Abstract
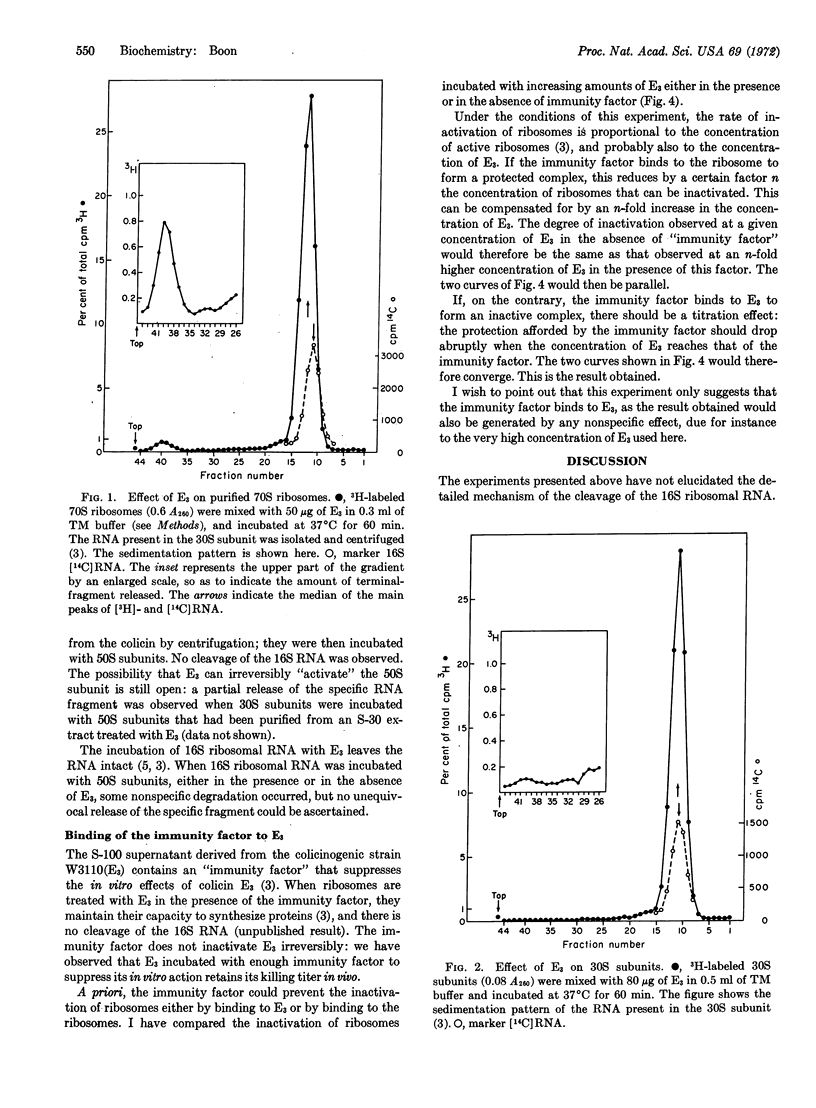
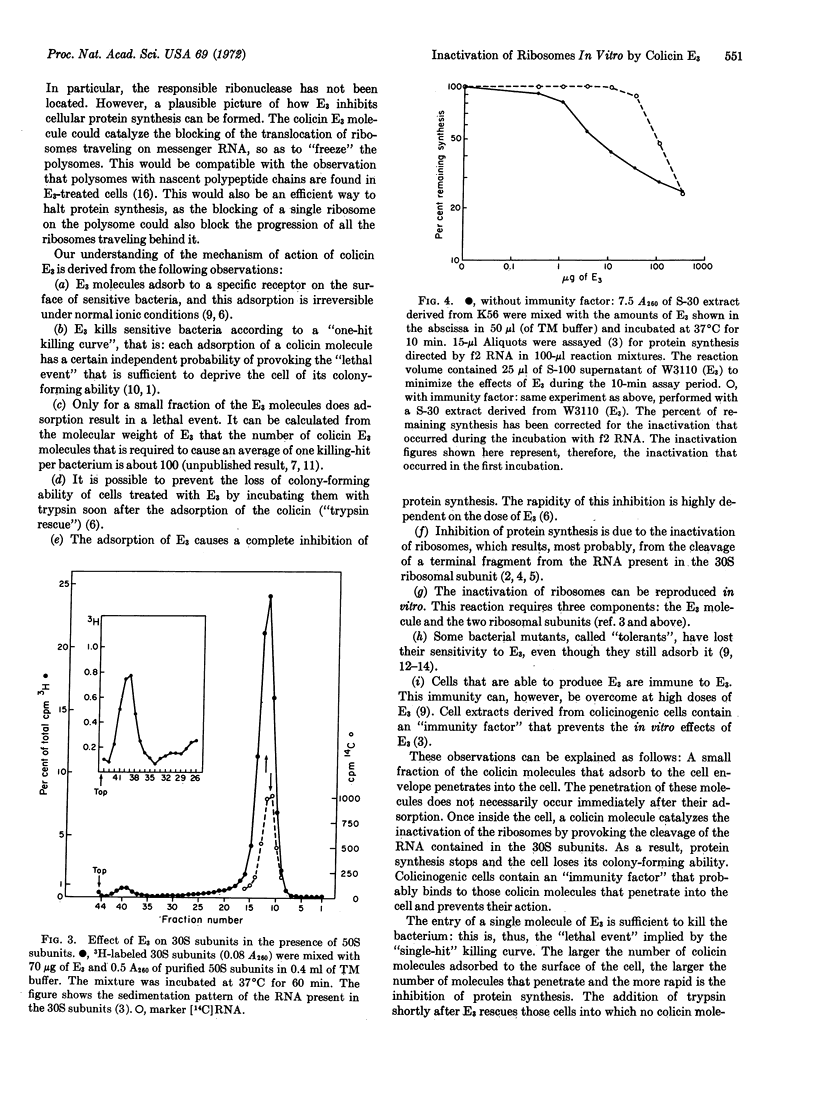
The incubation of purified ribosomes with colicin E3 results in the cleavage of a terminal fragment from the 16S ribosomal RNA. The cleavage reaction requires three components: colicin E3, the 30S ribosomal subunit, and the 50S ribosomal subunit. An immunity factor found in extracts derived from colicinogenic cells prevents the in vitro inactivation of ribosomes by colicin E3. Evidence is presented suggesting that it does so by binding to the colicin molecule. The mode of action of colicin E3in vivo can be explained by the assumption that a small fraction of the adsorbed colicin penetrates into the cell and catalytically inactivates the ribosomes.
Keywords: 30S and 50S ribosomal subunits; immunity factor; 16S ribosomal RNA; colicins E1, E2, and K
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boon T. Inactivation of ribosomes in vitro by colicin E 3 . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2421–2425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman C. M., Dahlberg J. E., Ikemura T., Konisky J., Nomura M. Specific inactivation of 16S ribosomal RNA induced by colicin E3 in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):964–968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman C. M., Sidikaro J., Nomura M. Specific inactivation of ribosomes by colicin E3 in vitro and mechanism of immunity in colicinogenic cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Dec 1;234(48):133–137. doi: 10.1038/newbio234133a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDERICQ P. Colicins and colicinogenic factors. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1958;12:104–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschman H. R., Helinski D. R. Purification and characterization of colicin E2 and colicin E3. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 25;242(22):5360–5368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C., Holland I. B. Genetic basis of colicin E susceptibility in Escherichia coli. I. Isolation and properties of refractory mutants and the preliminary mapping of their mutations. J Bacteriol. 1967 Sep;94(3):677–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.3.677-686.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., SIMINOVITCH L., WOLLMAN E. Sur la biosynthèse d'une colicine et sur son mode d'action. