Abstract
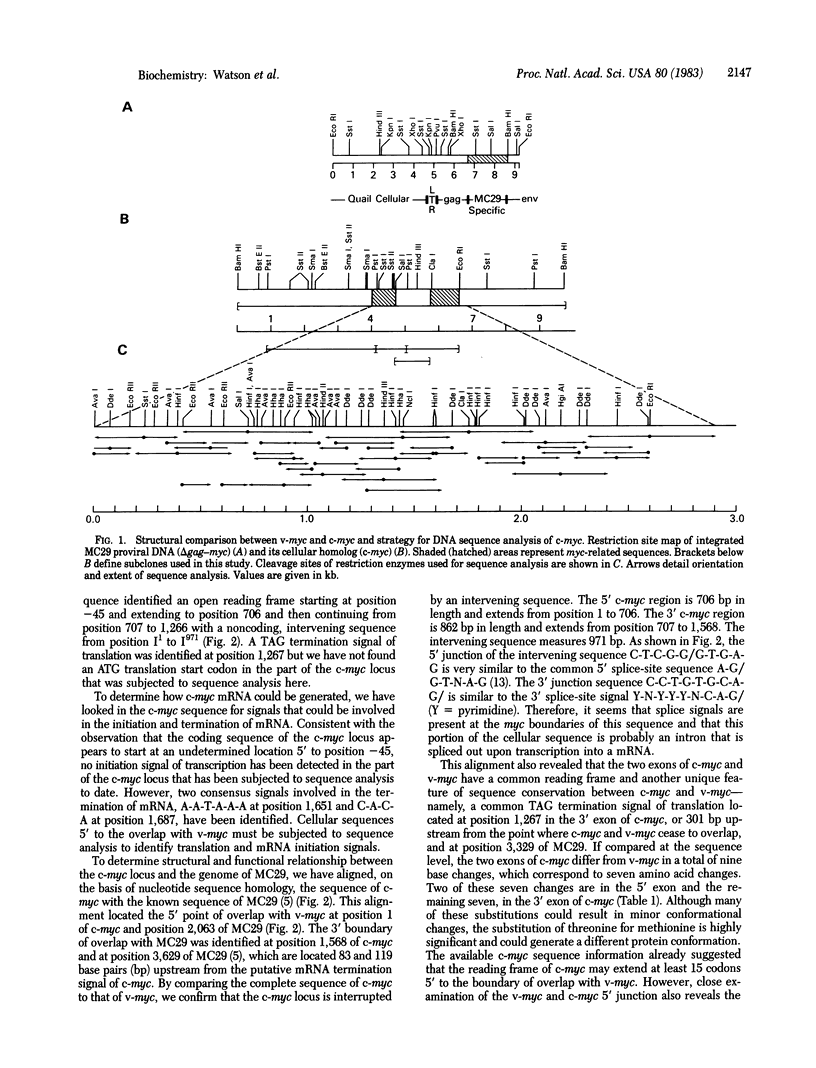
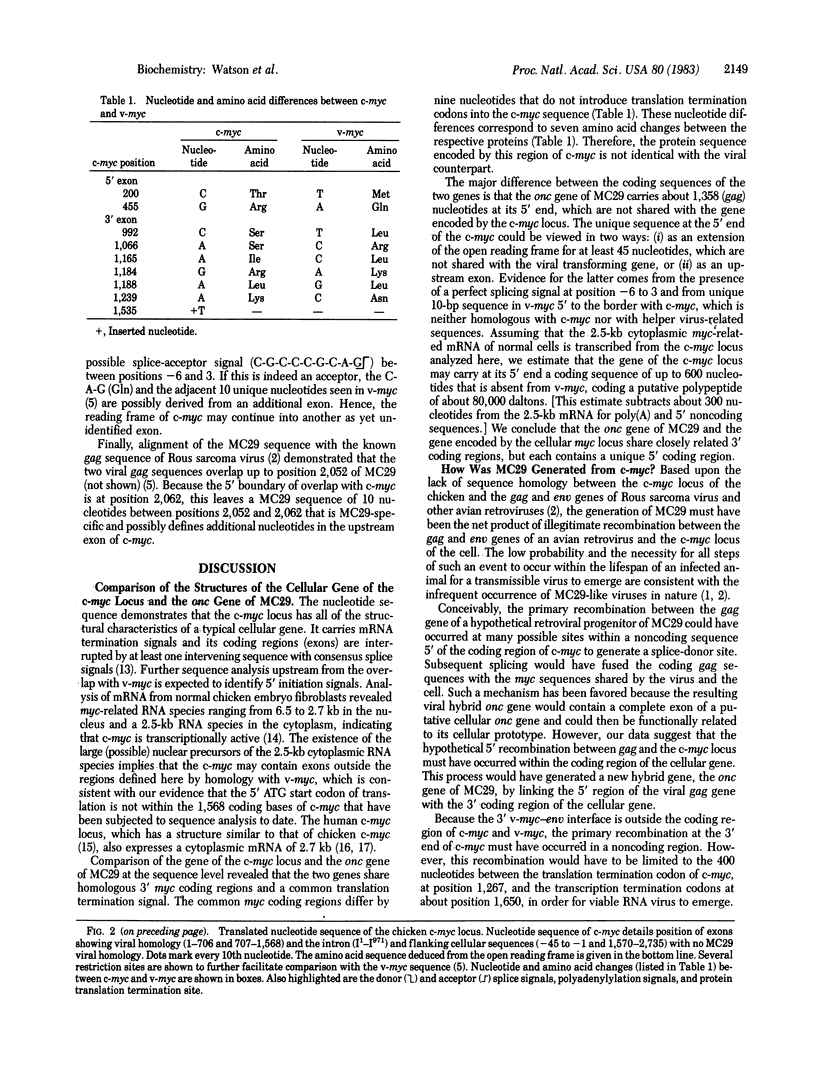
Myelocytomatosis virus MC29 is a defective avian retrovirus with a hybrid transforming gene (delta gag-myc) consisting of a 1,358-base pair (bp) sequence from the retroviral gag gene and a 1,568-bp sequence (v-myc) shared with a cellular locus, termed c-myc. We have subjected to sequence analysis 2,735 bp of the cloned c-myc gene, which includes the v-myc-related region of 1,568 bp, an intervening sequence of 971 bp, and unique flanking sequences of 45 bp and 195 bp at the 5' and 3' ends, respectively. Analysis of the genetic information and alignment of the c-myc sequence with the known sequence of MC29 indicates that: (i) the two myc sequences share the same reading frame, including the translational termination signal; (ii) there are nine nucleotide changes between c-myc and v-myc that correspond to seven amino acid changes; (iii) the 971-bp intervening sequence of c-myc can be defined as an intron by consensus splice signals; (iv) the unique 5' sequence of c-myc could either extend its reading frame beyond the homology with v-myc or could be an intron because its junction with the myc region of the locus is a canonical 3' splice-acceptor site; (v) the v-myc contains 10 nucleotides at its 5' end not shared with the c-myc analyzed here and also not with known gag genes, probably derived from an upstream exon; and (vi) the c-myc locus can generate a mRNA whose termination signals have been identified to be located 83 bp and 119 bp from the point of divergence between the v-myc and c-myc. We conclude that the gene of the c-myc locus of the chicken and the onc gene of MC29 share homologous myc regions and differ in unique 5' coding regions and we speculate, on this basis, that their protein products may have different functions. The hybrid onc gene of MC29 must have been generated from the c-myc gene by deletion of the 5' cellular coding sequence, followed by substitution with the 5' region of the viral gag gene.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams H. D., Rohrschneider L. R., Eisenman R. N. Nuclear location of the putative transforming protein of avian myelocytomatosis virus. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):427–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90159-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Enemies within: the genesis of retrovirus oncogenes. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Hayman M. J., Vogt P. K. Defectiveness of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29: isolation of long-term nonproducer cultures and analysis of virus-specific polypeptide synthesis. Virology. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):431–448. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Lee W. H., Duesberg P. H. Phosphorylation of the nonstructural proteins encoded by three avian acute leukemia viruses and by avian fujinami sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):617–621. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.617-621.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. M., Neiman P. E. Two distinct candidate transforming genes of lymphoid leukosis virus-induced neoplasms. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):857–858. doi: 10.1038/292857a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Gelmann E. P., Martinotti S., Franchini G., Papas T. S., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Cloning and characterization of different human sequences related to the onc gene (v-myc) of avian myelocytomatosis virus (MC29). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6497–6501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner P., Greiser-Wilke I., Moelling K. Nuclear localization and DNA binding of the transforming gene product of avian myelocytomatosis virus. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):262–269. doi: 10.1038/296262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eva A., Robbins K. C., Andersen P. R., Srinivasan A., Tronick S. R., Reddy E. P., Ellmore N. W., Galen A. T., Lautenberger J. A., Papas T. S. Cellular genes analogous to retroviral onc genes are transcribed in human tumour cells. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):116–119. doi: 10.1038/295116a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lautenberger J. A., Schulz R. A., Garon C. F., Tsichlis P. N., Papas T. S. Molecular cloning of avian myelocytomatosis virus (MC29) transforming sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1518–1522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Pawson A., Bister K., Martin G. S., Duesberg P. H. Specific RNA sequences and gene products of MC29 avian acute leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5874–5878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel B. G., Gasic G. P., Rogler C. E., Skalka A. M., Ju G., Hishinuma F., Papas T., Astrin S. M., Hayward W. S. Molecular analysis of the c-myc locus in normal tissue and in avian leukosis virus-induced lymphomas. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):158–166. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.158-166.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G. S., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Multiple arrangements of viral DNA and an activated host oncogene in bursal lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):209–214. doi: 10.1038/295209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins T., Bister K., Garon C., Papas T., Duesberg P. Structural relationship between a normal chicken DNA locus and the transforming gene of the avian acute leukemia virus MC29. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):635–642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.635-642.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow K. E., Lautenberger J. A., Papas T. S., Baluda M. A., Perbal B., Chirikjian J. G., Reddy E. P. Nucleotide sequence of the transforming gene of avian myeloblastosis virus. Science. 1982 Jun 25;216(4553):1421–1423. doi: 10.1126/science.6283631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Speculations on RNA splicing. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):643–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90425-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shilo B. Z., Weinberg R. A. DNA sequences homologous to vertebrate oncogenes are conserved in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6789–6792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennstrom B., Sheiness D., Zabielski J., Bishop J. M. Isolation and characterization of c-myc, a cellular homolog of the oncogene (v-myc) of avian myelocytomatosis virus strain 29. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):773–779. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.773-779.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin E. H., Wong-Staal F., Gelmann E. P., Dalla-Favera R., Papas T. S., Lautenberger J. A., Eva A., Reddy E. P., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Expression of cellular homologues of retroviral onc genes in human hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2490–2494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


