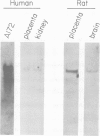
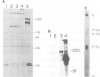
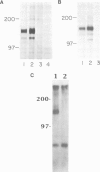
Abstract
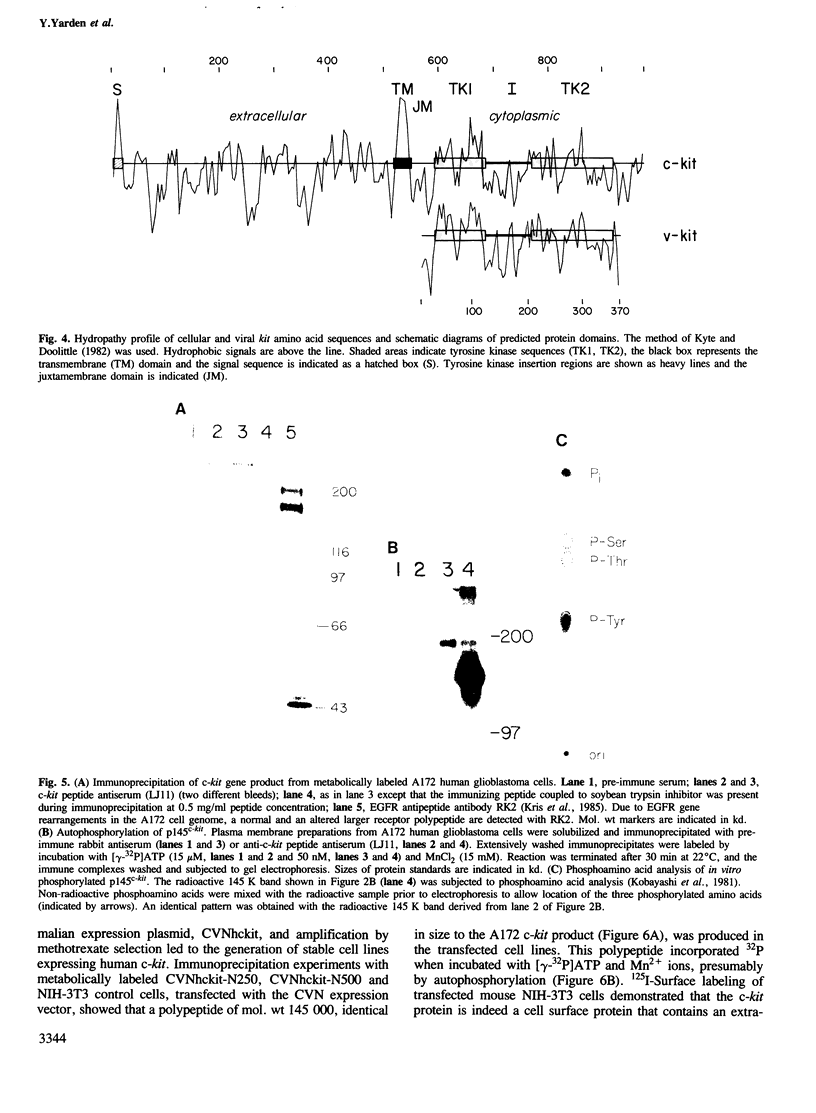
Structural features of v-kit, the oncogene of HZ4 feline sarcoma virus, suggested that this gene arose by transduction and truncation of cellular sequences. Complementary DNA cloning of the human proto-oncogene coding for a receptor tyrosine kinase confirmed this possibility: c-kit encodes a transmembrane glycoprotein that is structurally related to the receptor for macrophage growth factor (CSF-1) and the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor. The c-kit gene is widely expressed as a single, 5-kb transcript, and it is localized to human chromosome 4 and to mouse chromosome 5. A c-kit peptide antibody permitted the identification of a 145,000 dalton c-kit gene product that is inserted in the cellular plasma membrane and is capable of self-phosphorylation on tyrosine residues in both human glioblastoma cells and transfected mouse fibroblasts. Our results suggest that p145c-kit functions as a cell surface receptor for an as yet unidentified ligand. Furthermore, carboxy- and amino-terminal truncations that occurred during the viral transduction process are likely to have generated the transformation potential of v-kit.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bargmann C. I., Hung M. C., Weinberg R. A. Multiple independent activations of the neu oncogene by a point mutation altering the transmembrane domain of p185. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90779-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann C. I., Hung M. C., Weinberg R. A. The neu oncogene encodes an epidermal growth factor receptor-related protein. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):226–230. doi: 10.1038/319226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besmer P., Murphy J. E., George P. C., Qiu F. H., Bergold P. J., Lederman L., Snyder H. W., Jr, Brodeur D., Zuckerman E. E., Hardy W. D. A new acute transforming feline retrovirus and relationship of its oncogene v-kit with the protein kinase gene family. Nature. 1986 Apr 3;320(6061):415–421. doi: 10.1038/320415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brissenden J. E., Ullrich A., Francke U. Human chromosomal mapping of genes for insulin-like growth factors I and II and epidermal growth factor. 1984 Aug 30-Sep 5Nature. 310(5980):781–784. doi: 10.1038/310781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Gould K. L., Cartwright C. A., Hunter T. Tyr527 is phosphorylated in pp60c-src: implications for regulation. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1431–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.2420005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A. Activation of the pp60c-src kinase by middle T antigen binding or by dephosphorylation. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1471–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens L., Van Beveren C., Smith D., Chen E., Mitchell R. L., Isacke C. M., Verma I. M., Ullrich A. Structural alteration of viral homologue of receptor proto-oncogene fms at carboxyl terminus. Nature. 1986 Mar 20;320(6059):277–280. doi: 10.1038/320277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens L., Yang-Feng T. L., Liao Y. C., Chen E., Gray A., McGrath J., Seeburg P. H., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J., Francke U. Tyrosine kinase receptor with extensive homology to EGF receptor shares chromosomal location with neu oncogene. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1132–1139. doi: 10.1126/science.2999974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Parker P., Waterfield M. D. Autophosphorylation sites on the epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):483–485. doi: 10.1038/311483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Waterfield M. D., Parker P. J. Autophosphorylation and protein kinase C phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Effect on tyrosine kinase activity and ligand binding affinity. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14538–14546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groffen J., Heisterkamp N., Spurr N., Dana S., Wasmuth J. J., Stephenson J. R. Chromosomal localization of the human c-fms oncogene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6331–6339. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannink M., Donoghue D. J. Lysine residue 121 in the proposed ATP-binding site of the v-mos protein is required for transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7894–7898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Ling N., Cooper J. A. Protein kinase C phosphorylation of the EGF receptor at a threonine residue close to the cytoplasmic face of the plasma membrane. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):480–483. doi: 10.1038/311480a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iba H., Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. Low level of cellular protein phosphorylation by nontransforming overproduced p60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1058–1066. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi N., Tanaka A., Kaji A. In vitro phosphorylation of the 36K protein in extract from Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chicken fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):3053–3058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kris R. M., Lax I., Gullick W., Waterfield M. D., Ullrich A., Fridkin M., Schlessinger J. Antibodies against a synthetic peptide as a probe for the kinase activity of the avian EGF receptor and v-erbB protein. