Abstract
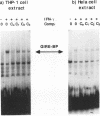
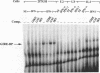
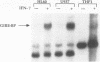
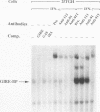
The human high-affinity receptor for the constant region of immunoglobulin G (human Fc gamma R1) is encoded by two mRNAs induced selectively by gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and expressed in cells of myeloid lineage. The cis-DNA element (GRR) previously found to confer IFN-gamma responsiveness to this gene acts as an inducible enhancer and is the target of an IFN-gamma-activated factor(s) (GIRE-BP) in cells of different origins. Although the GRR motif is not related to the DNA elements involved in the regulation of other IFN-stimulated genes, GIRE-BP binding depends on the IFN-gamma-dependent activation of the 91-kDa protein known to be one of the factors of a transcriptional complex activated by IFN-alpha. Deletions of the Fc gamma R1 promoter allowed us to identify a 25-bp element, downstream from the GRR motif, conferring cell-type-specific expression. This element, called MATE (myeloid activating transcription element), is the DNA target for constitutive factors forming two complexes, MATE-BP1 and MATE-BP2. In accordance with the functional analysis, MATE-BP binding activities were detected in extracts prepared from myeloid cell lines such as THP-1, HL-60, and U-937 but not in HeLa cell extracts. The MATE motif is present not only in the promoter of other Fc receptor genes but also in several promoters of genes whose expression is restricted to monocytic cells. Our results suggest that human Fc gamma R1 gene expression in myeloid cells is initiated by the interaction of IFN-gamma-activated factors with cell-type-specific factors through their binding to the GRR and MATE motifs.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcalay M., Antolini F., Van de Ven W. J., Lanfrancone L., Grignani F., Pelicci P. G. Characterization of human and mouse c-fes cDNA clones and identification of the 5' end of the gene. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):267–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. M., Seed B. Isolation and expression of functional high-affinity Fc receptor complementary DNAs. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):378–381. doi: 10.1126/science.2911749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr C. L., Saunders G. F. Interferon-gamma-inducible regulation of the human invariant chain gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3475–3481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basta P. V., Sherman P. A., Ting J. P. Detailed delineation of an interferon-gamma-responsive element important in human HLA-DRA gene expression in a glioblastoma multiform line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8618–8622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benech P. D., Sastry K., Iyer R. R., Eichbaum Q. G., Raveh D. P., Ezekowitz R. A. Definition of interferon gamma-response elements in a novel human Fc gamma receptor gene (Fc gamma RIb) and characterization of the gene structure. J Exp Med. 1992 Oct 1;176(4):1115–1123. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.4.1115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benech P., Mory Y., Revel M., Chebath J. Structure of two forms of the interferon-induced (2'-5') oligo A synthetase of human cells based on cDNAs and gene sequences. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2249–2256. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benech P., Vigneron M., Peretz D., Revel M., Chebath J. Interferon-responsive regulatory elements in the promoter of the human 2',5'-oligo(A) synthetase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4498–4504. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Flavell R. A., Sharp P. A. A gamma-interferon-induced factor that binds the interferon response sequence of the MHC class I gene, H-2Kb. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1139–1144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Boettger E. C., Flavell R. A. Transcriptional activation of HLA-DR alpha by interferon gamma requires a trans-acting protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4672–4676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boss J. M., Strominger J. L. Regulation of a transfected human class II major histocompatibility complex gene in human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9139–9143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttger E. C., Blanar M. A., Flavell R. A. Cycloheximide, an inhibitor of protein synthesis, prevents gamma-interferon-induced expression of class II mRNA in a macrophage cell line. Immunogenetics. 1988;28(4):215–220. doi: 10.1007/BF00345497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castrillo J. L., Bodner M., Karin M. Purification of growth hormone-specific transcription factor GHF-1 containing homeobox. Science. 1989 Feb 10;243(4892):814–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2563596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B., Peretz D., Vaiman D., Benech P., Chebath J. Enhancer-like interferon responsive sequences of the human and murine (2'-5') oligoadenylate synthetase gene promoters. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1411–1419. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02958.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart M. A., Belin D., Vassalli J. D., de Kossodo S., Vassalli P. Gamma interferon enhances macrophage transcription of the tumor necrosis factor/cachectin, interleukin 1, and urokinase genes, which are controlled by short-lived repressors. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):2113–2118. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.2113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale T. C., Imam A. M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Rapid activation by interferon alpha of a latent DNA-binding protein present in the cytoplasm of untreated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1203–1207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Cheng Y. S., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Interactions of alpha- and gamma-interferon in the transcriptional regulation of the gene encoding a guanylate-binding protein. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2009–2014. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Mirkovitch J., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of GAF, an IFN-gamma-regulated DNA-binding factor. