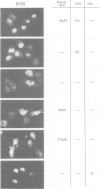
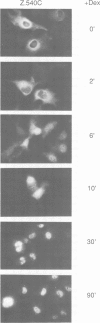
Abstract
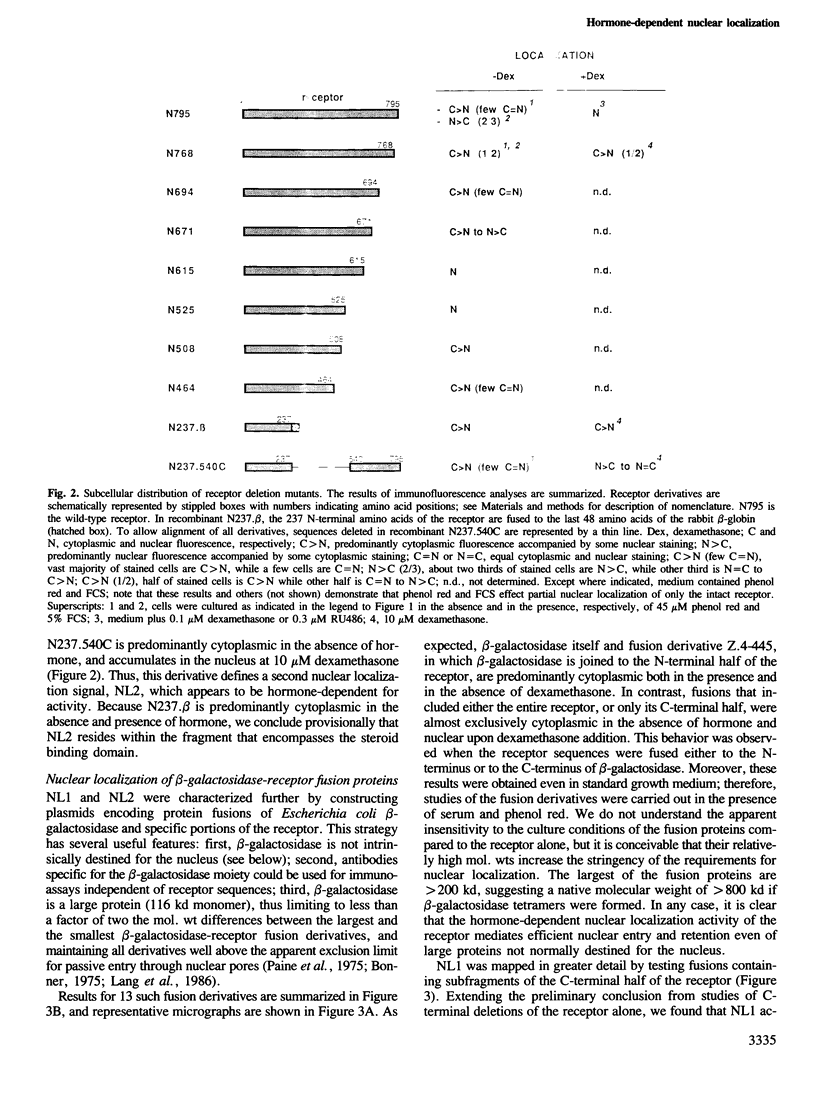
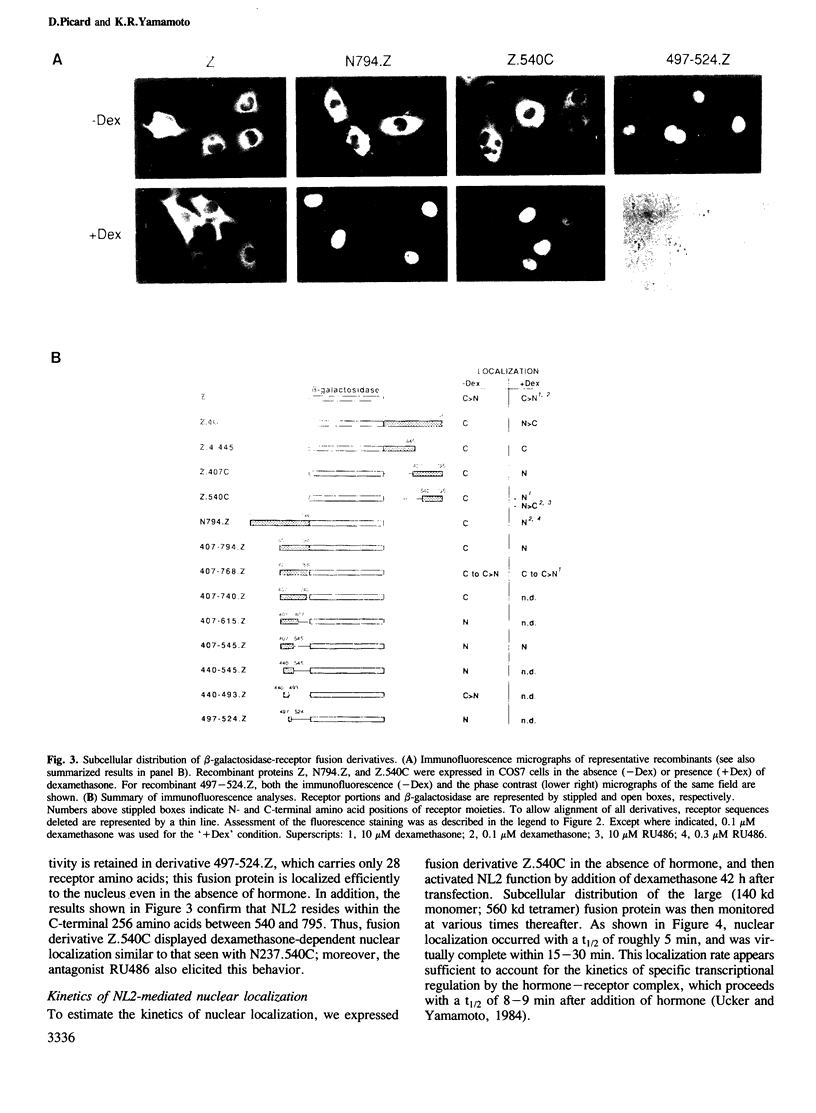
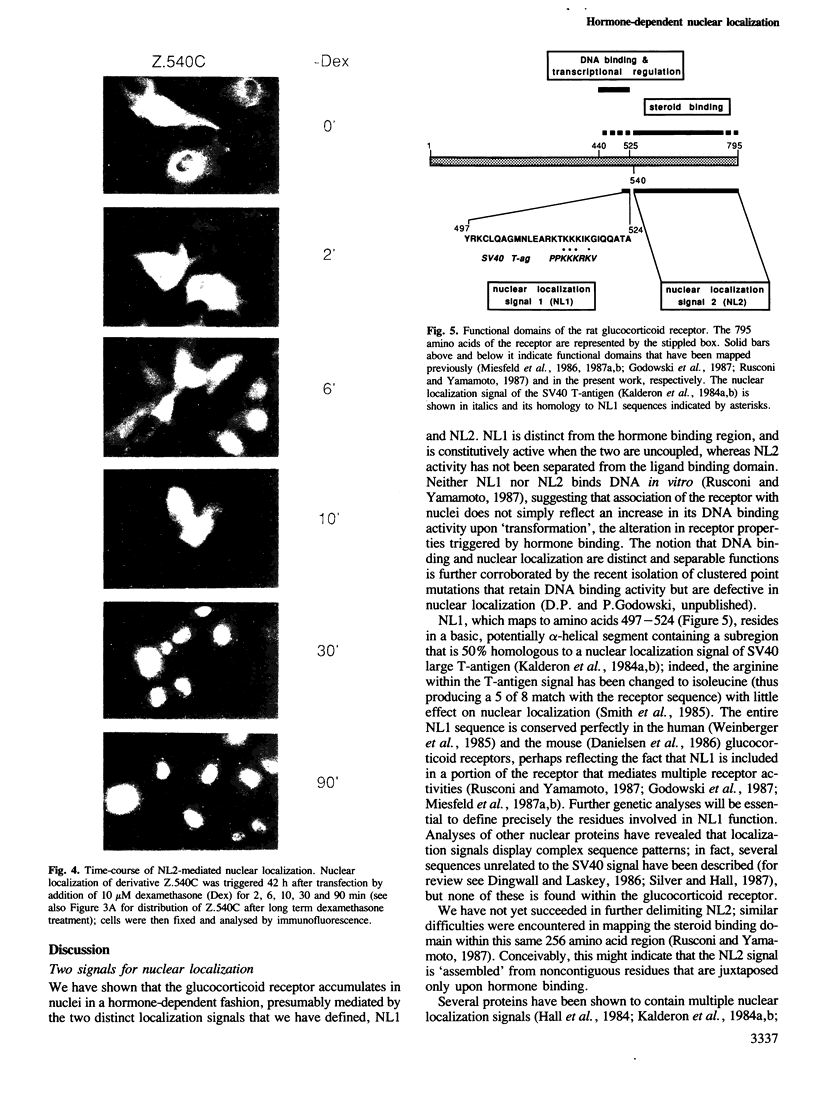
We have detected nuclear localization signals within the 795 amino acid rat glucocorticoid receptor. Using a transient expression assay, we monitored by immunofluorescence the subcellular distribution of receptor derivatives and beta-galactosidase-receptor fusion proteins. Two distinct nuclear localization signals, NL1 and NL2, were defined. NL1 maps to a 28 amino acid segment closely associated, but not coincident with the DNA binding domain; NL2 resides within a 256 amino acid region that also includes the hormone binding domain. Most importantly, nuclear localization of fusion proteins containing either the full-length receptor or the NL2 region alone is fully hormone-dependent; similar results were obtained with the wild-type receptor, provided the analysis was performed in medium lacking serum and phenol red. The rate of hormone-induced nuclear localization of an NL2-containing fusion protein is consistent with the rapid kinetics of hormone-regulated transcription mediated by the receptor. Thus, hormonal control of nuclear localization contributes to the modulation of glucocorticoid receptor transcriptional regulatory activity.
