Abstract
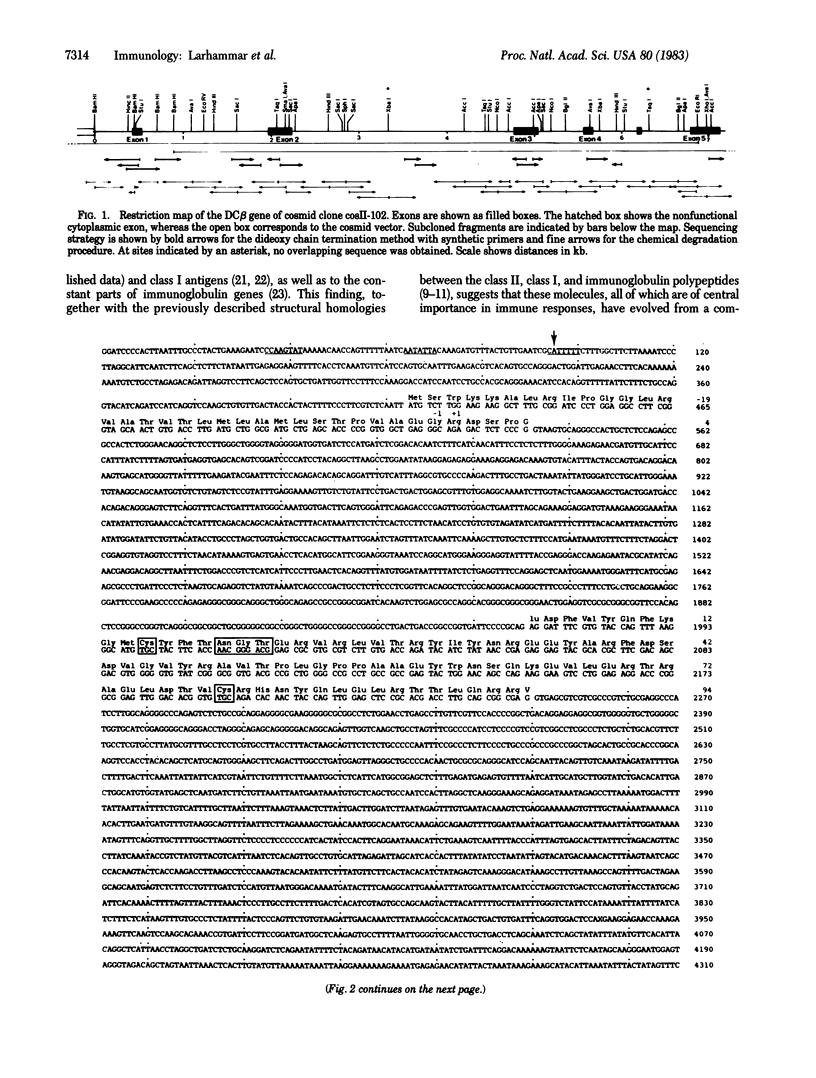
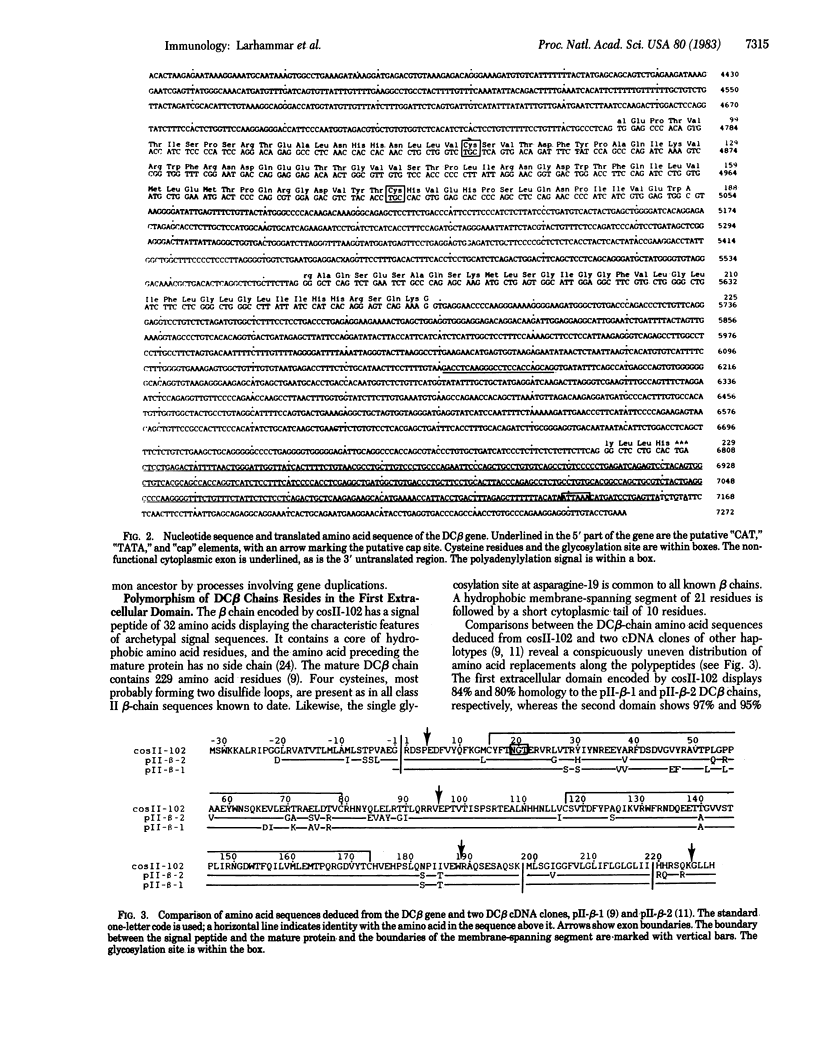
We have determined the complete nucleotide sequence of a human class II histocompatibility antigen DC beta gene. The gene spans more than 7 kilobases and contains five exons corresponding to the different domains of the DC beta polypeptide. The exon-intron organization is thus analogous to that of class II antigen alpha-chain genes, class I antigen heavy chain genes, and the constant parts of immunoglobulin genes, emphasizing further the evolutionary relationship among these molecules. The mature polypeptide deduced from the DC beta gene shows 93% and 88% homology, respectively, to sequences derived from two DC beta cDNA clones of other haplotypes. The allelic polymorphism of DC beta chains resides predominantly in the first extracellular domain, whereas the rest of the polypeptide is virtually constant. The exons of the DC beta gene display high homology to the corresponding exons of a murine I-A beta gene. Also, the introns show significant homology. The DC beta chains lack eight amino acids in the cytoplasmic tail, as compared to DR and I-A beta chains. This is probably due to a nonfunctional splice junction of DC beta genes, causing a separate cytoplasmic exon to be nonexpressed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. Gene conversion: some implications for immunoglobulin genes. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):592–594. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benacerraf B. Role of MHC gene products in immune regulation. Science. 1981 Jun 12;212(4500):1229–1238. doi: 10.1126/science.6165083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boss J. M., Gillam S., Zitomer R. S., Smith M. Sequence of the yeast iso-1-cytochrome c mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12958–12961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell A. L., Paskind M., Reth M., Imanishi-Kari T., Rajewsky K., Baltimore D. Heavy chain variable region contribution to the NPb family of antibodies: somatic mutation evident in a gamma 2a variable region. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):625–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhme J., Owerbach D., Denaro M., Lernmark A., Peterson P. A., Rask L. Human class II major histocompatibility antigen beta-chains are derived from at least three loci. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):82–84. doi: 10.1038/301082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron D. J., McDevitt H. O. Analysis of HLA-D region-associated molecules with monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6567–6571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das H. K., Lawrance S. K., Weissman S. M. Structure and nucleotide sequence of the heavy chain gene of HLA-DR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3543–3547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F. G., Dahl H. H., de Boer E., Flavell R. A. Isolation of beta-globin-related genes from a human cosmid library. Gene. 1981 Apr;13(3):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F. G., Lund T., Murray E. J., Mellor A. L., Dahl H. H., Flavell R. A. The construction of cosmid libraries which can be used to transform eukaryotic cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6715–6732. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hämmerling G. J. Tissue distribution of Ia antigens and their expression on lymphocyte subpopulations. Transplant Rev. 1976;30:64–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J. F., Strominger J. L. HLA-DR light chain has a polymorphic N-terminal region and a conserved immunoglobulin-like C-terminal region. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):694–697. doi: 10.1038/297694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klareskog L., Sandgerg-Trägårdh L., Rask L., Lindblom J. B., Curman B., Peterson P. A. Chemical properties of human Ia antigens. Nature. 1977 Jan 20;265(5591):248–251. doi: 10.1038/265248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreil G. Transfer of proteins across membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:317–348. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larhammar D., Gustafsson K., Claesson L., Bill P., Wiman K., Schenning L., Sundelin J., Widmark E., Peterson P. A., Rask L. Alpha chain of HLA-DR transplantation antigens is a member of the same protein superfamily as the immunoglobulins. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):153–161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larhammar D., Hammerling U., Denaro M., Lund T., Flavell R. A., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Structure of the murine immune response I-A beta locus: sequence of the I-A beta gene and an adjacent beta-chain second domain exon. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):179–188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larhammar D., Schenning L., Gustafsson K., Wiman K., Claesson L., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Complete amino acid sequence of an HLA-DR antigen-like beta chain as predicted from the nucleotide sequence: similarities with immunoglobulins and HLA-A, -B, and -C antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3687–3691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen M., Malissen B., Jordan B. R. Exon/intron organization and complete nucleotide sequence of an HLA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):893–897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Benoist C. O., Williams V. E., 2nd, Kanter M. R., McDevitt H. O. The murine E alpha immune response gene. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):745–754. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Seidman J. G. Structure of wild-type and mutant mouse beta 2-microglobulin genes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):661–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90182-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pease L. R., Schulze D. H., Pfaffenbach G. M., Nathenson S. G. Spontaneous H-2 mutants provide evidence that a copy mechanism analogous to gene conversion generates polymorphism in the major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):242–246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechavi G., Bienz B., Ram D., Ben-Neriah Y., Cohen J. B., Zakut R., Givol D. Organization and evolution of immunoglobulin VH gene subgroups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4405–4409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsing E., Miller J., Wilson R., Storb U. Evolution of mouse immunoglobulin lambda genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4681–4685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S., Johnson A. H., Shearer G. M. Evidence for a new segregant series of B cell antigens that are encoded in the HLA-D region and that stimulate secondary allogenic proliferative and cytotoxic responses. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):565–580. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Moore K. W., Frelinger J. G., Sher B. T., Shen F. W., Boyse E. A., Hood L. A pseudogene homologous to mouse transplantation antigens: transplantation antigens are encoded by eight exons that correlate with protein domains. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):683–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanigaki N., Tosi R. The genetic control of human Ia alloantigens: a three-loci model derived from the immunochemical analysis of 'supertypic' specificities. Immunol Rev. 1982;66:5–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00432.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi R., Tanigaki N., Centis D., Ferrara G. B., Pressman D. Immunological dissection of human Ia molecules. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1592–1611. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Golden L., Zakut R., Mellor A., Fahrner K., Kvist S., Flavell R. A. The DNA sequence of the H-2kb gene: evidence for gene conversion as a mechanism for the generation of polymorphism in histocompatibilty antigens. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):453–462. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


