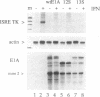
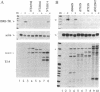
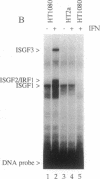
Abstract
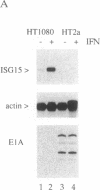
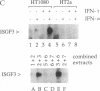
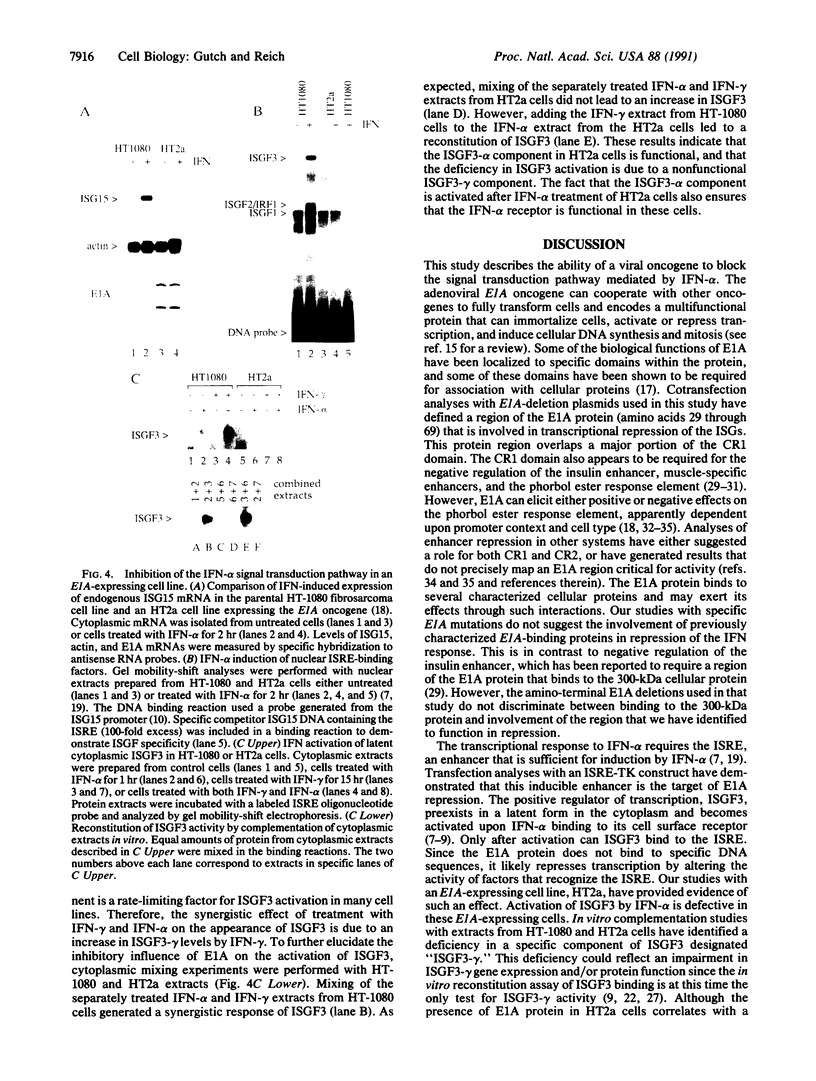
The signal transduction pathway initiated by type I interferon (alpha and beta interferons) is inhibited by expression of the adenovirus type 5 E1A oncogene. Cotransfection analyses with the E1A oncogene and an interferon-stimulated reporter gene show that mutations within an amino-terminal domain of the E1A oncoprotein are defective in transcriptional repression. Cotransfection experiments also revealed that the transcriptional repression is mediated through the interferon-stimulated response element (ISRE) found within the promoter of interferon-stimulated genes. Since interferon treatment activates a latent cytoplasmic DNA-binding factor that can recognize the ISRE and subsequently stimulate transcription, the appearance of this factor was analyzed in a cell line that constitutively expresses the E1A oncogene. The DNA binding activity of this transcriptional activator was found to be inhibited in the E1A-expressing cell line. In vitro cytoplasmic mixing experiments with extracts from control and E1A-expressing cells identified a specific component of this multimeric transcription factor to be defective.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagchi S., Raychaudhuri P., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus E1A proteins can dissociate heteromeric complexes involving the E2F transcription factor: a novel mechanism for E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):659–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90112-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi S., Raychaudhuri P., Nevins J. R. Phosphorylation-dependent activation of the adenovirus-inducible E2F transcription factor in a cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4352–4356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi S., Weinmann R., Raychaudhuri P. The retinoblastoma protein copurifies with E2F-I, an E1A-regulated inhibitor of the transcription factor E2F. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1063–1072. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90558-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandara L. R., Adamczewski J. P., Hunt T., La Thangue N. B. Cyclin A and the retinoblastoma gene product complex with a common transcription factor. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):249–251. doi: 10.1038/352249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay S. K., Kalvakolanu D. V., Sen G. C. Gene induction by interferons: functional complementation between trans-acting factors induced by alpha interferon and gamma interferon. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5055–5063. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J. Functions of adenovirus E1A. Cancer Surv. 1986;5(2):367–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chellappan S. P., Hiebert S., Mudryj M., Horowitz J. M., Nevins J. R. The E2F transcription factor is a cellular target for the RB protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90557-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale T. C., Imam A. M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Rapid activation by interferon alpha of a latent DNA-binding protein present in the cytoplasm of untreated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1203–1207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enkemann S. A., Konieczny S. F., Taparowsky E. J. Adenovirus 5 E1A represses muscle-specific enhancers and inhibits expression of the myogenic regulatory factor genes, MyoD1 and myogenin. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Aug;1(8):375–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Manly S. P., McMahon M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of interferon-induced gene expression in human cells. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):745–755. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisch S. M., Reich R., Collier I. E., Genrich L. T., Martin G., Goldberg G. I. Adenovirus E1A represses protease gene expression and inhibits metastasis of human tumor cells. Oncogene. 1990 Jan;5(1):75–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Kessler D. S., Veals S. A., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr ISGF3, the transcriptional activator induced by interferon alpha, consists of multiple interacting polypeptide chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8555–8559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano A., McCall C., Whyte P., Franza B. R., Jr Human cyclin A and the retinoblastoma protein interact with similar but distinguishable sequences in the adenovirus E1A gene product. Oncogene. 1991 Mar;6(3):481–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Franza B. R., Jr, Schley C. Monoclonal antibodies specific for adenovirus early region 1A proteins: extensive heterogeneity in early region 1A products. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):533–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.533-546.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler W. K., Kovelman R., Roeder R. G. Activation of transcription factor IIIC by the adenovirus E1A protein. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):907–920. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90409-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelsma T. N., Howe J. A., Mymryk J. S., Evelegh C. M., Cunniff N. F., Bayley S. T. Sequences in E1A proteins of human adenovirus 5 required for cell transformation, repression of a transcriptional enhancer, and induction of proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):120–130. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90518-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler D. S., Veals S. A., Fu X. Y., Levy D. E. Interferon-alpha regulates nuclear translocation and DNA-binding affinity of ISGF3, a multimeric transcriptional activator. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1753–1765. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelman D., Miller J. S., Porter D., Roberts B. E. E1a regions of the human adenoviruses and of the highly oncogenic simian adenovirus 7 are closely related. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):399–409. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.399-409.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajewski J., Schneider R. J., Safer B., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E., Thimmappaya B., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA antagonizes the antiviral action of interferon by preventing activation of the interferon-induced eIF-2 alpha kinase. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90383-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner A. C., Jonak G., Cheng Y. S., Korant B., Knight E., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional induction of two genes in human cells by beta interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6733–6737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of ISGF3, the positive regulator of interferon-alpha-stimulated transcription, reconstituted in vitro. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1362–1371. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Reich N., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced nuclear factors that bind a shared promoter element correlate with positive and negative transcriptional control. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):383–393. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Lew D. J., Decker T., Kessler D. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Synergistic interaction between interferon-alpha and interferon-gamma through induced synthesis of one subunit of the transcription factor ISGF3. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1105–1111. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08216.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama M., Fujita T., Taniguchi T. Sequence of a cDNA coding for human IRF-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3292–3292. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Mathews M. B. Multiple functional domains in the adenovirus E1A gene. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):177–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90418-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudryj M., Devoto S. H., Hiebert S. W., Hunter T., Pines J., Nevins J. R. Cell cycle regulation of the E2F transcription factor involves an interaction with cyclin A. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1243–1253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90019-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U., Roberts M. P., Engel D. A., Doerfler W., Shenk T. Induction of transcription factor AP-1 by adenovirus E1A protein and cAMP. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1991–2002. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley R. P., Mariano T. M., Siekierka J., Mathews M. B. A mechanism for the control of protein synthesis by adenovirus VA RNAI. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offringa R., Gebel S., van Dam H., Timmers M., Smits A., Zwart R., Stein B., Bos J. L., van der Eb A., Herrlich P. A novel function of the transforming domain of E1a: repression of AP-1 activity. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):527–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perricaudet M., Akusjärvi G., Virtanen A., Pettersson U. Structure of two spliced mRNAs from the transforming region of human subgroup C adenoviruses. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):694–696. doi: 10.1038/281694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine R., Decker T., Kessler D. S., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Purification and cloning of interferon-stimulated gene factor 2 (ISGF2): ISGF2 (IRF-1) can bind to the promoters of both beta interferon- and interferon-stimulated genes but is not a primary transcriptional activator of either. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2448–2457. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Human cyclin A is adenovirus E1A-associated protein p60 and behaves differently from cyclin B. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):760–763. doi: 10.1038/346760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. C., Chernajovsky Y., Dale T. C., Gilbert C. S., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Interferon response element of the human gene 6-16. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):85–92. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02786.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raychaudhuri P., Bagchi S., Nevins J. R. DNA-binding activity of the adenovirus-induced E4F transcription factor is regulated by phosphorylation. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):620–627. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N. C., Darnell J. E., Jr Differential binding of interferon-induced factors to an oligonucleotide that mediates transcriptional activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3415–3424. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N. C., Pfeffer L. M. Evidence for involvement of protein kinase C in the cellular response to interferon alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8761–8765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N., Evans B., Levy D., Fahey D., Knight E., Jr, Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced transcription of a gene encoding a 15-kDa protein depends on an upstream enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6394–6398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N., Pine R., Levy D., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcription of interferon-stimulated genes is induced by adenovirus particles but is suppressed by E1A gene products. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):114–119. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.114-119.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochette-Egly C., Fromental C., Chambon P. General repression of enhanson activity by the adenovirus-2 E1A proteins. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):137–150. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R. W., Corrigan M., Yaciuk P., Whelan J., Moran E. Analysis of E1A-mediated growth regulation functions: binding of the 300-kilodalton cellular product correlates with E1A enhancer repression function and DNA synthesis-inducing activity. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4421–4427. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4421-4427.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Ruley H. E., Harlow E. Two regions of the adenovirus early region 1A proteins are required for transformation. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):257–265. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.257-265.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Williamson N. M., Harlow E. Cellular targets for transformation by the adenovirus E1A proteins. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90984-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dam H., Offringa R., Meijer I., Stein B., Smits A. M., Herrlich P., Bos J. L., van der Eb A. J. Differential effects of the adenovirus E1A oncogene on members of the AP-1 transcription factor family. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5857–5864. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]