Abstract
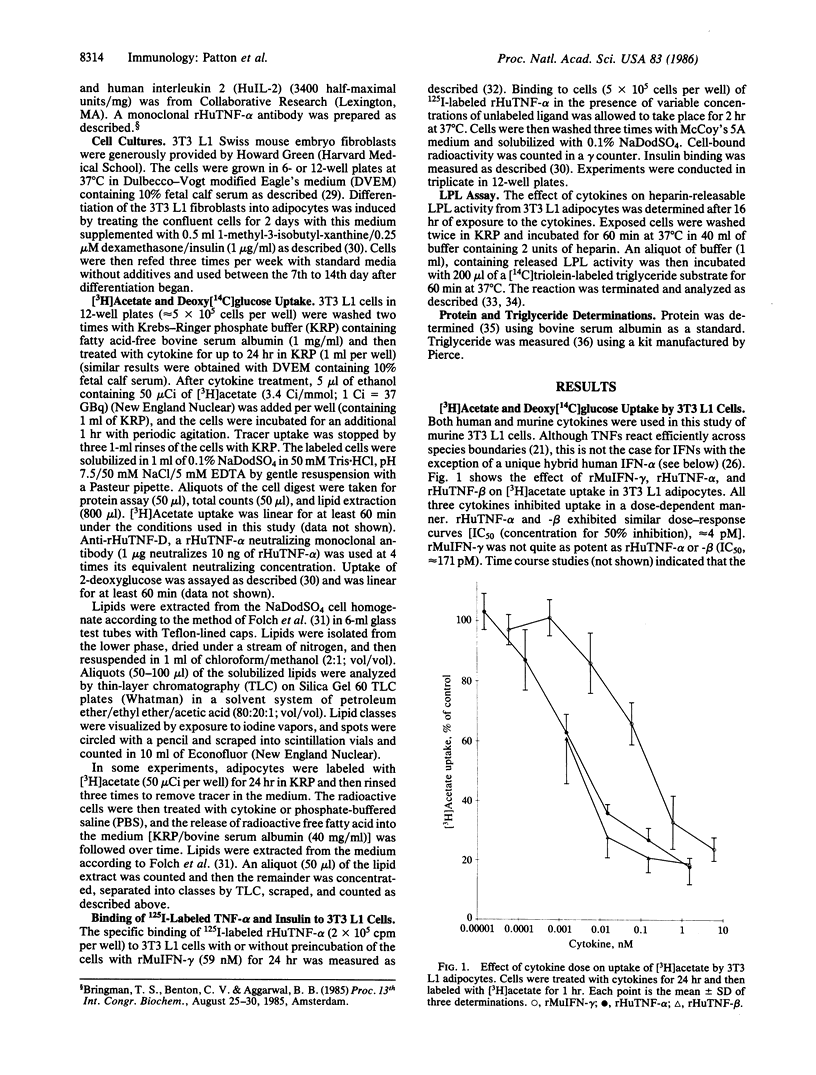
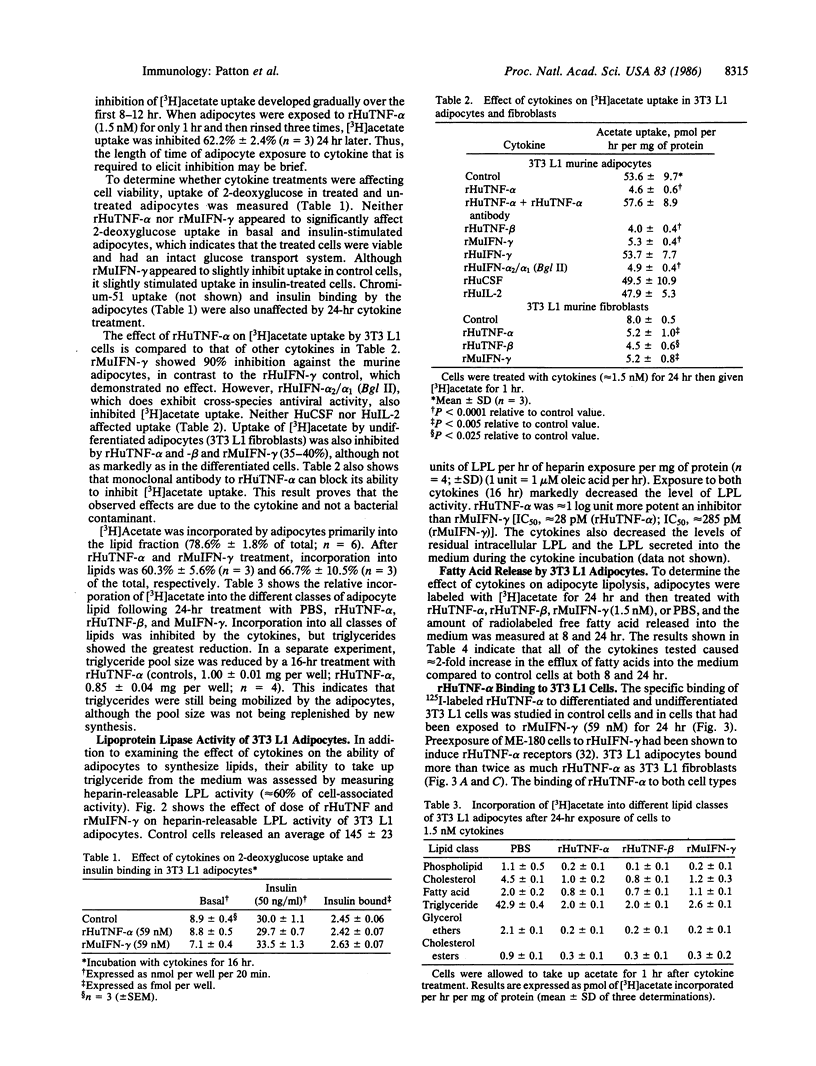
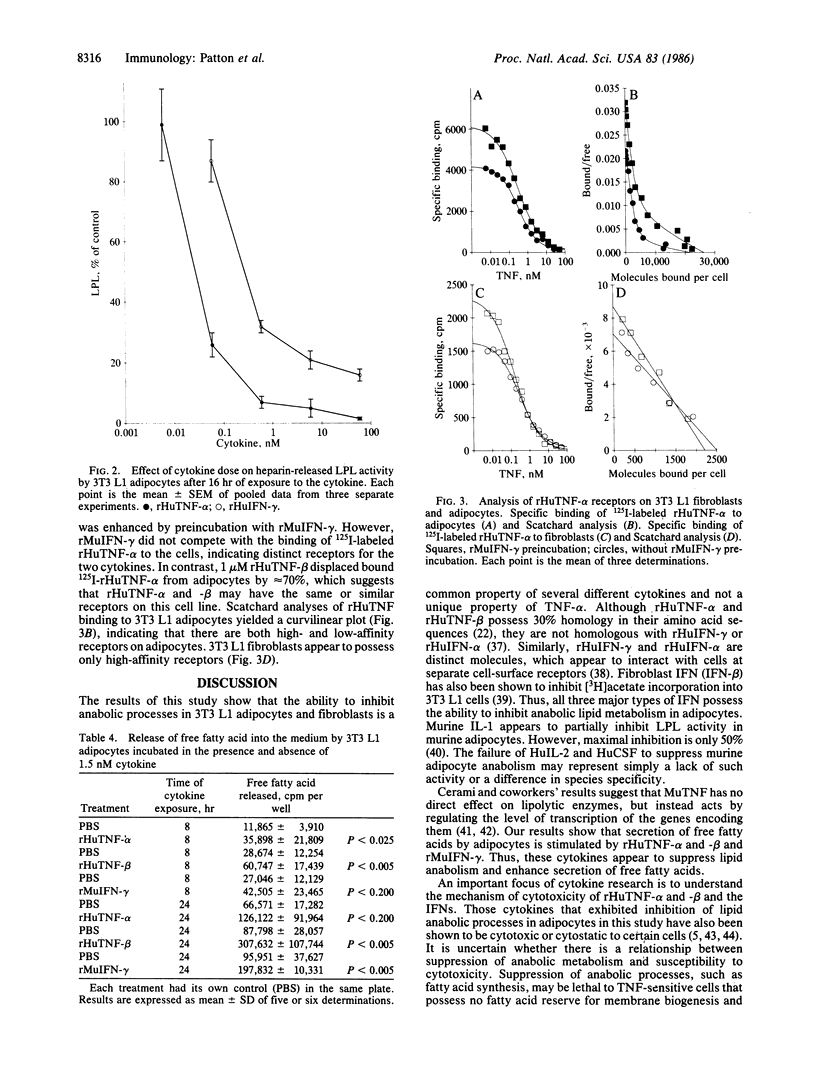
The effect of a variety of cytokines on lipid metabolism in 3T3 L1 mouse fibroblasts and adipocytes was studied. Uptake of [3H]acetate by adipocytes and heparin-releasable lipoprotein lipase activity was inhibited after treatments of the cells with picomolar concentrations of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor alpha (rHuTNF-alpha), human tumor necrosis factor beta (rHuTNF-beta, also called lymphotoxin), murine interferon-gamma (rMuIFN-gamma), and a human hybrid interferon-alpha [rHuIFN-alpha 2/alpha 1 (Bgl II)]. Recombinant human interferon-gamma (rHuIFN-gamma), natural human colony-stimulating factor (HuCSF), and human interleukin 2 (HuIL-2) had no effect. Similar though less-marked suppression of [3H]acetate uptake by cytokines was seen in 3T3 L1 fibroblasts. Cytokines inhibited the incorporation of [3H]acetate into both membrane and storage lipids in the adipocytes. In addition to blocking lipid uptake and synthesis, rHuTNF-alpha and -beta, and rMuIFN-gamma stimulated the release of free fatty acid into the medium from adipocytes. Binding studies suggest that rHuTNF-alpha and rHuTNF-beta compete for the same cell-surface receptor on 3T3 L1 adipocytes, while rMuIFN-gamma binds to a separate receptor. The binding of rTNF-alpha to both adipocytes and fibroblasts can be significantly enhanced by preexposure of the cells to rMuIFN-gamma. There appear to be both high- and low-affinity receptors for rHuTNF-alpha on adipocytes, whereas fibroblasts exhibit a single class of high-affinity receptors. These results suggest that a variety of structurally distinct cytokines possess lipid mobilization activity, which may be of critical importance to the host in defense against infection or malignancy.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal B. B., Eessalu T. E., Hass P. E. Characterization of receptors for human tumour necrosis factor and their regulation by gamma-interferon. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):665–667. doi: 10.1038/318665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal B. B., Kohr W. J., Hass P. E., Moffat B., Spencer S. A., Henzel W. J., Bringman T. S., Nedwin G. E., Goeddel D. V., Harkins R. N. Human tumor necrosis factor. Production, purification, and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2345–2354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auron P. E., Webb A. C., Rosenwasser L. J., Mucci S. F., Rich A., Wolff S. M., Dinarello C. A. Nucleotide sequence of human monocyte interleukin 1 precursor cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7907–7911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisel W. R. Metabolic response to infection. Annu Rev Med. 1975;26:9–20. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.26.020175.000301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin W. R., Farrar J. J. Biological and biochemical properties of lymphokines produced by the EL 4 thymoma cell line. Lymphokine Res. 1983;2(1):33–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B. A., Cerami A. Recombinant interleukin 1 suppresses lipoprotein lipase activity in 3T3-L1 cells. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3969–3971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Greenwald D., Hulmes J. D., Chang M., Pan Y. C., Mathison J., Ulevitch R., Cerami A. Identity of tumour necrosis factor and the macrophage-secreted factor cachectin. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):552–554. doi: 10.1038/316552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs H. G., Erikson J. M., Moorehead W. R. A manual colormetric assay of triglycerides in serum. Clin Chem. 1975 Mar;21(3):437–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarniecki C. W., Fennie C. W., Powers D. B., Estell D. A. Synergistic antiviral and antiproliferative activities of Escherichia coli-derived human alpha, beta, and gamma interferons. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):490–496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.490-496.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M. V., Brindley L., Kawasaki E., Larrick J. High level human interleukin 1 production by a hepatoma cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jul 31;130(2):768–773. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90482-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumonde D. C., Wolstencroft R. A., Panayi G. S., Matthew M., Morley J., Howson W. T. "Lymphokines": non-antibody mediators of cellular immunity generated by lymphocyte activation. Nature. 1969 Oct 4;224(5214):38–42. doi: 10.1038/224038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J. Macrophages and metastasis--a biological approach to cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 1985 Oct;45(10):4714–4726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin L. A., McMahon F., Moeller M. Modulation of adipose lipoprotein lipase by thyroid hormone and diabetes. The significance of the low T3 state. Diabetes. 1985 Dec;34(12):1266–1271. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.12.1266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Leung D. W., Dull T. J., Gross M., Lawn R. M., McCandliss R., Seeburg P. H., Ullrich A., Yelverton E., Gray P. W. The structure of eight distinct cloned human leukocyte interferon cDNAs. Nature. 1981 Mar 5;290(5801):20–26. doi: 10.1038/290020a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Aggarwal B. B., Benton C. V., Bringman T. S., Henzel W. J., Jarrett J. A., Leung D. W., Moffat B., Ng P., Svedersky L. P. Cloning and expression of cDNA for human lymphotoxin, a lymphokine with tumour necrosis activity. