Abstract
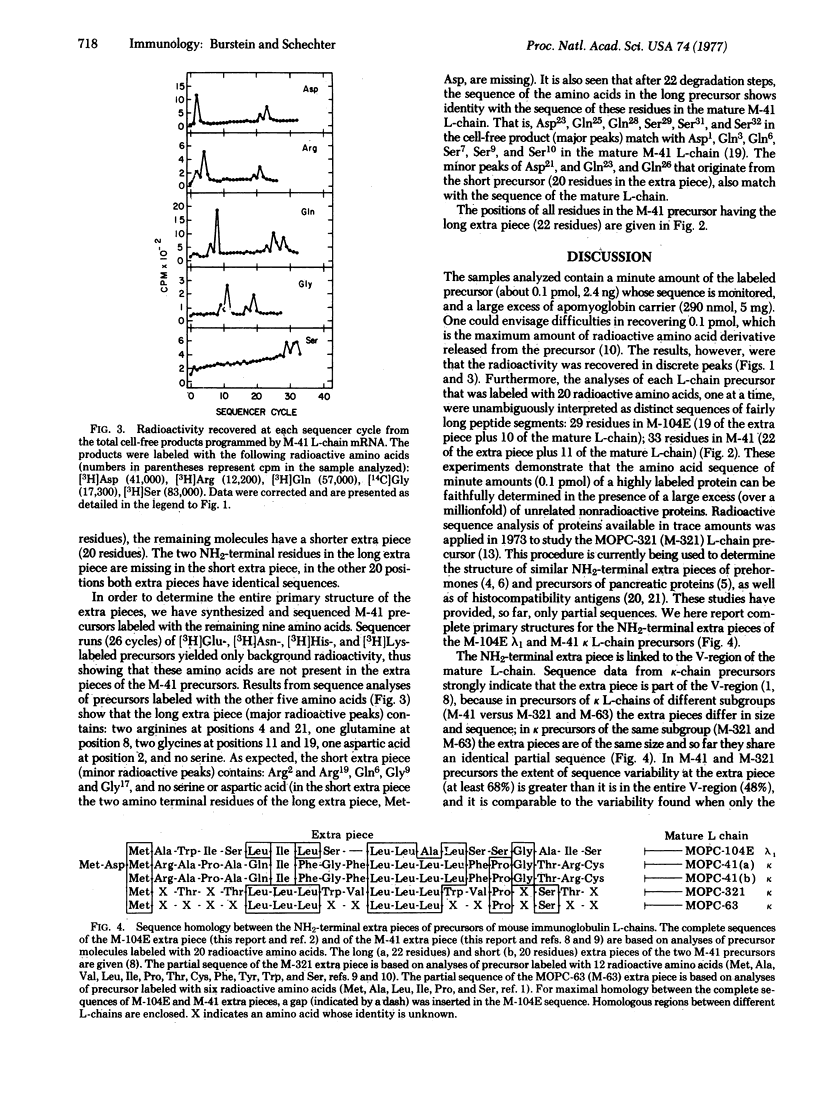
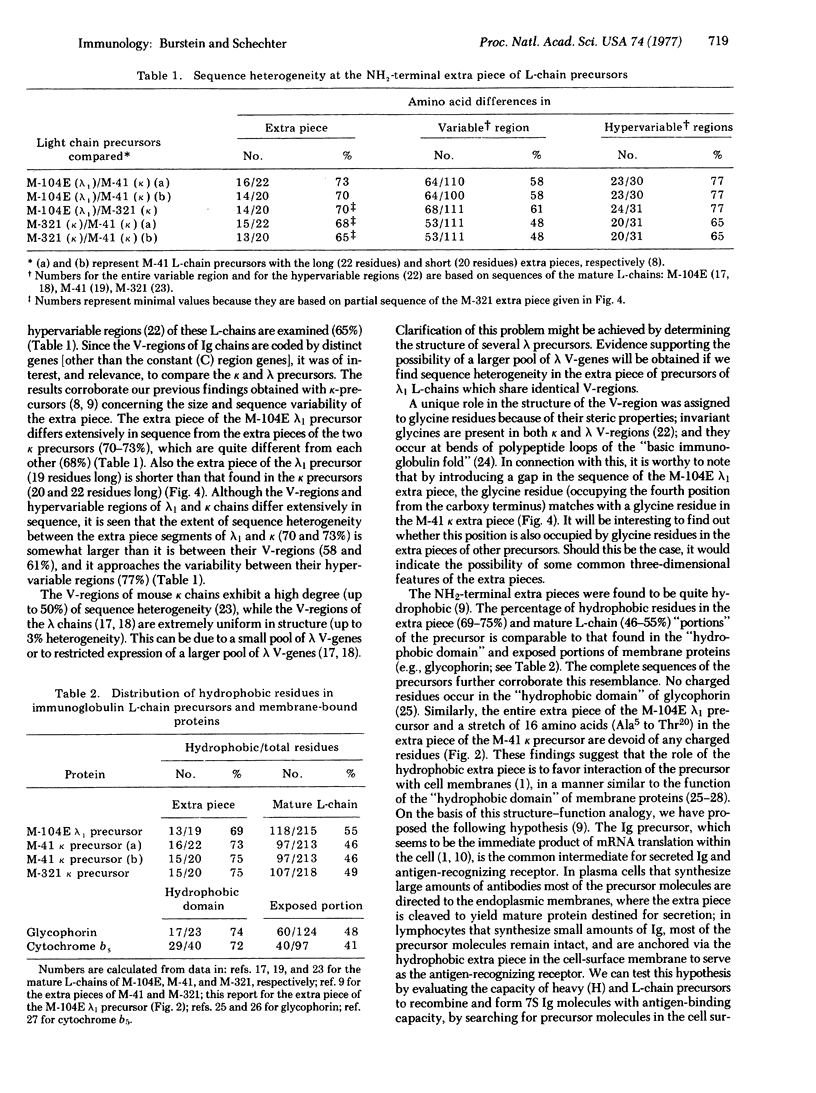
The mRNA molecules coding for mouse immunoglobulin light (L) chains direct the cell-free synthesis of precursors in which extra peptide segments precede the amino termini of the mature proteins. The results of amino acid sequence analyses of two precursors labeled with 20 radioactive amino acids enabled unambiguous determination of the complete primary structure of the extra piece segments. The complete sequences (and sizes) of the NH2-terminal extra pieces are: in MOPC-104E lambda1 L-chain precursor, Met-Ala-Trp-Ile-Ser-Leu-Ile-Leu-Ser-Leu-Leu-Ala-Leu-Ser-Ser-Gly-Ala-Ile-Ser (19 residues); in MOPC-41 kappa L-chain precursor, Met-Asp-Met-Arg-Ala-Pro-Ala-Gln-Ile-Phe-Gly-Phe-Leu-Leu-Leu-Leu-Phe-Pro-Gly-Thr-Arg-Cys (22 residues). The extra pieces in the precursors of MOPC-104E (lambda1), MOPC-41 (kappa), and MOPC-321 (kappa) L-chains differ extensively from each other in their amino acid sequence (65-73%). In addition to this sequence heterogeneity, the extra pieces are characterized by a high percentage of hydrophobic residues: 69% in the MOPC-104E lambda1 L-chain precursor (this report), 73-75% in the kappa L-chain precursors [Schechter, I. & Burstein, Y. (1976) Proc, Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 73, 3273-3277]. The marked hydrophobicity of the extra piece suggests that it may favor interaction of the precursor with cell membranes, in a manner similar to the function of the "hydrophobic domain" of membrane-bound proteins. We propose two possible targets for interaction: (i) the endoplasmic membranes, where the NH2-terminal extra piece is cleaved from the precursor to yield mature protein destined for secretion; (ii) the cell surface membrane, where the intact precursor is anchored by virtue of the hydrophobic extra piece to serve as the antigen-recognizing receptor.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appella E. Amino acid sequences of two mouse immunoglobulin lambda chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):590–594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S. C-terminal region of the major erythrocyte sialoglycoprotein is on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 15;98(4):831–833. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein Y., Kantour F., Schechter I. Partial amino-acid sequence of the precursor of an immunoglobulin light chain containing NH2-terminal pyroglutamic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2604–2608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein Y., Schechter I. Amino acid-sequence variability at the N-terminal extra piece of mouse immunoglobulin light-chain precursors of the same and different subgroups. