Abstract
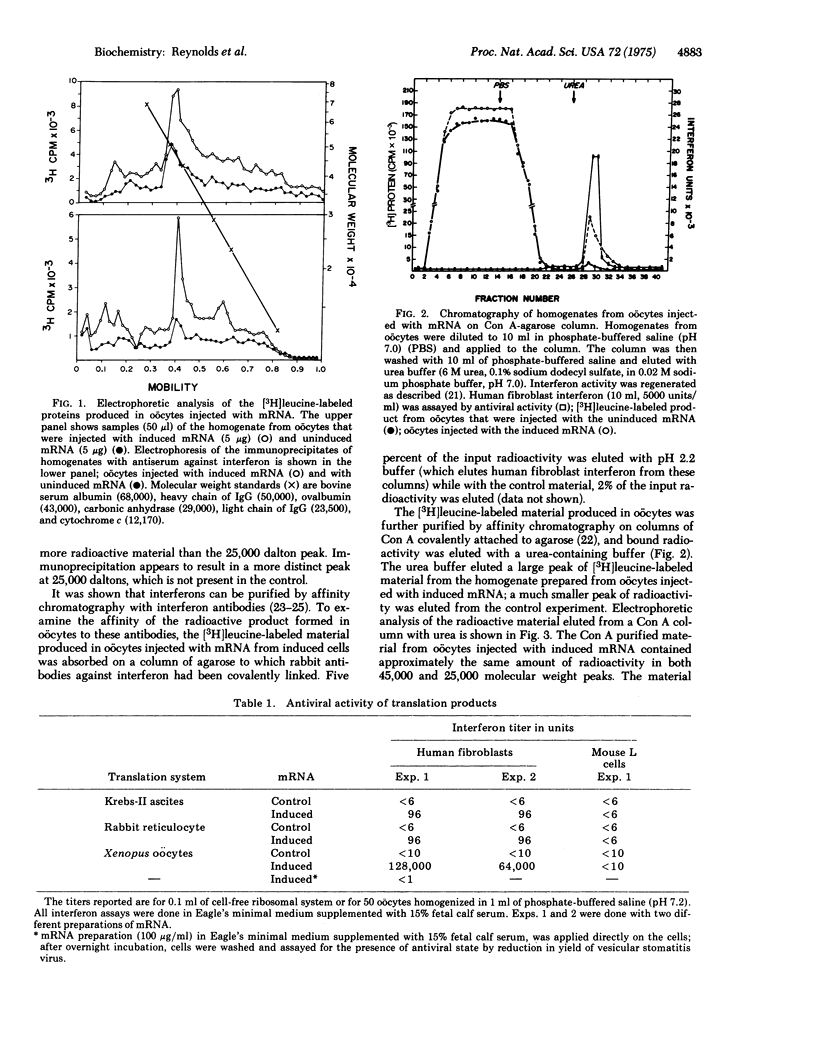
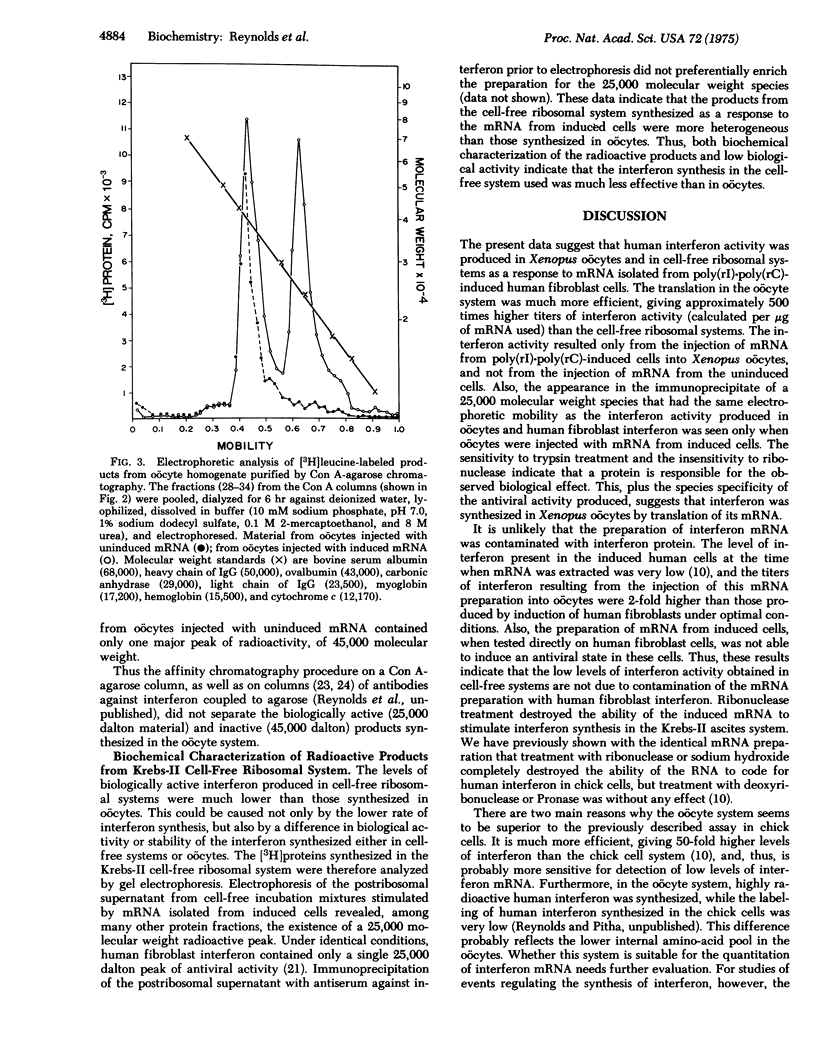
Translation of messenger RNA isolated from poly(rI)-poly(rC)-induced human fibroblasts in cell-free ribosomal systems and in Xenopus oocytes resulted in the production of biologically active proteins that had the properties of human fibroblast interferon. The translation in the oocytes was much more efficient, giving approximately 500 times higher titers of interferon activity than the cell-free systems. A control messenger RNA isolated from noninduced human fibroblasts, did not code for interferon synthesis in these systems. Both messenger RNA preparations stimulated [3H]amino-acid incorporation into trichloroacetic acid-insoluble material. The radioactive products and their immunoprecipitates were electrophoresed on polyacrylamide gels under denaturing conditions. The products resulting from the translation of the control (uninduced) messenger RNA in oocytes contained a major protein of approximately 45,000 molecular weight. The messenger RNA isolated from poly(rI)-poly(rC)-induced cells stimulated the synthesis of an additional 25,000 molecular weight protein that electrophoresed in the same position as human fibroblast interferon. These results suggest that human fibroblast interferon was synthesized by the translation of its messenger RNA in Xenopus oocytes and in cell-free ribosomal systems.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anfinsen C. B., Bose S., Corley L., Gurari-Rotman D. Partial purification of human interferon by affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3139–3142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Boime I., Leder P. Protein synthesis directed by encephalomyocarditis virus RNA: properties of a transfer RNA-dependent system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2303–2307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G., Mendecki J., Lee S. Y. A procedure for the isolation of mammalian messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 15;11(4):637–641. doi: 10.1021/bi00754a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey M. W., Huang J. W., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Hydrophobic interaction of human interferon with concanavalin A-agarose. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6354–6355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E., Hunt T. Double-stranded poliovirus RNA inhibits initiation of protein synthesis by reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):1075–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Lingrel J. B. Hemoglobin messenger ribonucleic acid. Distribution of the 9S ribonucleic acid in polysomes of different sizes. Biochemistry. 1969 Mar;8(3):829–831. doi: 10.1021/bi00831a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Lane C. D., Woodland H. R., Marbaix G. Use of frog eggs and oocytes for the study of messenger RNA and its translation in living cells. Nature. 1971 Sep 17;233(5316):177–182. doi: 10.1038/233177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallum J. V., Younger J. S. Quantitative aspects of inhibition of virus replication by interferon in chick embryo cell cultures. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1047–1050. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1047-1050.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACS A., LINDENMANN J. Virus interference. I. The interferon. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957 Sep 12;147(927):258–267. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1957.0048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metafora S., Terada M., Dow L. W., Marks P. A., Bank A. Increased efficiency of exogenous messenger RNA translation in a Krebs ascites cell lysate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1299–1303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montagnier L., Collandre H., De Maeyer-Guignard J., De Maeyer E. Two forms of mouse interferon messenger RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 5;59(3):1031–1038. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80083-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogburn C. A., Berg K., Paucker K. Purification of mouse interferon by affinity chromatography on anti-interferon globulin-sepharose. J Immunol. 1973 Oct;111(4):1206–1218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds F. H., Jr, Pitha P. M. Molecular weight study of human fibroblast interferon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):107–112. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds F. H., Jr, Pitha P. M. The induction of interferon and its messenger RNA in human fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 5;59(3):1023–1030. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipe J. D., de Maeyer-Guignard J., Fauconnier B., de Maeyer E. Purification of mouse interferon by affinity chromatography on a solid-phase immunoadsorbent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1037–1040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A., Levinson B. B., Tomkins G. M. "Superinduction" of tyrosine aminotransferase by actinomycin D: a reevaluation. Cell. 1975 May;5(1):29–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90088-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan Y. H., Armstrong J. A., Ke Y. H., Ho M. Regulation of cellular interferon production: enhancement by antimetabolites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):464–471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkins G. M., Levinson B. B., Baxter J. D., Dethlefsen L. Further evidence for posttranscriptional control of inducible tyrosine aminotransferase synthesis in cultured hepatoma cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 6;239(88):9–14. doi: 10.1038/newbio239009a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Havell E. A. Stabilization of interferon messenger RNA activity by treatment of cells with metabolic inhibitors and lowering of the incubation temperature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3909–3913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Maeyer-Guignard J., de Maeyer E., Montagnier L. Interferon messenger RNA: translation in heterologous cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1203–1207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