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):619–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalley P. A., McKusick V. A. Report of the Committee on Comparative Mapping. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):536–566. doi: 10.1159/000132187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Beau M. M., Westbrook C. A., Diaz M. O., Larson R. A., Rowley J. D., Gasson J. C., Golde D. W., Sherr C. J. Evidence for the involvement of GM-CSF and FMS in the deletion (5q) in myeloid disorders. Science. 1986 Feb 28;231(4741):984–987. doi: 10.1126/science.3484837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. B., Iba H., Hanafusa H. Activation of the transforming potential of p60c-src by a single amino acid change. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4228–4232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostov K. E., Friedlander M., Blobel G. The receptor for transepithelial transport of IgA and IgM contains multiple immunoglobulin-like domains. Nature. 1984 Mar 1;308(5954):37–43. doi: 10.1038/308037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellman D., Garber E. A., Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. An N-terminal peptide from p60src can direct myristylation and plasma membrane localization when fused to heterologous proteins. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):374–377. doi: 10.1038/314374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A., Lindquist P. B., Bringman T. S., Goeddel D. V., Derynck R. Expression in rat fibroblasts of a human transforming growth factor-alpha cDNA results in transformation. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90747-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M. F., Dull T. J., Rettenmier C. W., Ralph P., Ullrich A., Sherr C. J. Transforming potential of the c-fms proto-oncogene (CSF-1 receptor). Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):549–552. doi: 10.1038/325549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M. F., Rettenmier C. W., Look A. T., Sherr C. J. Cell surface expression of v-fms-coded glycoproteins is required for transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1999–2009. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacca R., Stanley E. R., Sherr C. J., Rettenmier C. W. Specific binding of the mononuclear phagocyte colony-stimulating factor CSF-1 to the product of the v-fms oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3331–3335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. Amino terminal myristylation of the protein kinase p60src, a retroviral transforming protein. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):427–429. doi: 10.1126/science.3917576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Trowbridge I. S., Cooper J. A., Scolnick E. M. The transforming proteins of Rous sarcoma virus, Harvey sarcoma virus and Abelson virus contain tightly bound lipid. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):465–474. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Rettenmier C. W., Sacca R., Roussel M. F., Look A. T., Stanley E. R. The c-fms proto-oncogene product is related to the receptor for the mononuclear phagocyte growth factor, CSF-1. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):665–676. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Isolation and expression of an altered mouse dihydrofolate reductase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2495–2499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Hanafusa H. Structure and sequence of the cellular gene homologous to the RSV src gene and the mechanism for generating the transforming virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):881–890. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. E. Compilation of published signal sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5145–5164. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler E. F., Rettenmier C. W., Look A. T., Sherr C. J. The v-fms oncogene induces factor independence and tumorigenicity in CSF-1 dependent macrophage cell line. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):377–380. doi: 10.1038/324377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Ikawa S., Akiyama T., Semba K., Nomura N., Miyajima N., Saito T., Toyoshima K. Similarity of protein encoded by the human c-erb-B-2 gene to epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):230–234. doi: 10.1038/319230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Feng T. L., Floyd-Smith G., Nemer M., Drouin J., Francke U. The pronatriodilatin gene is located on the distal short arm of human chromosome 1 and on mouse chromosome 4. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Nov;37(6):1117–1128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Feng T. L., Landau N. R., Baltimore D., Francke U. The terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase gene is located on human chromosome 10 (10q23----q24) and on mouse chromosome 19. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;43(3-4):121–126. doi: 10.1159/000132309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Escobedo J. A., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T. L., Daniel T. O., Tremble P. M., Chen E. Y., Ando M. E., Harkins R. N., Francke U. Structure of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor helps define a family of closely related growth factor receptors. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):226–232. doi: 10.1038/323226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]