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):145–151. doi: 10.1042/bj1570145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesari I. M., Weigert M. Mouse lambda-chain sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2112–2116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. J., Keim P., Steiner D. F. Cell-free synthesis of rat preproinsulins: characterization and partial amino acid sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1964–1968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devillers-Thiery A., Kindt T., Scheele G., Blobel G. Homology in amino-terminal sequence of precursors to pancreatic secretory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5016–5020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. R., Dreyer W. J., Hood L. Mechanism of antibody synthesis: size differences between mouse kappa chains. Science. 1967 Jan 27;155(3761):465–467. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3761.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habener J. F., Potts J. T., Jr, Rich A. Pre-proparathyroid hormone. Evidence for an early biosynthetic precursor of proparathyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 10;251(13):3893–3899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning R., Milner R. J., Reske K., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Subunit structure, cell surface orientation, and partial amino-acid sequences of murine histocompatibility antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):118–122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Housman D., Jacobs-Lorena M., Rajbhandary U. L., Lodish H. F. Initiation of haemoglobin synthesis by methionyl-tRNA. Nature. 1970 Aug 29;227(5261):913–918. doi: 10.1038/227913a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper B., Habener J. F., Ernst M. D., Potts J. T., Jr, Rich A. Pre-proparathyroid hormone: analysis of radioactive tryptic peptides and amino acid sequence. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 13;15(1):15–19. doi: 10.1021/bi00646a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKean D., Potter M., Hood L. Mouse immunoglobulin chains. Pattern of sequence variation among kappa chains with limited sequence differences. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):760–771. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C., Brownlee G. G., Harrison T. M., Mathews M. B. A possible precursor of immunoglobulin light chains. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 27;239(91):117–120. doi: 10.1038/newbio239117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poljak R. J. Three-dimensional structure, function and genetic control of immunoglobulins. Nature. 