Abstract
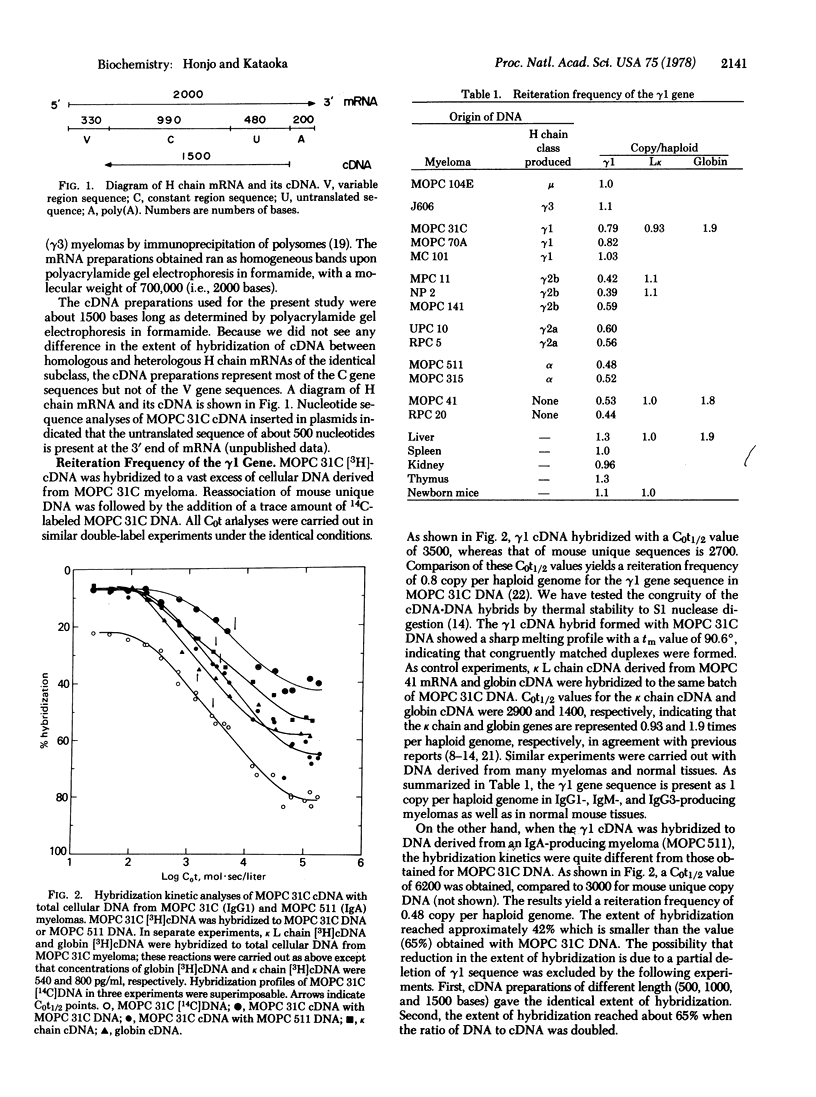
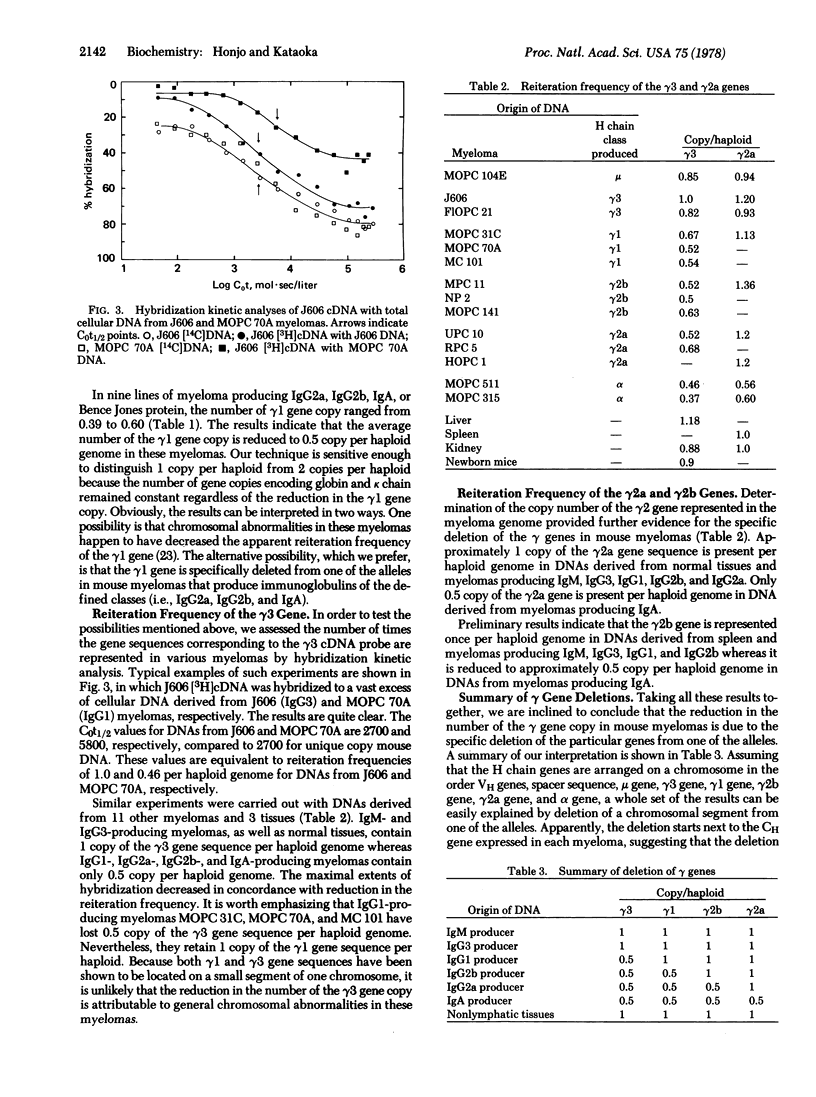
We have assessed the number of times the gene sequence encoding constant regions of mouse immunoglobulin heavy chains gamma1, gamma2a, and gamma3 are represented in the mouse genome by hybridization kinetic analysis. All three genes are present at one copy each per haploid genome in normal tissues and myelomas producing IgM or IgG3. IgG1-producing myelomas, however, contain 1 copy each of the gamma1 and gamma2a genes and 0.5 copy of the gamma3 gene per haploid genome. IgG2b-producing myelomas contain 1 copy of the gamma2a gene and 0.5 copy each of the gamma1 and gamma3 genes per haploid genome. IgG2a-producing myelomas contain 1 copy of the gamma2a gene and 0.5 copy each of the gamma1 and gamma3 genes per haploid genome. In myelomas producing IgA, all three gamma genes are represented 0.5 times per haploid genome. In order to account for the results we propose an allelic deletion model: (i) The specific deletion of heavy chain constant region genes accompanies the recombination of a variable region gene to a constant region gene. (ii) The portion of the chromosome that resides between two joining sequences is excised out of the chromosome. (iii) The recombination occurs on one of the alleles. Based on this model we also propose that heavy chain genes are arranged on one chromosome in the following order; variable region genes, unknown spacer sequence, mu, gamma3, gamma1, gamma2b, gamma2a, and alpha.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernardini A., Tonegawa S. Hybridization studies with an antibody heavy chain mRNA. FEBS Lett. 1974 Apr 15;41(1):73–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80957-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Kohne D. E. Repeated sequences in DNA. Hundreds of thousands of copies of DNA sequences have been incorporated into the genomes of higher organisms. Science. 1968 Aug 9;161(3841):529–540. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3841.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebra J. J., Colberg J. E., Dray S. Rabbit lymphoid cells differentiated with respect to alpha-, gamma-, and mu- heavy polypeptide chains and to allotypic markers Aa1 and Aa2. J Exp Med. 1966 Mar 1;123(3):547–558. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.3.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan N. J., Milstein C. Stability of cytoplasmic ribonucleic acid in a mouse myeloma: estimation of the half-life of the messenger RNA coding for an immunoglobulin light chain. J Mol Biol. 1974 Feb 5;82(4):469–481. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90242-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer W. J., Bennett J. C. The molecular basis of antibody formation: a paradox. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):864–869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farace M. G., Aellen M. F., Briand P. A., Faust C. H., Vassalli P., Mach B. No detectable reiteration of genes coding for mouse MOPC 41 immunoglobulin light-chain mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):727–731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust C. H., Diggelmann H., Mach B. Estimation of the number of genes coding for the constant part of the mouse immunoglobulin kappa light chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2491–2495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fudenberg H. H., Wang A. C., Pink J. R., Levin A. S. Studies of an unusual biclonal gammopathy: implications with regard to genetic control of normal immunoglobulin synthesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Dec 31;190:501–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb13559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gally J. A., Edelman G. M. Somatic translocation of antibody genes. Nature. 1970 Jul 25;227(5256):341–348. doi: 10.1038/227341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Packman S. Quantitation of constant and variable region genes for mouse immunoglobulin lambda chains. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2780–2785. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Packman S., Swan D., Nau M., Leder P. Organization of immunoglobulin genes: reiteration frequency of the mouse kappa chain constant region gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3659–3663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. P., Tacier-Eugster H., Herzenberg L. A. Lymphocyte commitment to Ig allotype and class. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1974 Jan;125C(1-2):271–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat D. Gene selection in hemoglobin and in antibody-synthesizing cells. Science. 1972 Jan 14;175(4018):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4018.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincade P. W., Lawton A. R., Bockman D. E., Cooper M. D. Suppression of immunoglobulin G synthesis as a result of antibody-mediated suppression of immunoglobulin M synthesis in chickens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1918–1925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindt T. J., Mandy W. J. Recombination of genes coding for constant and variable regions of immunoglobulin heavy chains. J Immunol. 1972 Apr;108(4):1110–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindt T. J., Mandy W. J., Todd C. W. Association of allotypic specificities of group a with allotypic specificities A11 and A12 in rabbit immunoglobulin. Biochemistry. 1970 Apr 28;9(9):2028–2032. doi: 10.1021/bi00811a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Honjo T., Seidman J., Swan D. Origin of immunoglobulin gene diversity: the evidence and a restriction-modification model. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):855–862. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman R., Potter M. Close linkage in genes controlling gamma-A and gamma-G heavy chain structure in BALB/c mice. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jul;18(3):516–528. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80040-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman R., Potter M. Crossing over between genes in the immunoglobulin heavy chain linkage group of the mouse. J Exp Med. 1969 Sep 1;130(3):519–541. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.3.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mage R. G., Young-Cooper G. O., Alexander C. Genetic control of variable and constant regions of immunoglobulin heavy chains. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 10;230(10):63–64. doi: 10.1038/newbio230063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monahan J. J., Harris S. E., Woo S. L., Robberson D. L., O'Malley B. W. The synthesis and properties of the complete complementary DNA transcript of ovalbumin mRNA. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 13;15(1):223–233. doi: 10.1021/bi00646a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä O., Cross A. M. The diversity and specialization of immunocytes. Prog Allergy. 1970;14:145–207. doi: 10.1159/000289379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Kondo T., Kawakami M., Honjo T. Purification of immunoglobulin heavy chain messenger RNA by immunoprecipitation from the mouse myeloma tumor, MOPC-31C. J Biochem. 1977 Apr;81(4):949–954. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman S., Aviv H., Ross J., Leder P. A comparison of globin genes in duck reticulocytes and liver cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 1;49(3):813–819. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90483-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkhouse R. M., Abney E. R., Bourgois A., Willcox H. N. Functional and structural characterization of immunoglobulin on murine B lymphocytes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 1):193–200. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernis B., Chiappino G., Kelus A. S., Gell P. G. Cellular localization of immunoglobulins with different allotypic specificities in rabbit lymphoid tissues. J Exp Med. 1965 Nov 1;122(5):853–876. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.5.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernis B., Forni L., Luzzati A. L. Synthesis of multiple immunoglobulin classes by single lymphocytes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 1):175–183. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce C. W., Solliday S. M., Asofsky R. Immune responses in vitro. IV. Suppression of primary M, G, and A plaque-forming cell responses in mouse spleen cell cultures by class-specific antibody to mouse immunoglobulins. J Exp Med. 1972 Mar 1;135(3):675–697. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M., Lieberman R. Genetics of immunoglobulins in the mouse. Adv Immunol. 1967;7:91–145. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60127-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premkumar E., Shoyab M., Williamson A. R. Germ line basis for antibody diversity: immunoglobulin VH-and CH-gene frequencies measured by DNA-RNA hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):99–103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preud'Homme J. L., Birshtein B. K., Scharff M. D. Variants of a mouse myeloma cell line that synthesize immunoglobulin heavy chains having an altered serotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1427–1430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Jarvis J. M., Milstein C. Demonstration that a mouse immunoglobulin light chain messenger RNA hybridizes exclusively with unique DNA. Cell. 1975 Sep;6(1):5–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90067-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sledge C., Fair D. S., Black B., Krueger R. G., Hood L. Antibody differentiation: apparent sequence identity between variable regions shared by IgA and IgG immunoglobulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):923–927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavnezer J., Huang R. C., Stavnezer E., Bishop J. M. Isolation of messenger RNA for an immunoglobulin kappa chain and enumeration of the genes for the constatn region of kappa chain in the mouse. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 5;88(1):43–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90294-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S., Hozumi N., Matthyssens G., Schuller R. Somatic changes in the content and context of immunoglobulin genes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):877–889. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Reiteration frequency of immunoglobulin light chain genes: further evidence for somatic generation of antibody diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):203–207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S., Steinberg C., Dube S., Bernardini A. Evidence for somatic generation of antibody diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4027–4031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi S. L., Dubiski S., Mage R. G. Distribution of allotypic specificities A1, A2, A14, and A15 among immunoglobulin G molecules. J Immunol. 1970 Mar;104(3):641–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Cambier J., Forman J., Kettman J. R., Yuan D., Uhr J. W. Immunoglobulin receptors on murine B lymphocytes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 1):185–191. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. C., Gergely J., Fudenberg H. H. Amino acid sequences at constant and variable regions of heavy chains of monotypic immunoglubulins G and M of a single patient. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 30;12(3):528–534. doi: 10.1021/bi00727a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yosida T. H., Imai H. T., Potter M. Chromosomal alteration and development of tumors. XIX. Chromosome constitution of tumor cells in 16 plasma cell neoplasms of BALB-c mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Nov;41(5):1083–1097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