Full text
PDF
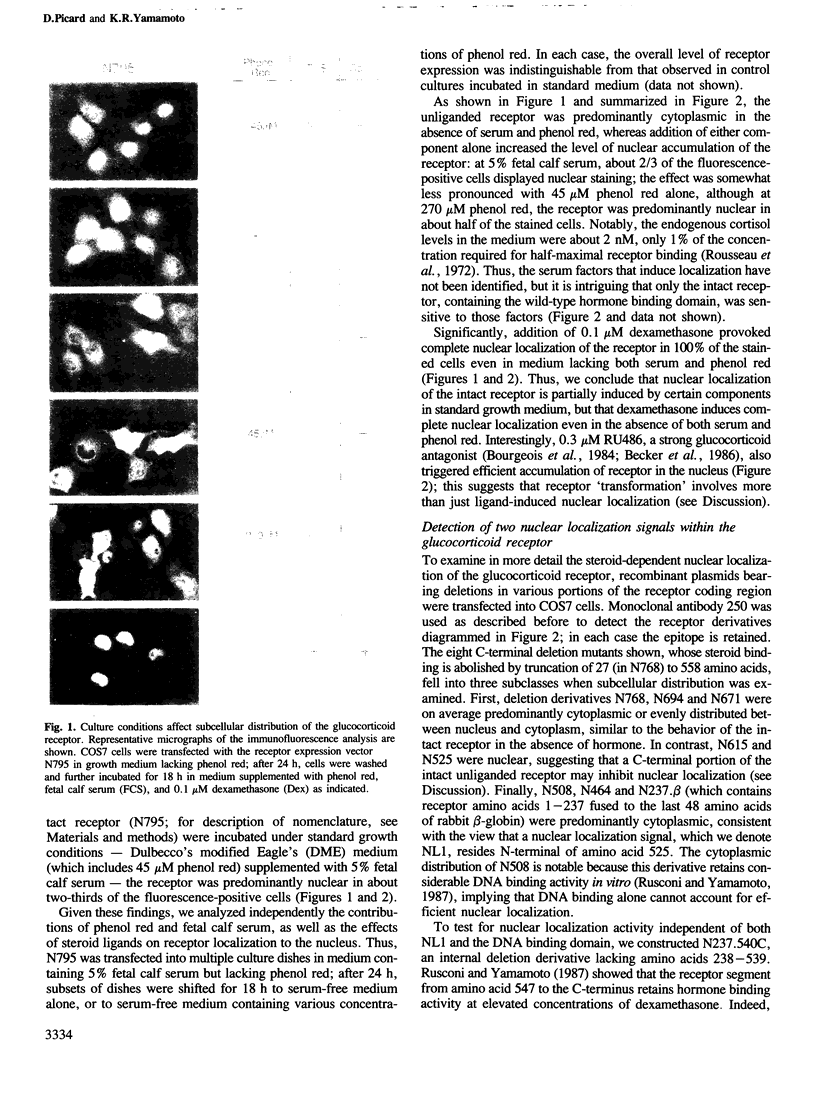



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antakly T., Eisen H. J. Immunocytochemical localization of glucocorticoid receptor in target cells. Endocrinology. 1984 Nov;115(5):1984–1989. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-5-1984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter J. D., Rousseau G. G., Benson M. C., Garcea R. L., Ito J., Tomkins G. M. Role of DNA and specific cytoplasmic receptors in glucocorticoid action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1892–1896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P. B., Gloss B., Schmid W., Strähle U., Schütz G. In vivo protein-DNA interactions in a glucocorticoid response element require the presence of the hormone. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):686–688. doi: 10.1038/324686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthois Y., Katzenellenbogen J. A., Katzenellenbogen B. S. Phenol red in tissue culture media is a weak estrogen: implications concerning the study of estrogen-responsive cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2496–2500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M. Protein migration into nuclei. I. Frog oocyte nuclei in vivo accumulate microinjected histones, allow entry to small proteins, and exclude large proteins. J Cell Biol. 1975 Feb;64(2):421–430. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.2.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeois S., Pfahl M., Baulieu E. E. DNA binding properties of glucocorticosteroid receptors bound to the steroid antagonist RU-486. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):751–755. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01879.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Martinez-Arias A., Shapira S. K., Chou J. Beta-galactosidase gene fusions for analyzing gene expression in escherichia coli and yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:293–308. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsen M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M. The mouse glucocorticoid receptor: mapping of functional domains by cloning, sequencing and expression of wild-type and mutant receptor proteins. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2513–2522. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04529.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. M. Nucleocytoplasmic segregation of proteins and RNAs. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1021–1025. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90285-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Walker M. D., Barr P. J., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression of the rat insulin gene: evidence for role of two distinct 5' flanking elements. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):912–916. doi: 10.1126/science.3904002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuxe K., Wikström A. C., Okret S., Agnati L. F., Härfstrand A., Yu Z. Y., Granholm L., Zoli M., Vale W., Gustafsson J. A. Mapping of glucocorticoid receptor immunoreactive neurons in the rat tel- and diencephalon using a monoclonal antibody against rat liver glucocorticoid receptor. Endocrinology. 1985 Nov;117(5):1803–1812. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-5-1803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Hollenberg S. M., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Functional domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godowski P. J., Rusconi S., Miesfeld R., Yamamoto K. R. Glucocorticoid receptor mutants that are constitutive activators of transcriptional enhancement. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):365–368. doi: 10.1038/325365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb D. S., Gariépy J., Schoolnik G., Kornberg R. D. Synthetic peptides as nuclear localization signals. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):641–644. doi: 10.1038/322641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govindan M. V. Immunofluorescence microscopy of the intracellular translocation of glucocorticoid-receptor complexes in rat hepatoma (HTC) cells. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Jun;127(2):293–297. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90435-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Oestradiol induction of a glucocorticoid-responsive gene by a chimaeric receptor. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):75–78. doi: 10.1038/325075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Hereford L., Herskowitz I. Targeting of E. coli beta-galactosidase to the nucleus in yeast. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1057–1065. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook N. J., Bodwell J. E., Jeffries M., Munck A. Characterization of nonactivated and activated glucocorticoid-receptor complexes from intact rat thymus cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6477–6485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg S. M., Giguere V., Segui P., Evans R. M. Colocalization of DNA-binding and transcriptional activation functions in the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90753-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Richardson W. D., Markham A. F., Smith A. E. Sequence requirements for nuclear location of simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):33–38. doi: 10.1038/311033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura G., Dulbecco R. Isolation and characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of simian virus 40. Virology. 1972 Aug;49(2):394–403. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90492-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W. J., Greene G. L. Monoclonal antibodies localize oestrogen receptor in the nuclei of target cells. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):745–747. doi: 10.1038/307745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Kanda P., Kennedy R. C. Induction of nuclear transport with a synthetic peptide homologous to the SV40 T antigen transport signal. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):575–582. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90883-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang I., Scholz M., Peters R. Molecular mobility and nucleocytoplasmic flux in hepatoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1183–1190. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel D. B., Bodwell J. E., Munck A. Glucocorticoid receptors lacking hormone-binding activity are bound in nuclei of ATP-depleted cells. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):478–480. doi: 10.1038/324478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Godowski P. J., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. Glucocorticoid receptor mutants that define a small region sufficient for enhancer activation. Science. 1987 Apr 24;236(4800):423–427. doi: 10.1126/science.3563519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Rusconi S., Godowski P. J., Maler B. A., Okret S., Wikström A. C., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Genetic complementation of a glucocorticoid receptor deficiency by expression of cloned receptor cDNA. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90659-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Finlay D. R., Forbes D. J. In vitro transport of a fluorescent nuclear protein and exclusion of non-nuclear proteins. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2091–2102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Lucocq J. M., Bürglin T. R., De Robertis E. M. Assembly in vitro of nuclei active in nuclear protein transport: ATP is required for nucleoplasmin accumulation. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):501–510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Hilz H., Eppenberger H. M., Dutly F. Rapid and reversible translocation of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase type II from the Golgi complex to the nucleus. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2801–2806. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04006.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okret S., Wikström A. C., Wrange O., Andersson B., Gustafsson J. A. Monoclonal antibodies against the rat liver glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1609–1613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine P. L., Moore L. C., Horowitz S. B. Nuclear envelope permeability. Nature. 1975 Mar 13;254(5496):109–114. doi: 10.1038/254109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papamichail M., Tsokos G., Tsawdaroglou N., Sekeris C. E. Immunocytochemical demonstration of glucocorticoid receptors in different cell types and their translocation from the cytoplasm to the cell nucleus in the presence of dexamethasone. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Feb;125(2):490–493. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90144-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrot-Applanat M., Groyer-Picard M. T., Logeat F., Milgrom E. Ultrastructural localization of the progesterone receptor by an immunogold method: effect of hormone administration. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1191–1199. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrot-Applanat M., Logeat F., Groyer-Picard M. T., Milgrom E. Immunocytochemical study of mammalian progesterone receptor using monoclonal antibodies. Endocrinology. 1985 Apr;116(4):1473–1484. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-4-1473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Päbo S., Weber F., Nilsson T., Schaffner W., Peterson P. A. Structural and functional dissection of an MHC class I antigen-binding adenovirus glycoprotein. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1921–1927. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04445.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raaka B. M., Samuels H. H. The glucocorticoid receptor in GH1 cells. Evidence from dense amino acid labeling and whole cell studies for an equilibrium model explaining the influence of hormone on the intracellular distribution of receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):417–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. D., Roberts B. L., Smith A. E. Nuclear location signals in polyoma virus large-T. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90486-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau G. G., Baxter J. D., Tomkins G. M. Glucocorticoid receptors: relations between steroid binding and biological effects. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 14;67(1):99–115. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90389-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusconi S., Yamamoto K. R. Functional dissection of the hormone and DNA binding activities of the glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1309–1315. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02369.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Easy identification of cDNA clones. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1791–1794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez E. R., Toft D. O., Schlesinger M. J., Pratt W. B. Evidence that the 90-kDa phosphoprotein associated with the untransformed L-cell glucocorticoid receptor is a murine heat shock protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12398–12401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman M. R., Moran M. C., Tuazon F. B., Stevens Y. W. Structure, dissociation, and proteolysis of mammalian steroid receptors. Multiplicity of glucocorticoid receptor forms and proteolytic enzymes in rat liver and kidney cytosols. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10366–10377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Colledge W. H., Edge M., Gillett P., Markham A., Paucha E., Richardson W. D. The nuclear location signal. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Oct 22;226(1242):43–58. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucker D. S., Yamamoto K. R. Early events in the stimulation of mammary tumor virus RNA synthesis by glucocorticoids. Novel assays of transcription rates. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7416–7420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedeckis W. V. Subunit dissociation as a possible mechanism of glucocorticoid receptor activation. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 12;22(8):1983–1989. doi: 10.1021/bi00277a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger C., Hollenberg S. M., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Domain structure of human glucocorticoid receptor and its relationship to the v-erb-A oncogene product. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):670–672. doi: 10.1038/318670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J. D., Swimmer C., Cocke T., Shenk T. A second domain of simian virus 40 T antigen in which mutations can alter the cellular localization of the antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2207–2212. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welshons W. V., Krummel B. M., Gorski J. Nuclear localization of unoccupied receptors for glucocorticoids, estrogens, and progesterone in GH3 cells. Endocrinology. 1985 Nov;117(5):2140–2147. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-5-2140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welshons W. V., Lieberman M. E., Gorski J. Nuclear localization of unoccupied oestrogen receptors. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):747–749. doi: 10.1038/307747a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström A. C., Bakke O., Okret S., Brönnegård M., Gustafsson J. A. Intracellular localization of the glucocorticoid receptor: evidence for cytoplasmic and nuclear localization. Endocrinology. 1987 Apr;120(4):1232–1242. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-4-1232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R. Steroid receptor regulated transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:209–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ooyen A., van den Berg J., Mantei N., Weissmann C. Comparison of total sequence of a cloned rabbit beta-globin gene and its flanking regions with a homologous mouse sequence. Science. 1979 Oct 19;206(4416):337–344. doi: 10.1126/science.482942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]