1975 Jul 31;256(5516):373–376. doi: 10.1038/256373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I. Biologically and chemically pure mRNA coding for a mouse immunoglobulin L-chain prepared with the aid of antibodies and immobilized oligothymidine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2256–2260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Burstein Y. Identification of N-terminal methionine in the precursor of immunoglobulin light chain. Initiation of translation of messenger ribonucleic acid in plants and animals. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 1;153(3):543–550. doi: 10.1042/bj1530543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Burstein Y. Marked hydrophobicity of the NH2-terminal extra piece of immunoglobulin light-chain precursors: possible physiological functions of the extra piece. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3273–3277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Burstein Y. Partial sequence of the precursors of immunoglobulin light-chains of different subgroups: evidence that the immunoglobulin variable-region gene is larger than hitherto known. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jan 26;68(2):489–496. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I. Partial amino acid sequence of the precursor of immunoglobulin light chain programmed by messenger RNA in vitro. Science. 1975 Apr 11;188(4184):160–162. doi: 10.1126/science.803715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I. Use of antibodies for the isolation of biologically pure messenger ribonucleic acid from fully functional eukaryotic cells. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 23;13(9):1875–1885. doi: 10.1021/bi00706a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segrest J. P., Jackson R. L., Marchesi V. T., Guyer R. B., Terry W. Red cell membrane glycoprotein: amino acid sequence of an intramembranous region. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 15;49(4):964–969. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segrest J. P., Kahane I., Jackson R. L., Marchesi V. T. Major glycoprotein of the human erythrocyte membrane: evidence for an amphipathic molecular structure. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Mar;155(1):167–183. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(73)80019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spatz L., Strittmatter P. A form of cytochrome b5 that contains an additional hydrophobic sequence of 40 amino acid residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):1042–1046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Capra J. D., Klapper D. G., Klein J., Uhr J. W. The partial amino-acid sequence of an H-2K molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):905–909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Kabat E. A. An analysis of the sequences of the variable regions of Bence Jones proteins and myeloma light chains and their implications for antibody complementarity. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):211–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


