Abstract
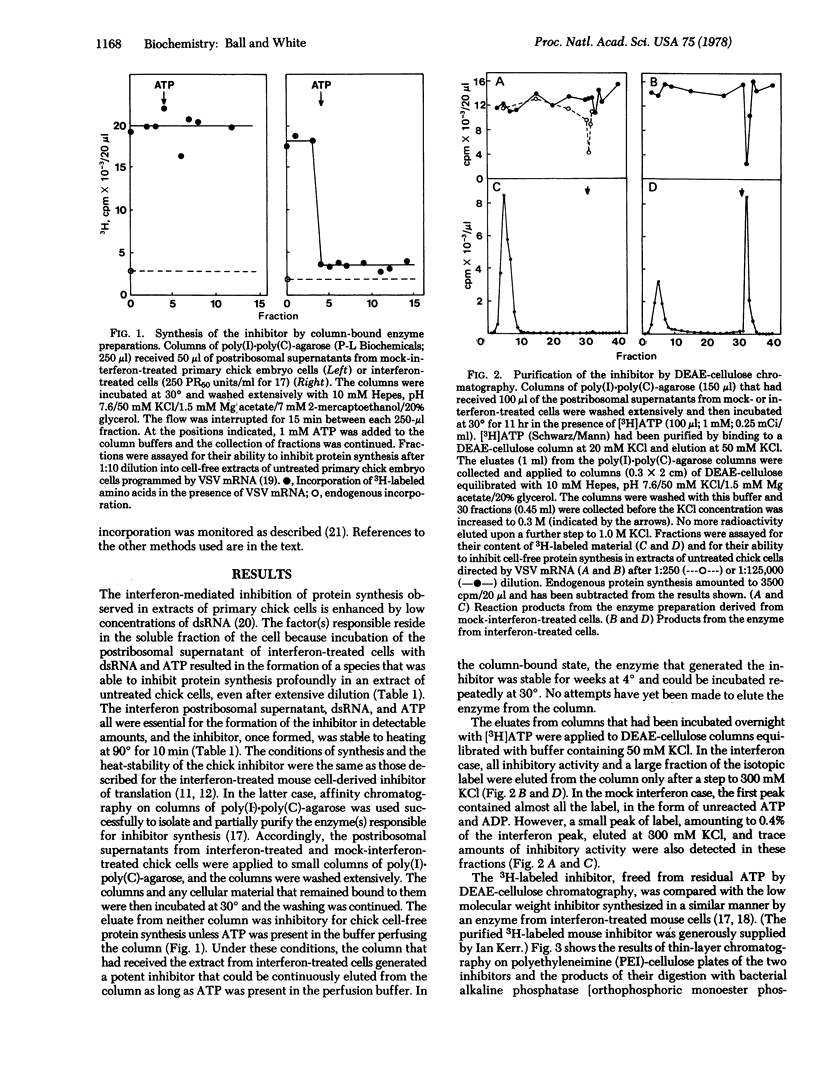
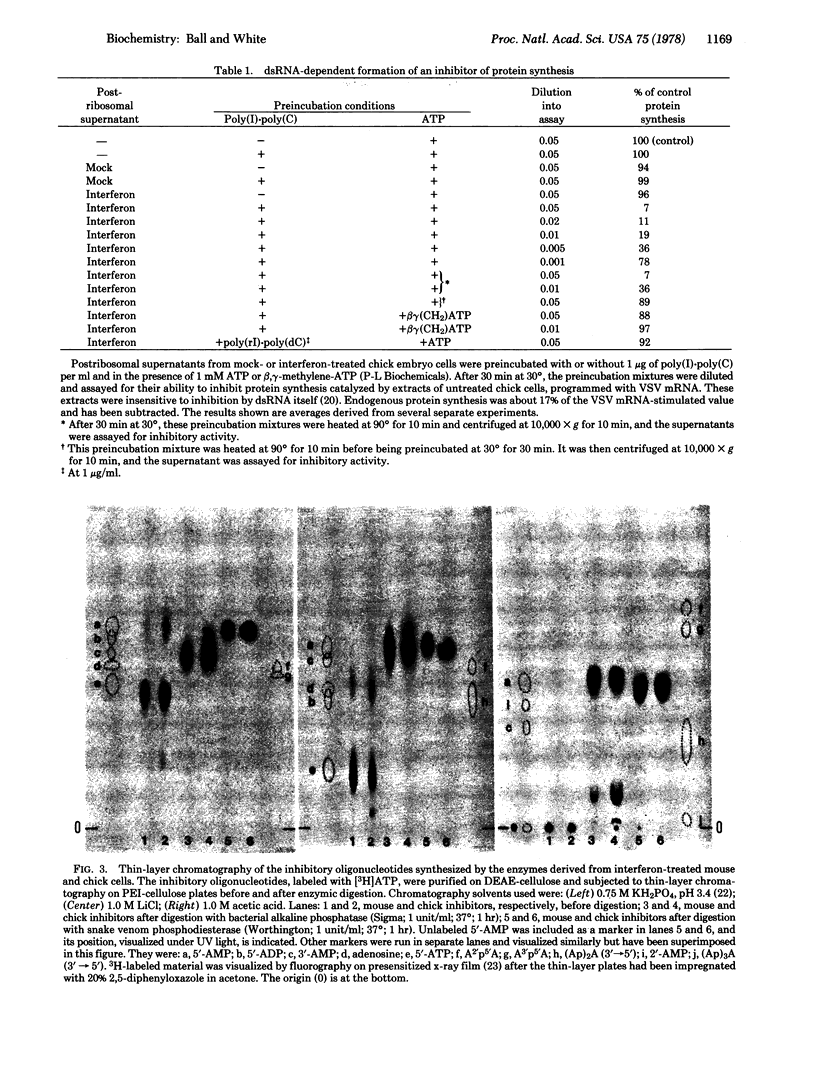
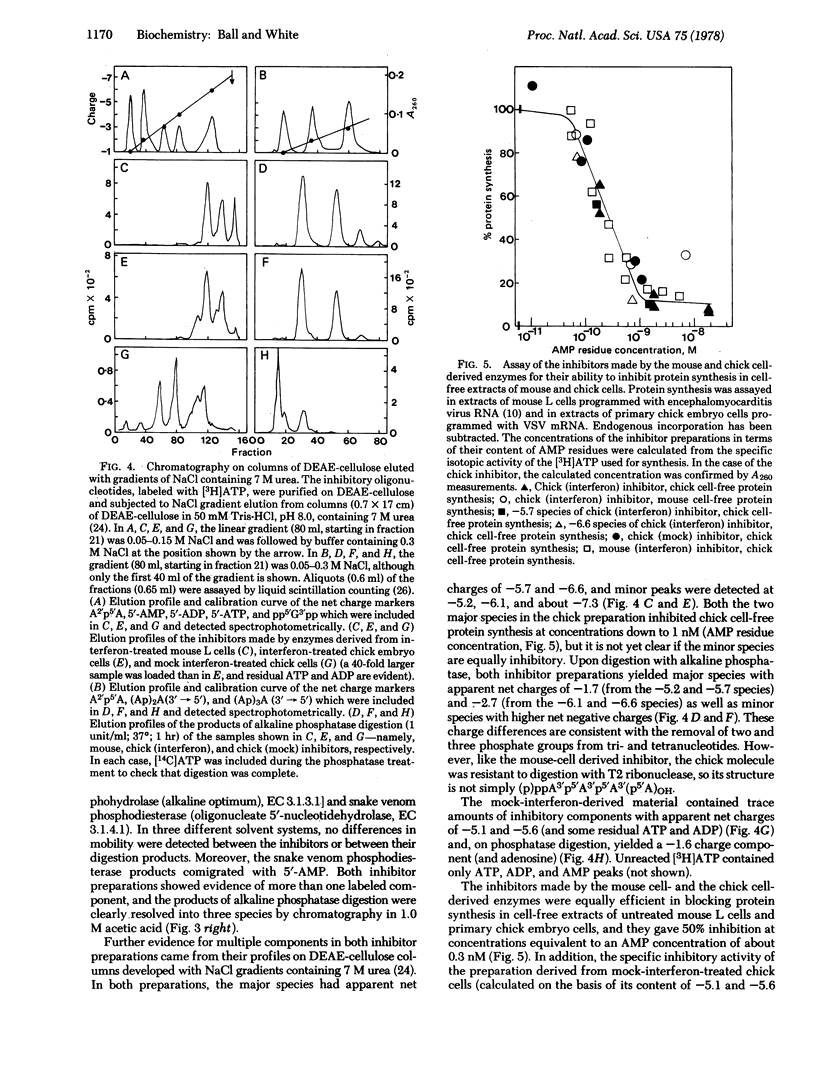
Cytoplasmic extracts of interferon-treated primary chick embryo cells contain an enzyme activity that synthesized an inhibitor of chick cell-free protein synthesis. The same activity was detected in extracts of cells treated with mock preparations of interferon, but at <0.3% of the level found in interferon-treated cell extracts. The enzyme was activated by double-stranded RNA and could be isolated by binding to columns of poly(I)-poly(C)-agarose. In the column-bound state, the enzyme reacted with ATP to synthesize the inhibitor, which could then be continuously eluted from the column. The inhibitor was purified and its structure and function were compared with those of the low molecular weight inhibitor of protein synthesis made by an enzyme from interferon-treated mouse L cells. The avian and mammalian inhibitors comigrated on thin layers of polyethyleneimine-cellulose during chromatography in three different solvent systems, and they coeluted as a series of peaks from columns of DEAE-cellulose during sodium chloride gradient elution. Digestion with bacterial alkaline phosphatase or snake venom phosphodiesterase yielded products that similarly comigrated. Functionally, the two inhibitors were interchangeable: both inhibited protein synthesis in extracts of mammalian and avian cells, producing 50% inhibition at a concentration of about 0.3 nM (AMP equivalents). We conclude that the chick cell-derived oligonucleotide inhibitor has a structure that is closely related or identical to that of the inhibitor made in the mouse system, and that both preparations inhibit cell-free protein synthesis in a non-species-specific manner.
