Abstract
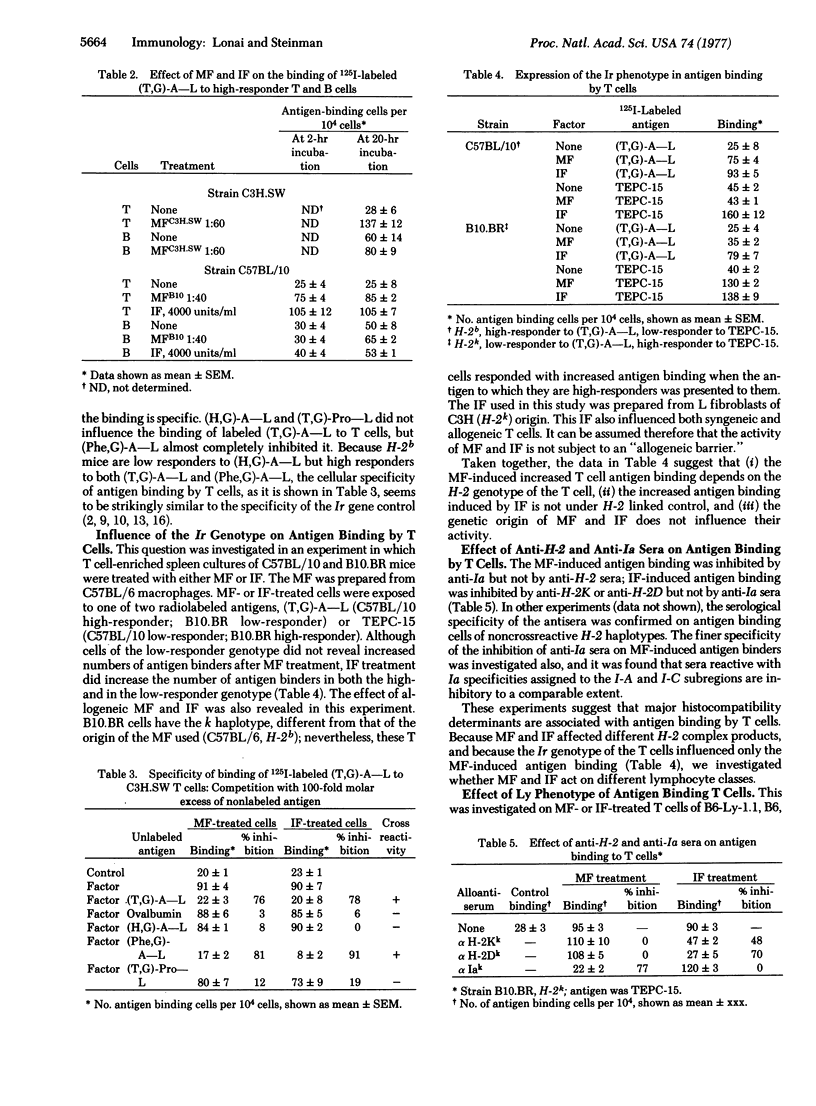
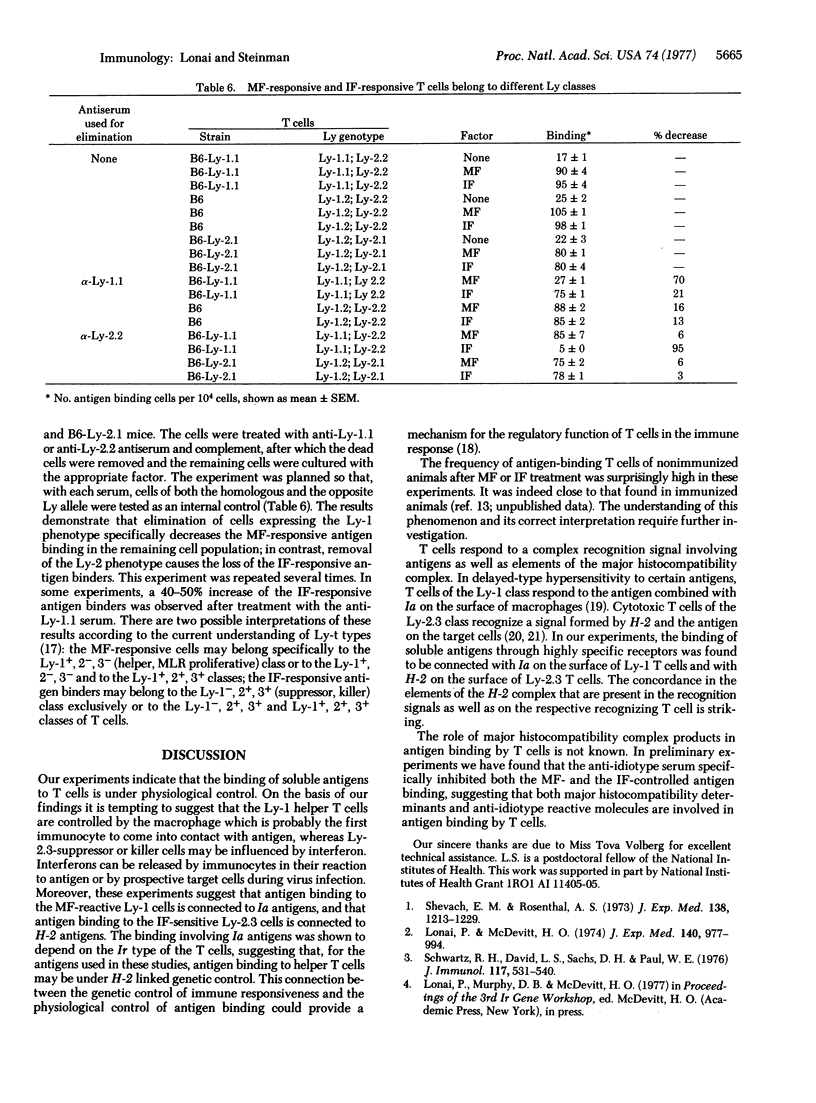
A soluble product of macrophages (MF) and mouse viral interferon (IF) increase both major histocompatibility antigenic determinants and the number of antigen-binding cells in nonstimulated T cell-enriched mouse lymphocyte cultures. MF increases Ia and not H-2 antigens; IF increases H-2 but not Ia antigens. The increased antigen binding due to MF can be inhibited by anti-Ia but not by anti-H-2 sera, whereas IF-induced binding is sensitive to anti-H-2 but not to anti-Ia sera. The specificity of IF- or MF-induced binding of branched synthetic polypeptides by T cells is different from that of B cells and similar to the specificity of the Ir gene regulation. MF increases antigen binding only in Ir high-responder animals. The IF-induced antigen binding is not dependent on the Ir genotype. MF-reactive cells express the Ly-1 marker, and the IF-reactive antigen binders express the Ly-2 phenotype. It is suggested that MF and IF are physiological mediators of antigen binding by T cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Lymphocytes as models for the study of mammalian cellular differentiation. Immunol Rev. 1977 Jan;33:105–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1977.tb00364.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hämmerling G. J., McDevitt H. O. Antigen binding T and B lymphocytes. I. Differences in cellular specificity and influence of metabolic activity on interaction of antigen with T and B cells. J Immunol. 1974 May;112(5):1726–1733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy L. J., Jr, Dorf M. E., Unanue E. R., Benacerraf B. Binding of poly (Glu-60 Ala-30 Tyr-10) by thymic lymphocytes from genetic responder and non-responder mice: effect of antihistocompatibility serum. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1670–1675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman R., Paul W. E., Humphrey W., Jr, Stimpfling J. H. H-2-linked immune response (Ir) genes. Independent loci for Ir-IgG and Ir-IgA genes. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1231–1240. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonai P., McDevitt H. O. Genetic control of the immune response: in vitro stimulation of lymphocytes by (T,G)-A--L, (H,G)-A--L, and (Phe,G)-A--L. J Exp Med. 1974 Oct 1;140(4):977–994. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.4.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt H. O., Sela M. Genetic control of the antibody response. II. Further analysis of the specificity of determinant-specific control, and genetic analysis of the response to (H,G)-A--L in CBA and C57 mice. J Exp Med. 1967 Nov 1;126(5):969–978. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.5.969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Vadas M. A., Whitelaw A., Gamble J. Role of major histocompatibility complex gene products in delayed-type hypersensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2486–2490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Benacerraf B. Functional specificity of thymus- dependent lymphocytes. Science. 1977 Mar 25;195(4284):1293–1300. doi: 10.1126/science.320663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce C. W., Kapp J. A., Solliday S. M., Dorf M. E., Benacerraf B. Immune responses in vitro. XI. Suppression of primary IgM and IgG plaque-forming cell responses in vitro by alloantisera against leukocyte alloantigens. J Exp Med. 1974 Oct 1;140(4):921–938. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.4.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H., David C. S., Sachs D. H., Paul W. E. T lymphocyte-enriched murine peritoneal exudate cells. III. Inhibition of antigen-induced T lymphocyte Proliferation with anti-Ia antisera. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):531–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H., Horton C. L., Paul W. E. T-lymphocyte-enriched murine peritoneal exudate cells. IV. Genetic control of cross-stimulation at the T-cell level. J Exp Med. 1977 Feb 1;145(2):327–343. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sela M. Antigen design and immune response. Harvey Lect. 1973;67:213–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer G. M., Rehn T. G., Garbarino C. A. Cell-mediated lympholysis of trinitrophenyl-modified autologous lymphocytes. Effector cell specificity to modified cell surface components controlled by H-2K and H-2D serological regions of the murine major histocompatibility complex. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1348–1364. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevach E. M., Rosenthal A. S. Function of macrophages in antigen recognition by guinea pig T lymphocytes. II. Role of the macrophage in the regulation of genetic control of the immune response. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1213–1229. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. H-2 compatability requirement for T-cell-mediated lysis of target cells infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Different cytotoxic T-cell specificities are associated with structures coded for in H-2K or H-2D;. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1427–1436. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


