Abstract
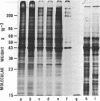
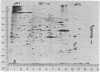
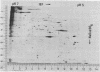
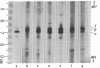
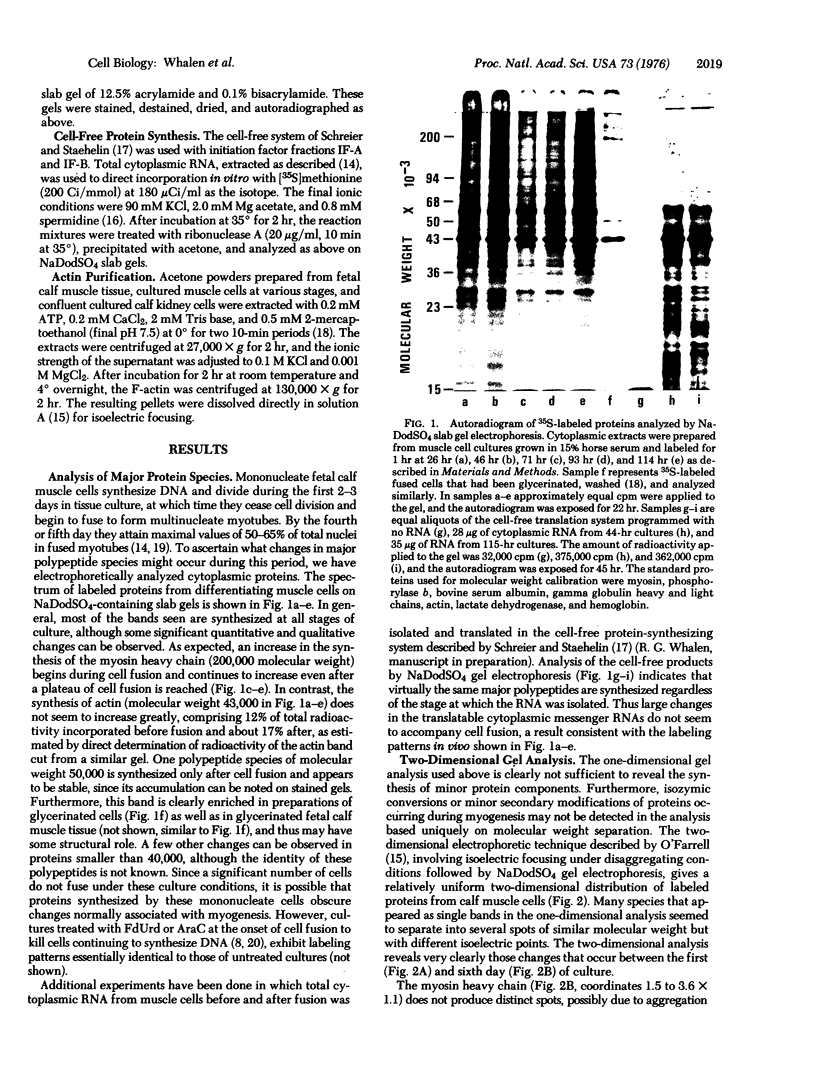
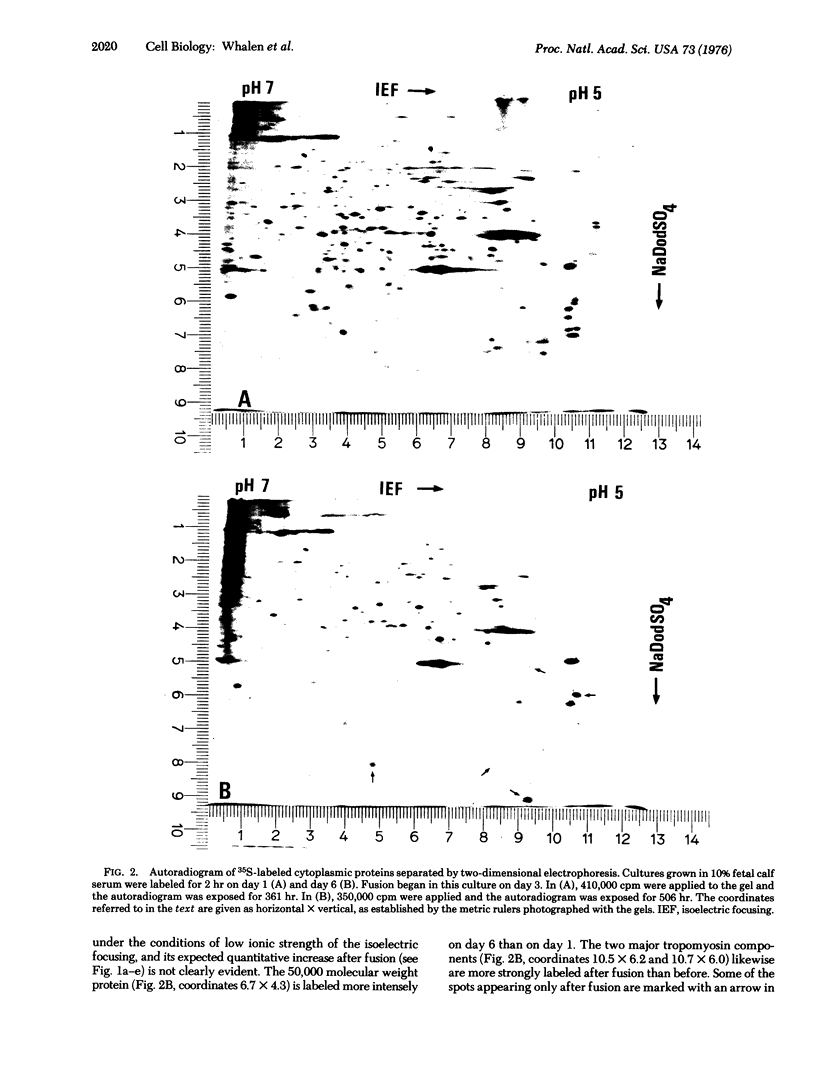
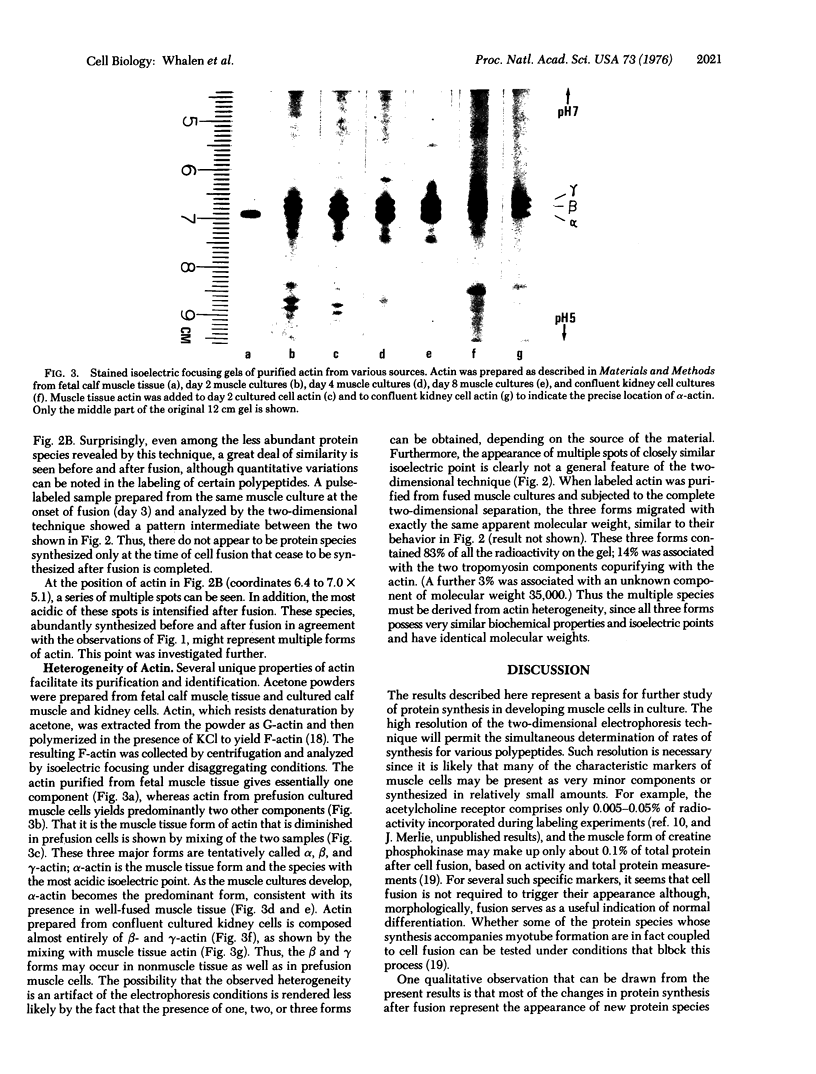
Pulse-labeled cytoplasmic proteins from cultured fetal calf-muscle cells at various stages of development were analyzed by one- and two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. The high resolution of the two-dimensional technique allows the determination of those protein species that begin to be synthesized after cell fusion. In addition, actin has been found to exist in three forms possessing similar biochemical properties and identical molecular weights but having slightly different isoelectric points. Two of the forms are found in prefusion dividing myoblasts and also in cultured kidney cells. The third form is the only one found in fetal muscle tissue and is predominant in cultures of fused muscle cells. Thus, it would seem that actin can exist in several isozymic forms of which one is specific to fused muscle tissue.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkins J. F., Lewis J. B., Anderson C. W., Gesteland R. F. Enhanced differential synthesis of proteins in a mammalian cell-free system by addition of polyamines. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5688–5695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckingham M. E., Caput D., Cohen A., Whalen R. G., Gros F. The synthesis and stability of cytoplasmic messenger RNA during myoblast differentiation in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1466–1470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Bray D. Purification and structural analysis of myosins from brain and other non-muscle tissues. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 25;99(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80154-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi J. C., Rubinstein N., Strahs K., Holtzer H. Synthesis of myosin heavy and light chains in muscle cultures. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):523–537. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson C. P., Jr, Beckner S. K. Activation of myosin synthesis in fusing and mononucleated myoblasts. J Mol Biol. 1975 Apr 25;93(4):431–447. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90238-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D., Rash J. E. Development of acetylcholine sensitivity during myogenesis. Dev Biol. 1971 Sep;26(1):55–68. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine R. E., Blitz A. L. A chemical comparison of tropomyosins from muscle and non-muscle tissues. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jul 5;95(3):447–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90202-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenstein E., Rich A. Non-identity of muscle and non-muscle actins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 May 19;64(2):472–477. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90345-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guth L. "Trophic" influences of nerve on muscle. Physiol Rev. 1968 Oct;48(4):645–687. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.4.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huszar G. Developmental changes of the primary structure and histidine methylation in rabbit skeletal muscle myosin. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 27;240(104):260–264. doi: 10.1038/newbio240260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Weber K. Actin antibody: the specific visualization of actin filaments in non-muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2268–2272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Gros F. In vitro myogenesis. Expression of muscle specific function in the absence of cell fusion. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Feb;97(2):406–412. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90632-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Sobel A., Changeux J. P., Gros F. Synthesis of acetylcholine receptor during differentiation of cultured embryonic muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4028–4032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson B., Strohman R. C. Myosin synthesis in cultures of differentiating chicken embryo skeletal muscle. Dev Biol. 1972 Oct;29(2):113–138. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Weihing R. R. Actin and myosin and cell movement. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):1–65. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives J. M., Paterson B. M. Differentiation of cell membranes in cultures of embryonic chick breast muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3208–3211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Staehelin T. Initiation of mammalian protein synthesis: the importance of ribosome and initiation factor quality for the efficiency of in vitro systems. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 19;73(3):329–349. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr R., Offer G. Polarity of the myosin molecule. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 25;81(1):17–31. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90244-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. C., Maier V., Eppenberger H. M. Creatine kinase and aldolase isoenzyme transitions in cultures of chick skeletal muscle cells. Dev Biol. 1974 Mar;37(1):63–89. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90170-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Trentham D. R., Kean C. J., Buller A. J. Myosin from cross-reinnervated cat muscles. Nature. 1974 Jan 18;247(5437):135–139. doi: 10.1038/247135a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. W., Nieberg P. S., Walker C. R., Linkhart T. A., Fry D. M. Production and release of acetylcholinesterase by cultured chick embryo muscle. Dev Biol. 1973 Aug;33(2):285–299. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90138-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. Z., Perdue J. F. Contractile proteins of cultured cells. I. The isolation and characterization of an actin-like protein from cultured chick embryo fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4503–4509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]