Abstract
We have determined the cDNA sequence corresponding to chicken muscle pyruvate kinase mRNA; the predicted coding region spans 529 amino acids and establishes the complete amino acid sequence for the vertebrate enzyme. We demonstrate that the level of mRNA for this enzyme is under developmental control and suggest a structural model for the protein kinase-mediated regulation of the mammalian liver isozyme. We report a method for the direct analysis of, and the preparation of cDNA probes from, mRNA which has been fractionated on methylmercury/agarose gels.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERER F. A., UHLIG H., WEBER E., SCHRAMM G. Primary structure of the protein of tobacco mosaic virus. Nature. 1960 Jun 18;186:922–925. doi: 10.1038/186922a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P. J., Randall R. F. Comparison of the subunit and primary structures of the pyruvate kinases from rabbit and sturgeon muscles. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;145(3):575–579. doi: 10.1042/bj1450575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummel M. C., Boaz D. P., Flashner M., Stegink L. D. Rabbit muscle pyruvate kinase. Amino- and carboxyl-terminal studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 7;438(1):102–107. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90226-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. L., Tekamp-Olson P., Najarian R. The isolation, characterization, and sequence of the pyruvate kinase gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2193–2201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas J. M., Bandman E., Walker C., Strohman R. C. Pyruvate kinase isozymic shifts of differentiating chick myogenic cells in vivo and in culture. Dev Biol. 1979 Jan;68(1):326–333. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90266-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas J. M., Blachly E. G., Ceccotti P. L., Dyson R. D. Properties of chicken skeletal muscle pyruvate kinase and a proposal for its evolutionary relationship to the other avian and mammalian isozymes. Biochemistry. 1975 May 20;14(10):2247–2252. doi: 10.1021/bi00681a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. L., Lifton R. P., Stark G. R., Williams J. G. Isolation of specific RNA's using DNA covalently linked to diazobenzyloxymethyl cellulose or paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:206–220. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilley H., Jonard G., Kukla B., Richards K. E. Sequence of 1000 nucleotides at the 3' end of tobacco mosaic virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Apr;6(4):1287–1308. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.4.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall E. R., Kohl E. A., Cottam G. L. The subunit structure of rat liver pyruvate kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 14;80(3):586–592. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91609-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkins R. N., Black J. A., Rittenberg M. B. M2 isozyme of pyruvate kinase from human kidney as the product of a separate gene: its purification and characterization. Biochemistry. 1977 Aug 23;16(17):3831–3837. doi: 10.1021/bi00636a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humble E. Amino acid sequence around the phosphorylated sites of porcine and rat liver pyruvate kinase, type L. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 20;626(1):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90209-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibsen K. H. Interrelationships and functions of the pyruvate kinase isozymes and their variant forms: a review. Cancer Res. 1977 Feb;37(2):341–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. C., Bailey T., Becker R. R., Cardenas J. M. Isolation and sequence determination of a peptide located in or near the active site of bovine muscle pyruvate kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 27;90(2):525–530. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Grez M., Hauser H., Lindenmaier W., Schütz G. 5'-Terminal sequences of eucaryotic mRNA can be cloned with high efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2251–2266. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P. T., Saunders G. F. Preparation of pancreatic mRNA: cell-free translation of an insulin-immunoreactive polypeptide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Feb;3(2):381–391. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. J., Bulfield G. An allele (Pk-1b) from wild-caught mice that affects the activity and kinetics of erythrocyte and liver pyruvate kinase. Biochem Genet. 1981 Aug;19(7-8):771–781. doi: 10.1007/BF00484008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J., Nash H. R., Eicher E. M., Bulfield G. Polymorphism of kidney pyruvate kinase in the mouse is determined by a gene, Pk-3, on chromosome 9. Biochem Genet. 1981 Aug;19(7-8):757–769. doi: 10.1007/BF00484007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riou J. P., Claus T. H., Pilkis S. J. Stimulation of glucagon of in vivo phosphorylation of rat hepatic pyruvate kinase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):656–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury R., Jay E., Wu R. Terminal labeling and addition of homopolymer tracts to duplex DNA fragments by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Apr;3(4):863–877. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.4.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
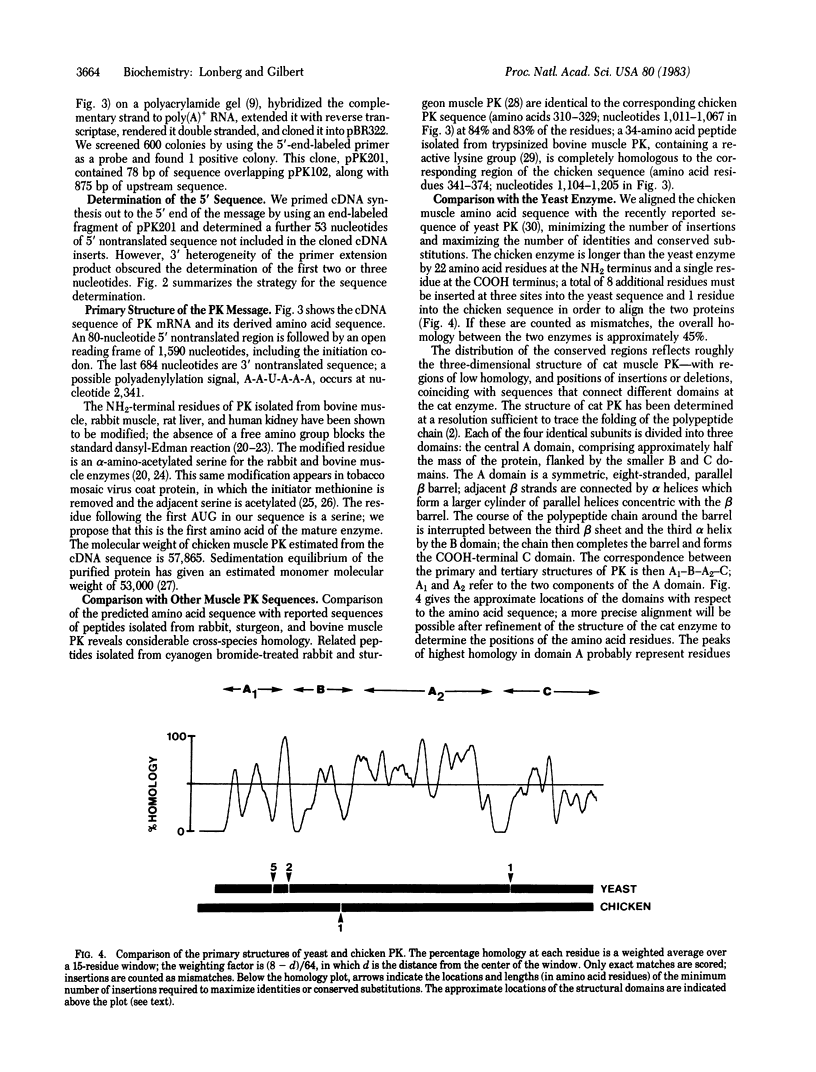
- Stuart D. I., Levine M., Muirhead H., Stammers D. K. Crystal structure of cat muscle pyruvate kinase at a resolution of 2.6 A. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 15;134(1):109–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90416-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa-Komaroff L., Efstratiadis A., Broome S., Lomedico P., Tizard R., Naber S. P., Chick W. L., Gilbert W. A bacterial clone synthesizing proinsulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3727–3731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M. P., Buell G. N., Schimke R. T. Synthesis of double-stranded DNA complementary to lysozyme, ovomucoid, and ovalbumin mRNAs. Optimization for full length second strand synthesis by Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2483–2495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]