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1952 Sep;83(3):295–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konisky J., Nomura M. Interaction of colicins with bacterial cells. II. Specific alteration of Escherichia coli ribosomes induced by colicin E3 in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):181–195. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90290-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda A., Nomura M. Interaction of colicins with bacterial cells. I. Studies with radioactive colicins. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):685–694. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.685-694.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOMURA M. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF COLICINES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52:1514–1521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOMURA M., NAKAMURA M. Reversibility of inhibition of nucleic acids and protein synthesis by colicin K. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 May 4;7:306–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90196-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel de Zwaig R., Luria S. E. Genetics and physiology of colicin-tolerant mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1112–1123. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1112-1123.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Witten C. Interaction of colicins with bacterial cells. 3. Colicin-tolerant mutations in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1093–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1093-1111.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips L. A., Hotham-Iglewski B., Franklin R. M. Polyribosomes of Escherichia coli. I. Effects of monovalent cations on the distribution of polysomes, ribosomes and ribosomal subunits. J Mol Biol. 1969 Mar 14;40(2):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90475-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior B. W., Holland I. B. Effect of colicin E3 upon the 30S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):959–963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior B. W., Kwasniak J., Holland I. B. Colicin E3-directed changes in ribosome function and polyribosome metabolism in Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 28;53(2):205–220. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90295-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


