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Sato K., Shimizu A., Kataoka T., Mano Y., Ono M., Kawakami M., Honjo T. Mutual homology of mouse immunoglobulin gamma-chain gene sequences. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 6;18(3):490–494. doi: 10.1021/bi00570a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]