Keywords: mechanism of interferon action, double-stranded RNA, avian cell-free systems
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball L. A., White C. N. Order of transcription of genes of vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):442–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A. K., Shatkin A. J. Guanosine-5'-diphosphate at the 5' termini of reovirus RNA: evidence for a segmented genome within the virion. J Mol Biol. 1971 Nov 14;61(3):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. E., Lebleu B., Kawakita M., Shaila S., Sen G. C., Lengyel P. Increased endonuclease activity in an extract from mouse Ehrlich ascites tumor cells which had been treated with a partially purified interferon preparation: dependence of double-stranded RNA;. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 8;69(1):114–122. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashel M., Lazzarini R. A., Kalbacher B. An improved method for thin-layer chromatography of nucleotide mixtures containing 32P-labelled orthophosphate. J Chromatogr. 1969 Mar 11;40(1):103–109. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)96624-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Content J., Lebleu B., Nudel U., Zilberstein A., Berissi H., Revel M. Blocks in elongation and initiation of protein synthesis induced by interferon treatment in mouse L cells. Eur J Biochem. 1975 May;54(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN R. M., SONNABEND J. A. INHIBITION OF INTERFERON ACTION BY P-FLUOROPHENYLALANINE. Nature. 1964 Jul 25;203:366–367. doi: 10.1038/203366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcoff E., Falcoff R., Lebleu B., Revel M. Correlation between the antiviral effect of interferon treatment and the inhibition of in vitro mRNA translation in noninfected L cells. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):421–430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.421-430.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Metz D. H., Esteban R. M., Tovell D. R., Ball L. A., Kerr I. M. Mechanism of interferon action: inhibition of viral messenger ribonucleic acid translation in L-cell extracts. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1184–1198. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1184-1198.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. L., Sopori M. L., Lengyel P. Inhibition of protein synthesis directed by added viral and cellular messenger RNAs in extracts of interferon-treated Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Location and dominance of the inhibitor(s). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Sep 18;54(2):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91491-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M., Armstrong J. A. Interferon. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:131–161. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Brown R. E., Ball L. A. Increased sensitivity of cell-free protein synthesis to double-stranded RNA after interferon treatment. Nature. 1974 Jul 5;250(461):57–59. doi: 10.1038/250057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Brown R. E., Hovanessian A. G. Nature of inhibitor of cell-free protein synthesis formed in response to interferon and double-stranded RNA. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):540–542. doi: 10.1038/268540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Brown R. E. pppA2'p5'A2'p5'A: an inhibitor of protein synthesis synthesized with an enzyme fraction from interferon-treated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):256–260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebleu B., Sen G. C., Shaila S., Cabrer B., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA, and protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3107–3111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D. P., Moyer S. A., Banerjee A. K. In vitro synthesis of methylated messenger RNA by the virion-associated RNA polymerase of vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1974 Dec;3(4):327–333. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. K., Clemens M. J., Kerr I. M. Interferon-induced inhibition of protein synthesis in L-cell extracts: an ATP-dependent step in the activation of an inhibitor by double-stranded RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3136–3140. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. K., Hovanessian A., Brown R. E., Clemens M. J., Kerr I. M. Interferon-mediated protein kinase and low-molecular-weight inhibitor of protein synthesis. Nature. 1976 Dec 2;264(5585):477–480. doi: 10.1038/264477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E., Joklik W. K. A protein synthesizing system from interferon-treated cells that discriminates between cellular and viral messenger RNAs. Virology. 1974 Apr;58(2):476–491. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90082-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Lebleu B., Brown G. E., Kawakita M., Slattery E., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA and mRNA degradation. Nature. 1976 Nov 25;264(5584):370–373. doi: 10.1038/264370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. Inhibition of interferon action by actinomycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964;14:447–451. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein A., Federman P., Shulman L., Revel M. Specific phosphorylation in vitro of a protein associated with ribosomes of interferon-treated mouse L cells. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 15;68(1):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80418-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