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):721–724. doi: 10.1038/312721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Goeddel D. V. Cloning and expression of murine immune interferon cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5842–5846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Leung D. W., Pennica D., Yelverton E., Najarian R., Simonsen C. C., Derynck R., Sherwood P. J., Wallace D. M., Berger S. L. Expression of human immune interferon cDNA in E. coli and monkey cells. Nature. 1982 Feb 11;295(5849):503–508. doi: 10.1038/295503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunfeld C., Baird K., Van Obberghen E., Kahn C. R. Glucocorticoid-induced insulin resistance in vitro: evidence for both receptor and postreceptor defects. Endocrinology. 1981 Nov;109(5):1723–1730. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-5-1723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson F. A., Grunfeld C., Kahn C. R., Roth J. Regulation of insulin receptors and insulin responsiveness in 3T3-L1 fatty fibroblasts. Endocrinology. 1979 May;104(5):1383–1392. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-5-1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami M., Pekala P. H., Lane M. D., Cerami A. Lipoprotein lipase suppression in 3T3-L1 cells by an endotoxin-induced mediator from exudate cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):912–916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keay S., Grossberg S. E. Interferon inhibits the conversion of 3T3-L1 mouse fibroblasts into adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4099–4103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzrock R., Rosenblum M. G., Sherwin S. A., Rios A., Talpaz M., Quesada J. R., Gutterman J. U. Pharmacokinetics, single-dose tolerance, and biological activity of recombinant gamma-interferon in cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1985 Jun;45(6):2866–2872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer J. A., Pestka S. Structure of interferons. Pharmacol Ther. 1985;27(3):371–401. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(85)90076-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedwin G. E., Svedersky L. P., Bringman T. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Goeddel D. V. Effect of interleukin 2, interferon-gamma, and mitogens on the production of tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2492–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Nedwin G. E., Hayflick J. S., Seeburg P. H., Derynck R., Palladino M. A., Kohr W. J., Aggarwal B. B., Goeddel D. V. Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):724–729. doi: 10.1038/312724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Kelder B., Familletti P. C., Moschera J. A., Crowl R., Kempner E. S. Molecular weight of the functional unit of human leukocyte, fibroblast, and immune interferons. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9706–9709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins C. H. Immunoregulation by lymphokines: immune interferon and lymphotoxin induction of lymphokine activity in human peripheral blood leukocyte cultures. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1983;166:37–44. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-1410-4_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin B. Y., Anderson S. L., Sullivan S. A., Williamson B. D., Carswell E. A., Old L. J. Purification and characterization of a human tumor necrosis factor from the LuKII cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6637–6641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schotz M. C., Garfinkel A. S., Huebotter R. J., Stewart J. E. A rapid assay for lipoprotein lipase. J Lipid Res. 1970 Jan;11(1):68–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott G. M. The toxic effects of interferon in man. Interferon. 1983;5:85–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman C. L., Marshall J. D., Shultz L. D., Gray P. W., Johnson H. M. Gamma-interferon is one of several direct B cell-maturing lymphokines. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):801–804. doi: 10.1038/309801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman B. J., Aggarwal B. B., Hass P. E., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Shepard H. M. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha: effects on proliferation of normal and transformed cells in vitro. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):943–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3933111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Matsui H., Fujita T., Takaoka C., Kashima N., Yoshimoto R., Hamuro J. Structure and expression of a cloned cDNA for human interleukin-2. Nature. 1983 Mar 24;302(5906):305–310. doi: 10.1038/302305a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torti F. M., Dieckmann B., Beutler B., Cerami A., Ringold G. M. A macrophage factor inhibits adipocyte gene expression: an in vitro model of cachexia. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):867–869. doi: 10.1126/science.3839597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto M., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor: specific binding and internalization in sensitive and resistant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7626–7630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weck P. K., Apperson S., Stebbing N., Gray P. W., Leung D., Shepard H. M., Goeddel D. V. Antiviral activities of hybrids of two major human leukocyte interferons. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6153–6166. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