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):927–932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Durand B., Marfing C., Le Meur M., Benoist C., Mathis D. Conserved major histocompatibility complex class II boxes--X and Y--are transcriptional control elements and specifically bind nuclear proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6249–6253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driggers P. H., Ennist D. L., Gleason S. L., Mak W. H., Marks M. S., Levi B. Z., Flanagan J. R., Appella E., Ozato K. An interferon gamma-regulated protein that binds the interferon-inducible enhancer element of major histocompatibility complex class I genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3743–3747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. M. A collection of mRNA species that are inducible in the RAW 264.7 mouse macrophage cell line by gamma interferon and other agents. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1535–1545. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Kessler D. S., Veals S. A., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr ISGF3, the transcriptional activator induced by interferon alpha, consists of multiple interacting polypeptide chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8555–8559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Shibuya H., Ohashi T., Yamanishi K., Taniguchi T. Regulation of human interleukin-2 gene: functional DNA sequences in the 5' flanking region for the gene expression in activated T lymphocytes. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):401–405. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90660-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J. Homeo boxes in the study of development. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1245–1252. doi: 10.1126/science.2884726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn P. A., Popescu N. C., Hanson R. D., Salvesen G., Ley T. J. Genomic organization and chromosomal localization of the human cathepsin G gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13412–13419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel A., Kimura A., Fournier A., Fellous M., Kourilsky P. Interferon response sequence potentiates activity of an enhancer in the promoter region of a mouse H-2 gene. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):743–746. doi: 10.1038/322743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyer R. R. A matched set of cat vectors for rapid mutational analysis of eukaryotic promoters and enhancers. Gene. 1991 Aug 30;105(1):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90518-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John J., McKendry R., Pellegrini S., Flavell D., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Isolation and characterization of a new mutant human cell line unresponsive to alpha and beta interferons. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4189–4195. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler D. S., Veals S. A., Fu X. Y., Levy D. E. Interferon-alpha regulates nuclear translocation and DNA-binding affinity of ISGF3, a multimeric transcriptional activator. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1753–1765. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A. The macrophage and B cell-specific transcription factor PU.1 is related to the ets oncogene. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouskoff V., Mantovani R. M., Candéias S. M., Dorn A., Staub A., Lisowska-Grospierre B., Griscelli C., Benoist C. O., Mathis D. J. NF-X, a transcription factor implicated in MHC class II gene regulation. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):3197–3204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of ISGF3, the positive regulator of interferon-alpha-stimulated transcription, reconstituted in vitro. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1362–1371. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Reich N., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced nuclear factors that bind a shared promoter element correlate with positive and negative transcriptional control. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):383–393. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Lew D. J., Decker T., Kessler D. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Synergistic interaction between interferon-alpha and interferon-gamma through induced synthesis of one subunit of the transcription factor ISGF3. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1105–1111. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08216.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D., Larner A., Chaudhuri A., Babiss L. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-stimulated transcription: isolation of an inducible gene and identification of its regulatory region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8929–8933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Decker T., Strehlow I., Darnell J. E. Overlapping elements in the guanylate-binding protein gene promoter mediate transcriptional induction by alpha and gamma interferons. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):182–191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luster A. D., Ravetch J. V. Genomic characterization of a gamma-interferon-inducible gene (IP-10) and identification of an interferon-inducible hypersensitive site. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3723–3731. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKendry R., John J., Flavell D., Müller M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. High-frequency mutagenesis of human cells and characterization of a mutant unresponsive to both alpha and gamma interferons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11455–11459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. M., Ruppert S., Schaffner W., Matthias P. A cloned octamer transcription factor stimulates transcription from lymphoid-specific promoters in non-B cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):544–551. doi: 10.1038/336544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nezu N., Ryu K., Koide Y., Yoshida T. O. Regulation of HLA class II molecule expressions by IFN-gamma. The signal transduction mechanism in glioblastoma cell lines. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):3126–3135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace J. L., Russell S. W., LeBlanc P. A., Murasko D. M. Comparative effects of various classes of mouse interferons on macrophage activation for tumor cell killing. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):977–981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahl H. L., Rosmarin A. G., Tenen D. G. Characterization of the myeloid-specific CD11b promoter. Blood. 1992 Feb 15;79(4):865–870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulnock-King D., Sizer K. C., Freund Y. R., Jones P. P., Parnes J. R. Coordinate induction of Ia alpha, beta, and Ii mRNA in a macrophage cell line. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):632–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse R. N., Feinman R., Ravetch J. V. Characterization of the promoter of the human gene encoding the high-affinity IgG receptor: transcriptional induction by gamma-interferon is mediated through common DNA response elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11305–11309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petterson M., Schaffner W. A purine-rich DNA sequence motif present in SV40 and lymphotropic papovavirus binds a lymphoid-specific factor and contributes to enhancer activity in lymphoid cells. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):962–972. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinney D. F., Pearson-White S. H., Konieczny S. F., Latham K. E., Emerson C. P., Jr Myogenic lineage determination and differentiation: evidence for a regulatory gene pathway. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):781–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90095-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. C., Chernajovsky Y., Dale T. C., Gilbert C. S., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Interferon response element of the human gene 6-16. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):85–92. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02786.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid L. E., Brasnett A. H., Gilbert C. S., Porter A. C., Gewert D. R., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. A single DNA response element can confer inducibility by both alpha- and gamma-interferons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):840–844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Shuai K., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of a latent cytoplasmic transcription factor. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):809–813. doi: 10.1126/science.1496401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalnik D. G., Strauss E. C., Orkin S. H. CCAAT displacement protein as a repressor of the myelomonocytic-specific gp91-phox gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16736–16744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita K., Miyazaki J., Appella E., Ozato K. Interferons increase transcription of a major histocompatibility class I gene via a 5' interferon consensus sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2625–2630. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Nukiwa T., Yoshimura K., Quick C. D., States D. J., Holmes M. D., Whang-Peng J., Knutsen T., Crystal R. G. Structure of the human neutrophil elastase gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14739–14747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Thayer M. J., Cheng P. F., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. MyoD1: a nuclear phosphoprotein requiring a Myc homology region to convert fibroblasts to myoblasts. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):405–411. doi: 10.1126/science.3175662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanos D., Mavrothalassitis G., Papamatheakis J. Multiple regulatory regions on the 5' side of the mouse E alpha gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3075–3079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari R. K., Kusari J., Kumar R., Sen G. C. Gene induction by interferons and double-stranded RNA: selective inhibition by 2-aminopurine. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4289–4294. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trainor C. D., Evans T., Felsenfeld G., Boguski M. S. Structure and evolution of a human erythroid transcription factor. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):92–96. doi: 10.1038/343092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. F., Martin D. I., Zon L. I., D'Andrea A. D., Wong G. G., Orkin S. H. Cloning of cDNA for the major DNA-binding protein of the erythroid lineage through expression in mammalian cells. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):446–451. doi: 10.1038/339446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang S. Y., Nakanishi M., Peterlin B. M. B-cell-specific and interferon-gamma-inducible regulation of the HLA-DR alpha gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8598–8602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaiman D., Pietrokovsky S., Cohen B., Benech P., Chebath J. Synergism of type I and type II interferons in stimulating the activity of the same DNA enhancer. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 4;265(1-2):12–16. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80871-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velazquez L., Fellous M., Stark G. R., Pellegrini S. A protein tyrosine kinase in the interferon alpha/beta signaling pathway. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):313–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90105-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil J., Epstein C. J., Epstein L. B., Sedmak J. J., Sabran J. L., Grossberg S. E. A unique set of polypeptides is induced by gamma interferon in addition to those induced in common with alpha and beta interferons. Nature. 1983 Feb 3;301(5899):437–439. doi: 10.1038/301437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinshank R. L., Luster A. D., Ravetch J. V. Function and regulation of a murine macrophage-specific IgG Fc receptor, Fc gamma R-alpha. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1909–1925. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wietzerbin J., Gaudelet C., Catinot L., Chebath J., Falcoff R. Synergistic effect of interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on antiviral activity and (2'-5') oligo (A) synthetase induction in a myelomonocytic cell line. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 Aug;48(2):149–155. doi: 10.1002/jlb.48.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth T., Staudt L., Baltimore D. An octamer oligonucleotide upstream of a TATA motif is sufficient for lymphoid-specific promoter activity. Nature. 1987 Sep 10;329(6135):174–178. doi: 10.1038/329174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright T. M., Farber J. M. 5' regulatory region of a novel cytokine gene mediates selective activation by interferon gamma. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):417–422. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. E., Sassoon D. A., Lin V. K. Myogenin, a factor regulating myogenesis, has a domain homologous to MyoD. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z., Sugawara M., Ponath P. D., Wessendorf L., Banerji J., Li Y., Strominger J. L. Interferon gamma response region in the promoter of the human DPA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9226–9230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimarino V., Wu C. Induction of sequence-specific binding of Drosophila heat shock activator protein without protein synthesis. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):727–730. doi: 10.1038/327727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Winkel J. G., Ernst L. K., Anderson C. L., Chiu I. M. Gene organization of the human high affinity receptor for IgG, Fc gamma RI (CD64). Characterization and evidence for a second gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13449–13455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]